* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download 1 st major battle of the Civil War.
East Tennessee bridge burnings wikipedia , lookup
Battle of Forts Jackson and St. Philip wikipedia , lookup
Red River Campaign wikipedia , lookup
Battle of Stones River wikipedia , lookup
Battle of Roanoke Island wikipedia , lookup
Battle of Antietam wikipedia , lookup
Battle of Wilson's Creek wikipedia , lookup
Texas in the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
Baltimore riot of 1861 wikipedia , lookup
Battle of Island Number Ten wikipedia , lookup
First Battle of Lexington wikipedia , lookup
Cavalry in the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
Battle of Lewis's Farm wikipedia , lookup
Blockade runners of the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
Fort Fisher wikipedia , lookup
Anaconda Plan wikipedia , lookup
Battle of Shiloh wikipedia , lookup
Battle of Port Royal wikipedia , lookup
Virginia in the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
Battle of Gaines's Mill wikipedia , lookup
Opposition to the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
Battle of Namozine Church wikipedia , lookup
Battle of Seven Pines wikipedia , lookup
Battle of Cedar Creek wikipedia , lookup
Capture of New Orleans wikipedia , lookup
Battle of New Bern wikipedia , lookup
Commemoration of the American Civil War on postage stamps wikipedia , lookup
South Carolina in the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
Issues of the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
Western Theater of the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
First Battle of Bull Run wikipedia , lookup
Alabama in the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
Economy of the Confederate States of America wikipedia , lookup
Border states (American Civil War) wikipedia , lookup
Battle of Fort Pillow wikipedia , lookup
Conclusion of the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
United Kingdom and the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
Military history of African Americans in the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
Union (American Civil War) wikipedia , lookup
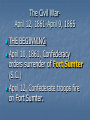
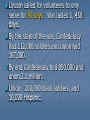
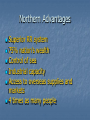
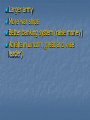
Civil War The Civil WarApril 12, 1861-April 9, 1865 THE BEGINNING April 10, 1861, Confederacy orders surrender of Fort Sumter (S.C.) April 12, Confederate troops fire on Fort Sumter. Preparations for War Both, North and South began training troops and gathering supplies. Number of seceded states rose to 11 by start of war. (MS, FL, AL, GA, LA, TX, SC, VA, NC, TN, AK) MO, KY, MD, and DE all remained in Union, but allowed slavery (border states) Lincoln called for volunteers to only serve for 90 days. War lasted 1, 458 days. By the start of the war, Confederacy had 112,000 soldiers and union had 187,000. By end Confederacy had 850,000 and union 2.1 million. Union: 200,000 black soldiers, and 10,000 Hispanic. Northern Advantages Superior RR system 75% nation’s wealth Control of sea Industrial capacity Access to overseas supplies and markets 4 times as many people Resources Larger army More war ships Better banking system (raise money) Abraham Lincoln (great and wise leader) Southern Advantages Large territory Well trained officers Robert E. Lee Fighting for independence Didn’t need victory, only a draw Defensive Strategy Public opinion in the north was divided on war. Many northerners believed south would win based on American Revolution Strong support of white population to war. Conditions in North 22 million people Strong, well trained army Manufactured weapons RR built to carry heavy loads of manufactured goods Industrial society 23 northern and western states Smooth functioning governments Able to get into war quickly Conditions in South 9 million people (3 1/2 million slaves) No strong navy or trained army Didn’t manufacture guns or ammunition. RR built to carry light loads of farm products. Soldiers A soldiers Life •Nicknamed Johnny Reb and Billy Yank •Usually under 21 •25,000 were 16 yrs. Old or younger •Most came from lower economic group (not slave owners) •Most were not well trained in military. Soldier’s Clothing •The Union usually wore Blue uniforms and the Confederacy wore Gray. •Many did not have official uniforms and many were hand made. •Some soldiers did not receive uniforms and therefore only wore everyday clothing. Union Soldier Confederate Soldier Union soldier’s usually ate better than southern soldiers because they were able to get supplies easier than the south (blockades) Many times the food (especially from the South) was rotten and would be eaten at night so soldiers couldn’t see the worms. Dipped the hard tack in coffee to kill them. Many had to depend on food from the woods or taken from farms. Some of the weapons included: Bowie Knife, bayonet, field cannon, grenades, land mines, musket, navel mines, navel swivel cannon, pistol, revolving rifle, revolver, rockets, Gatling gun. Hot Air Balloons in the Military Ironclad Ships Gatling Gun Other firsts: •Railroad artillery •Submarine •“snorkel” breathing device •Periscope for trench warfare •Land-Mines •Field Trenches •Wire entanglements •Military telegraph •Navel torpedoes •Repeating rifles •Telescopic sights for rifles •Long-range rifles •The Medal of Honor •Photography of battle •Negro U.S. Army Officer (Major M.R. Delany) •American President assassinated War Strategies (North) Blockade Strategy: Obstruct all Confederate ports and seize the Mississippi river. Was put into place to stop south from selling cotton and from getting supplies. Seizing Mississippi was to split the Confederacy in half leaving Texas, Arkansas, and Louisiana stranded. This was the Anaconda Plan. Capture of Richmond: This plan failed because Robert E. Lee was able to hold off Union armies. Destroy Cities: This plan was very successful. The plan was to burn and destroy every city and town so that civilians would stop supporting the war. Ex: Sherman’s march through GA. War Strategies (South) Wear down the North: South thought that many casualties would wear the north down. Destroy the Blockades: Used ironclads and subs to sink the Union’s wooden ships. Also used raiders (fast ships) to get past blockades. King Cotton Diplomacy: Stop selling cotton to England and France and eventually they would come and help south win to keep receiving cotton. It did not work. Military Draft By 1862 few people were volunteering to be in the war and the Confederate government passed the first military draft- which required military service. The Union government did the same in 1863. Exemptions were given by hiring a substitute, being employed in a high need job, being ill, being the sole care for a widow or child One exemption was known as the 20-slave exemption for slave owners. Many saw this as a way out for the rich only. On Sept. 22, 1862 Lincoln issued the Emancipation Proclamation. This stated that unless the south surrendered by January 1, 1863, “all slaves in states and districts in rebellion against the United States on Jan. 1, 1863 will be thenceforth free.” If south had of surrendered, slavery would not have ended at this point. Battles Battle of Bull Run Bull Run: Also called the battle of Manassas because it was located at Manassas, Virginia. This was the 1st major battle of the Civil War. Both sides were not well trained. Stonewall Jackson (Confederacy) became famous during this battle. The Confederacy won, realization war could be long. •Antietam: The bloodiest one-day battle. Fought near Antietam Creek in Sharpsburg, MD. •About 6,000 died and 17,000 wounded. Neither army was defeated. •Robert E. Lee’s orders were found by a Union soldier, but George McClellan the Union General was still not able to defeat the south. Fired by Lincoln and replaced with Ambrose Burnside. Gettysburg: Occurred in Gettysburg, Pennsylvania. Robert E. Lee attempted to break through and head to Washington D.C. 3 things affected the battle: 1. Neither side had whole army when battle began. 2.General J.E.B. Stuart and his cavalry had gone in another direction. 3.James Longstreet failed to join Lee . • Largest battle of the Civil War (over 150,000 soldiers) Last major battle on northern soil. • 51,000 died. Lincoln gave Gettysburg Address shortly afterwards on this battlefield. Fort Pulaski: On Tybee Island off the coast of Savannah. First area to see action in GA. On Jan. 3, 1861 Confederate Troops captured it. In April 1862, Union took it back, after the commander refused to give it up. A day and a half battle took place. 1st use of rifled cannons in GA. Last fort made of bricks. Rifled Cannons •Chickamauga: Located 7 miles south of Chattanooga TN. •Braxton Bragg was the famous commander for the south. He did not allow the North to advance into GA. • Bragg mistakenly did not follow the Union army and push them further away from GA. This allowed Sherman to later advance into GA Chickamauga Battle Field General Joseph E. Johnston (South) General William Tecumseh Sherman (North) General John Bell Hood (South) •Sherman’s immediate goal was to capture Atlanta (transportation center of south) •The Atlanta Campaign was the name of the movement to take Atlanta •Because of the Joseph Johnston’s resistance forces it took Sherman 4 months to reach Atlanta. •Sherman was pushed back at Kennesaw, but used flanking moves and advanced on. •Jefferson replaced Johnston with Hood •After remaining in Atlanta for 2 months, he began his March to the Sea, cutting a path sixty miles wide and 300 miles long, destroying everything in the path. •On Dec. 24, 1864, Sherman gave Lincoln a gift of the city of Savannah. •Now the lower south was cut off from the rest of the confederacy. Andersonville (GA) • Overcrowded Andersonville prison houses Union POWs • Poor conditions, gangs, starvation, disease kills 13,000 at Andersonville. Large civil war cemetery and museum located on the site today. • 30,000 placed in prison met for less than 10, 000 Andersonville •On April 9, 1865, General Lee surrendered to General Grant of the Union at Appomattox Courthouse in Virginia. Terms of Surrender •All officers and enlisted men in the Confederate army would be paroled. •All military equipment and weapons had to be relinquished to the Union. General Ulysses S. Grant of the Union General Robert E. Lee of the Confederacy Cost of the War •The war cost the U.S. government about $2 million per day or about $6 billion total. •The south spent about $4 billion on the war effort. •Around 630,000 soldiers died in the Civil War •The south was devastated