* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download What are the key issues and events that led to the Civil War?
Survey
Document related concepts
Slavery in the United States wikipedia , lookup
Treatment of slaves in the United States wikipedia , lookup
Union (American Civil War) wikipedia , lookup
Military history of African Americans in the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
Border states (American Civil War) wikipedia , lookup
Mississippi in the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
United Kingdom and the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
South Carolina in the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
Origins of the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
Georgia in the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
United States presidential election, 1860 wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
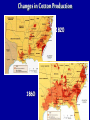
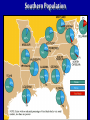
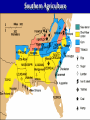
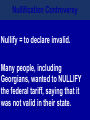
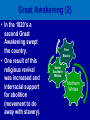
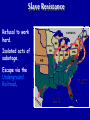
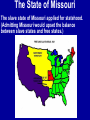
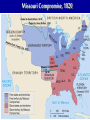
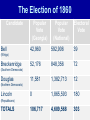
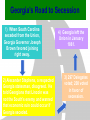
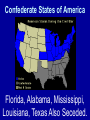
What are the key issues and events that led to the Civil War? Day 1 Slavery States’ Rights Nullification Missouri Compromise Compromise of 1850 Georgia Platform Kansas-Nebraska Act Dred Scott Case Election of 1860 Debate over the Secession in Georgia Role of Alexander Stephens Differences As the United States grew, clear differences showed up between the NORTH and the SOUTH. ◊Political ◊Cultural ◊Economic ◊Social SOUTH • Agriculture • Fertile Soil • Warmer Climate • Plantations • Farms • Rural • Self Sufficient • Expect Little Government Help NORTH • • • • • • • • Industry Rocky Soil Colder Climate Factories Cities Urban Interdependent Expect More Government Help Changes in Cotton Production 1820 1860 States’ Rights Structure (Classes) Secession Selection of Lincoln Causes of Civil War (8 Ss) Sectionalism Solvency (Ability to Pay Debt) Style Slavery Causes of the Civil War States’ Rights Structure (Classes) Solvency (Ability to Pay Debt) Style (Urban vs. Rural) Slavery Sectionalism Selection of Lincoln Secession SOUTH Believed that states had the right to rule themselves NORTH Believed in a strong national government SOUTH NORTH Government created by Government created the states. by the people. States have the right to Only the Supreme reject laws that would Court can declare a hurt them. law unconstitutional. Since states voluntarily joined the Union, they could voluntarily leave –secede. Only the people of the US could dissolve the Union. Attempting to destroy the Union was treason. Even though the United States had been established decades earlier, many people still felt that the states should have FINAL AUTHORITY, not the federal government. vs. FARMERS WITH SLAVES FREE BLACKS SLAVES Southern Population SOUTH Based on agriculture, including cotton, tobacco, and rice. Cotton was shipped north to make cloth and thread. NORTH Based on factories, mining, banks, stores, and railroads. Southern Agriculture Tariffs Made in Northern United States Cost = $50 +$20 Import Tax Made in Great Britain Cost = $70 Northerners wanted to sell their goods in the South, but it was often cheaper for Southerners to buy things from Europe. To help Northern industries, President Andrew Jackson put a tariff (taxes on imports) on imported goods in 1828. This made European goods very expensive, so Southerners would have to buy from Northern States. South North Favored high tariffs Favored low tariffs because on goods from they bought so other countries so many goods goods from other manufactured in countries. North cost less and would outsell foreign goods. Nullification Controversy Nullify = to declare invalid. Many people, including Georgians, wanted to NULLIFY the federal tariff, saying that it was not valid in their state. South Carolina Threatens to Secede! • Because a new tariff was too high. • Began to arm themselves and hold practice drills. Compromise Tariff Law • Reduced Tariff over a 10 year period. • Please South Carolinians. • Protests Ended. Panic of 1857 • Depression hit the country • Before this time, Northern Industrialists built their factories with borrowed money. • Nearly 5,000 went bankrupt. • Factory owners asked Congress to pass higher tariffs to stop British goods from being sold in the United States. • Debates followed… South North RURAL Had few large cities other than Richmond, Charleston, Savannah, Augusta. URBAN Had a number of large cities offering museums, opera, lectures, theaters. South North Many private schools, No formal educational including churchsystem in the sponsored schools, South. Private accepted both boys tutors or school and girls. Some abroad were private schools options for upper were open to both. class. Some community Private universities schools but such as Brown, teachers were not Harvard, and Yale usually trained. were opening. Some statechartered universities such as UGA. What are the key issues and events that led to the Civil War? Day 2 - Slavery Slavery States’ Rights Nullification Missouri Compromise Compromise of 1850 Georgia Platform Kansas-Nebraska Act Dred Scott Case Election of 1860 Debate over the Secession in Georgia Role of Alexander Stephens The Issue of Slavery South North Supported Slavery Wanted to Abolish Slavery Slave Population in 1860 • Slaves were about 4 million of the total black population in the country. • By far, the MAJORITY lived in the South. • About 11.5% of the slaves lived in Georgia. SOUTHERN SLAVEHOLDERS 1860 Census 3% Owned 20 + 4% 5% Owned 10 - 19 13% 75 % Owned 1 Owned 2-9 Owned 0 To plantations owners, was slavery a moral issue, an economic issue or both? Why? Do You Think the Idea of Manifest Destiny Had Anything to Do with Plantation Owners’ Views on Slavery? Muscogee County Old Slave Cabins Slave Auction Notice Slave Equipment Slave Master Brands Slave Muzzle Slave Equipment Slave Leg Irons Slave Shoes Slave Tag Real Georgia Plantations A Real Mammie & Her Charge A Slave Family Great Awakening (2) • In the 1820’s a second Great Awakening swept the country. • One result of this religious revival was increased and interracial support for abolition (movement to do away with slavery). Free Blacks Some Southern Whites Northern Whites ABOLITIONIST MOVEMENT Abolitionist = a person who demanded the immediate freeing of slaves • Morally wrong • Violates religious teachings • Results in cruel and inhumane treatment of slaves • Violates democracy Abolitionist Activities • Made speeches • Conducted meetings • Published newspapers • Organized and offered their homes as safe houses for runaway slaves in the Underground Railroad • Wrote books and articles Famous Abolitionists William Lloyd Garrison Best known abolitionist, published leading abolitionist newspaper, The Liberator. Frederick Douglass Former slave who escaped to freedom; public speaker who traveled around the country describing the evils of slavery. Harriet Tubman Former runaway slave; a leading worker on the Underground Railroad. Harriet Beecher Stowe • Author of book, Uncle Tom’s Cabin. • A dramatic picture of slave suffering. • Wrote about slaves as individuals rather than a group and described some of the worst things about slavery and the fugitive slave laws. • Book was a big success -over 300,000 copies in first 6 months . Nat Turner Believed God wanted him to end slavery in America; led a revolt that resulted in the deaths of over 50 whites and numerous slaves. Turner was captured and hanged. Slave Resistance Refusal to work hard. Isolated acts of sabotage. Escape via the Underground Railroad. Slave States vs. Free States In 1819, the US had 22 states: 11 were slave states (states that did allow slavery) 11 were free states (states that did not allow slavery) SENATE = Equal number of senators from slave states and from free states. HOUSE OF REPRESENTATIVES = Free states had more representatives than the slave states. The State of Missouri The slave state of Missouri applied for statehood. (Admitting Missouri would upset the balance between slave states and free states.) Missouri Compromise After a great deal of debate, Congress adopted the Missouri Compromise. Missouri would join the Union as a slave state, and Maine joined as a free state. Slavery would not be allowed north of the 36° 20´ line of latitude. This compromise kept a balance of power between the free states and slave states in the Senate and provided a temporary solution to the slavery question. Missouri Compromise, 1820 Dred Scott Decision (1857) a Supreme Court decision adds fuel to the fire... • Dred Scott was a Missouri slave. • He sued for his freedom because he had lived for a period of time with his master in the free state of Illinois and free territory of Wisconsin. • The Supreme Court said Scott could not sue because he was a slave, and slaves were not citizens. This Caused Further Division South North What are the key issues and events that led to the Civil War? Day 3 – Sectionalism Slavery States’ Rights Nullification Missouri Compromise Compromise of 1850 Georgia Platform Kansas-Nebraska Act Dred Scott Case Election of 1860 Debate over the Secession in Georgia Role of Alexander Stephens What is Sectionalism? • The belief by the people in a given region or area that their ideas and interests are better and more important than those of another region or area. • Sectionalism was quickly becoming a NATIONAL ISSUE! • As the country expanded westward, the slavery question would have to be answered (both Congress and the courts had tried)... South Southern states believed that their stand on slavery was just, their concerns over tariffs were fair, and their culture and lifestyle were to be treasured. They believed in the rights of states to determine their own destiny. They knew their section of the country was best. North Northern states believed that their stand against slavery and their concerns over tariffs, culture and lifestyle made them the favored, and therefore the best section of the country. California Gold Rush • After the gold rush in California, people from all over the world traveled there dreaming of riches. • By late 1849, the population was over 100,000 (enough to ask for statehood) In 1850, Slave States vs. Free States • There were 15 Slave States and 15 Free States. • California did NOT allow slavery. • If California became a state, the balance in the Senate between slave states and free states would change. THE GREAT DEBATE For 8 months, Congress tried to decide what to do about California! THE GREAT DEBATE For 8 months, Congress tried to decide what to do about California! Benefits of the Compromise South North • The territories of New Mexico • California came into the and Utah would determine Union as a free state. whether they wanted to be • Slave trading was ended slave or free. in the District of • The residents of the District of Columbia. Columbia could keep the slaves they already had. • Texas gave up its idea of • Congress would pass a law annexing New Mexico, (Fugitive Slave Act) stating thus taking that territory that slaves who ran away to away from a slave state. free states would be returned to their owners. Slavery Issue Would Not Die! As more and more people moved into the plains west of Missouri and Iowa, there was a need for a territorial government. Kansas-Nebraska Act • Created the territories of Kansas and Nebraska • Contained a clause about Popular Sovereignty (when a territory asked for statehood, the people of a territory could vote on whether they wanted to be a free or slave state). Northerners Were Angry! They felt that this law changed the Missouri Compromise, which did not permit slavery north of Missouri’s southern boundary. People began to move into Kansas to influence the vote. Bleeding Kansas Proslavery “Border Ruffians” For slavery Took over polls, prevented free soilers from voting, and ensured the election of a proslavery legislature. There was so much violence in Kansas between the proslavery people and the free soilers that the territory was called “Bleeding Kansas.” Free Soilers Against slavery Wanted land to be given to western settlers for farming. More Than 200 Died... What are the key issues and events that led to the Civil War? Day 4 – Georgia Slavery States’ Rights Nullification Missouri Compromise Compromise of 1850 Georgia Platform Kansas-Nebraska Act Dred Scott Case Election of 1860 Debate over the Secession in Georgia Role of Alexander Stephens Georgia’s Economy Backbone of Georgia’s Economy = Agriculture By 1860 • 68,000 Farms • Cotton was the Main Crop • Farms Produced More than 700,000 bales of cotton. • 115% increase from 1839. Plantation s • Only 3,500 farms had 500 + acres and could be called plantations. • Since the land itself did not cost much, a plantation owner’s worth was largely measured by the number of slaves he Only 236 Georgians owned more than 100 slaves, and 60% had no slaves at all. Cotton Mills Pottery Factories Tanneries Georgia’s Industry Brick Factories Grist Mills Iron Factories Shoe Factories • 1,890 Factories by 1860 • Value = $11 million • Georgia’s industrial base was no comparison for the A Discovery • Before any surgery, patients were given several swallows of alcohol or opiates (pain-killing drugs). • Physicians’ assistants stood over the patients holding down their legs and arms. • Some patients were simply knocked unconscious. • Dr. Crawford W. Long began trying sulfuric ether as an anesthetic. Education • Education was not an important element in the life of most antebellum Georgia. • In 1850, about 20% of Georgia’s whites could not read or write. • About 50% of Georgia’s children were black and did not go to school at all. • In 1858, state legislature set aside $100,000 to begin free school...but the CIVIL WAR begins... Religion • During the 1850s, church membership grew in Georgia. • By 1860, there were 2,393 churches in the state. • Two largest denominations: Methodists Baptists • Others: Episcopal, Slaves First African Baptist Church, Savannah, Georgia (1777- ) • There were few segregated churches. • Slaves usually attended the same churches as their masters. Politics Two major Political Parties Democrats Supported states’ rights Strong stand FOR slavery Leaders: Herschel V. Johnson Joseph E. Brown Howell Cobb Most Governors were democrats Whigs Mostly members of upper social classes Favored moderate protective tariff and federal help for the south. Leaders: Robert Toombs Alexander Stephens Most members of legislature were whigs The Georgia Platform • Many Georgians did not like the Compromise of 1850. • They felt that the South’s rights were being trampled... • However, Democrat Cobb and Whigs Stephens and Toombs asked the citizens of Georgia to accept it. • The legislature met to discuss the issue. They adopted a proclamation called GEORGIA PLATFORM. This act was instrumental in averting a national crisis. Stated that Georgia was willing to remain in the Union after the Compromise of 1850 as long as the North complied with the Fugitive Slave Act and would stop trying to ban slavery in new territories and states. What are the key issues and events that led to the Civil War? Day 5 – Selection of Lincoln & Secession Slavery Kansas-Nebraska Act States’ Rights Dred Scott Case Nullification Election of 1860 Missouri Compromise Compromise of 1850 Georgia Platform Debate over the Secession in Georgia Role of Alexander Stephens Division Continues... NORTH SOUTH Reconciliation Is Doubtful! Rise of the Republican Party • Grew quickly • Antislavery Whigs and Democrats became members Election of 1860 Democrats Couldn’t Agree on a Platform... Northern Democrats: *Wanted popular sovereignty *Supported of Stephen A. Douglas Southern Democrats: *Believed slavery should be allowed in all the territories *Nominated Vice President John Breckenridge Whigs • Supported the Union • Named John Bell of Tennessee as their presidential candidate. Republicans • Against Slavery (Said it would not try to end slavery in the slave states) • Supported a protective tariff • Proposed a plan to give free western land to settlers • Called for the construction of the transcontinental railroad with one end in the North. • NONE OF WHICH WOULD BENEFIT THE SOUTH!!! The Election of 1860 Candidate Bell Popular Vote (Georgia) Popular Vote (National) Electoral Vote 42,960 592,906 39 52,176 848,356 72 11,581 1,382,713 12 0 1,865,593 180 106,717 4,689,568 303 (Whigs) Breckenridge (Southern Democrats) Douglas (Northern Democrats) Lincoln (Republicans) TOTALS The Election of 1860 ____________ Party formed in early 1850’s opposed slavery nominated Abraham Lincoln ____________ Party split . . . 1- Northerners nominated Senator Stephen Douglas (IL) 2 - Southerners nominated John Beckinridge (KY) 3-Whigs nominated John Bell (TN) The Election Was a Revolution in Politics! • For the first time, a party getting votes from only one section of the nation won the election. • Abraham Lincoln received a MINORITY of the votes cast. • He won without receiving a single electoral vote in the South. Abraham Lincoln Becomes the President of the Union South Carolina Secedes First... • South Carolina had repeatedly promised that they would secede if Abraham Lincoln was elected President. • On December 20, 1860, South Carolina did just that – they left the Union. • Extremists in every other southern state were loudly yelling for their states to follow South Carolina’s lead. Georgia’s Road to Secession 1) When South Carolina seceded from the Union, Georgia Governor Joseph Brown favored joining right away. 2) Alexander Stephens, a respected Georgia statesman, disagreed. He told Georgians that Lincoln was not the South’s enemy and warned that economic ruin could occur if Georgia seceded. 4) Georgia left the Union in January 1861. 3) 297 Delegates voted; 208 voted in favor of secession. On January 19, 1861, Georgia was declared an independent republic with the following words... “The people of Georgia, having dissolved their political connection with the Government of the United States of America, present to their confederates and the world, the causes which have led to the separation.” Confederate States of America Florida, Alabama, Mississippi, Louisiana, Texas Also Seceded. Jefferson Davis Elected President of the Confederacy Alexander Stephens Elected Vice President of the Confederacy (Georgian who argued passionately against secession) Let’s Review . . . 1)The economy of the South depended largely on – a. slave labor b. new inventions c. manufacturing 2)What did Southerners want to get rid of in the nullification controversy? a. tariff on Northern goods b. tariff on European goods 3)Southerners belief that states should have higher authority than the federal government was called – a. Confederate rights b. States’ rights c. National rights 4) Under this compromise, if a slave state was added to the Union, a free state or territory must also be added – a. Missouri Compromise b. Compromise of 1850 c. Kansas-Nebraska Act 5) The Fugitive Slave Act was added to this compromise to please Southern states – a. Missouri Compromise b. Compromise of 1850 c. Kansas-Nebraska Act 6) This law allowed ‘popular sovereignty’ in several US territories – a. Missouri Compromise b. Compromise of 1850 c. Kansas-Nebraska Act 7) Abraham Lincoln was elected president in 1860. He was a a. Democrat b. Republican c. Independent More... 1) The North was becoming an economy based on – a. farming b. industry c. Music 2) The Southern economy was based ona. agriculture b. industry c. politics 3) A tariff on imported goods made thema. less expensive b. more scarce c. more expensive 4) Many southerners did not want to pay the tariff so they decided toa. ignore b. nullify c. trash 5) State’s rights advocates gave final authority toa. states b. federal c. Congress Match the Legislation with its Description . . . ____ Missouri Compromise ____ Compromise of 1850 ____ Georgia Platform A. State will remain in the Union if the North complies with the Compromise of 1850. B. When a free state is admitted to the Union, a slave state must be admitted to keep a balance. C. California admitted as a free state: New Mexico and Utah organized as territories.