* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download The Civil War
East Tennessee bridge burnings wikipedia , lookup
Battle of Appomattox Station wikipedia , lookup
Battle of Cumberland Church wikipedia , lookup
Fort Fisher wikipedia , lookup
Battle of Fredericksburg wikipedia , lookup
Battle of Roanoke Island wikipedia , lookup
United States presidential election, 1860 wikipedia , lookup
Battle of Harpers Ferry wikipedia , lookup
Battle of Island Number Ten wikipedia , lookup
Economy of the Confederate States of America wikipedia , lookup
Hampton Roads Conference wikipedia , lookup
Red River Campaign wikipedia , lookup
Kentucky in the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
Battle of Wilson's Creek wikipedia , lookup
South Carolina in the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
Virginia in the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
Battle of Malvern Hill wikipedia , lookup
Baltimore riot of 1861 wikipedia , lookup
Battle of New Bern wikipedia , lookup
Battle of Lewis's Farm wikipedia , lookup
Commemoration of the American Civil War on postage stamps wikipedia , lookup
Second Battle of Corinth wikipedia , lookup
Capture of New Orleans wikipedia , lookup
Battle of Fort Pillow wikipedia , lookup
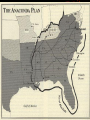
Anaconda Plan wikipedia , lookup
Battle of Shiloh wikipedia , lookup
Battle of Perryville wikipedia , lookup
Northern Virginia Campaign wikipedia , lookup
Battle of Antietam wikipedia , lookup
Eastern Theater of the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
Battle of Stones River wikipedia , lookup
Western Theater of the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
Maryland Campaign wikipedia , lookup
Battle of Namozine Church wikipedia , lookup
Opposition to the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
Issues of the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
Georgia in the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
Alabama in the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
Conclusion of the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
Border states (American Civil War) wikipedia , lookup
First Battle of Bull Run wikipedia , lookup
Battle of Seven Pines wikipedia , lookup
United Kingdom and the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
Military history of African Americans in the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
Battle of Gaines's Mill wikipedia , lookup
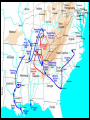
The Civil War • General Winfield Scott asked Robert E. Lee to command the Union’s troops. • Lee was one of the best officers in the U.S. Army. • Lee was from VA • One-third of the military officers chose to support the Confederacy • Seven of the eight military colleges were located in the South • The North had a strong Naval tradition Advantages/Disadvantages • North • Twice as many people living here • Industry gave the North an economic advantage • Produce 90% of the nation’s pig-iron • Most of the nation’s railroad tracks were found here • The North also controlled the treasury and could continue to collect tariffs • Legal Tender Act passed by Congress • South • One-third of the people were slaves • The South had to set up armories and foundries after the war began • The South could produce a lot of food • The South had the best leadership • Southerners felt that they were fighting for a cause Party Politics • Many Northern Democrats and Republicans challenged Lincoln’s policies, once the war began. • Lincoln wanted to preserve the Union, even if that meant allowing slavery to continue. • The War Democrats supported the Civil War and restoring the Union. They did not want to end slavery. • The Peace Democrats, referred to by Republicans as Copperheads, opposed the war. • In 1862 Congress passed a law that required the states to use conscription, or the draft. • Lincoln also suspended the writ of habeas corpus – a person’s right not to be imprisoned unless charged with a crime and given a trial. The First Modern War • New military technology. • Cone shaped bullets • Iron Clad ships • Cannon shot that would explode on impact • New Tactics • Huge armies made up of civilian volunteers • Trench warfare and barricades were used • Attrition – the wearing down of one side • Soldiers and resources • The Anaconda Plan Mobilizing Troops • Confederate reinforcements at the First Battle of Bull Run were led by Thomas J. Jackson, or “Stonewall” Jackson. • one of the most effective commanders in the Confederate army • The Union Army commander was General Irwin McDowell. He would panic at the sign of Confederate reinforcements, and order his troops to retreat. Naval War • The Union navy had blockaded all Confederate ports by 1862, except for Charleston, South Carolina, and Wilmington, North Carolina. • Lincoln wanted to cut the South’s trade from the rest of the world. • The Union couldn’t stop all of the blockade runners, small, fast vessels, used by the South to smuggle goods past the blockade. War in the West • Union troops were led by Ulysses S. Grant • Wanted to control the Cumberland and Tennessee Rivers – this would cut TN in two • Grant had victories at Forts Henry and Donelson • Grants troops launched a surprise attack at Shiloh – the Union army was victorious, however; they suffered twenty thousand casualties War in the West • Confederate troops led by General Braxton Bragg invaded Kentucky. • They were stopped by General Don Carlos Buell at the Battle of Perryville. • Buell was ordered by Lincoln to seize Chattanooga and cut the rail lines that passed there to deprive the Confederacy of supplies they needed. • Buell moved too slowly and Lincoln replaced him with General William Rosecrans. • Bragg’s forces attacked Rosecrans’ forces near Murfreesboro. Union reinforcements convinced Bragg to retreat to Chattanooga. War in the East • General George B. McClellan took over the Union army in the east after General McDowell’s loss at the First Battle of Bull Run. • The Union wanted to capture Richmond. • McClellan took too long to capture Yorktown. This gave the Confederates time to move troops to protect Richmond • Joseph Johnston attacked McClellan’s troops. • Divided McClellan’s forces • The Union suffered great casualties War in the East • Robert E. Lee took over Johnston’s forces and began a series of attacks against McClellan known as the Seven Days’ Battle. • Heavy Union casualties • Lee then attacked Union forces surrounding Washington D.C. • This was known as the Second Battle of Bull Run • Union troops had to retreat and the Confederate troops were just 20 miles from D.C. • The Battle of Antietam followed. This was the bloodiest one-day battle of the war. (23,000) • McClellan inflicted so many casualties on the Confederate army that Lee decided to retreat to Virginia. • This convinced Lincoln to put an end to slavery. The Emancipation Proclamation • September of 1862 • Lincoln announced that he would free all enslaved persons in states in rebellion after January 1, 1863 • The Emancipation Proclamation changed the Civil War from a conflict over preserving the Union to a war to free the slaves.