* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download July 1863-1864
Battle of Fort Donelson wikipedia , lookup
Georgia in the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
Military history of African Americans in the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
Kentucky in the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
Union (American Civil War) wikipedia , lookup
East Tennessee bridge burnings wikipedia , lookup
Battle of Appomattox Station wikipedia , lookup
Battle of Fort Pillow wikipedia , lookup
Conclusion of the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
First Battle of Lexington wikipedia , lookup
Ulysses S. Grant and the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
Battle of Sailor's Creek wikipedia , lookup
Battle of Cumberland Church wikipedia , lookup
First Battle of Bull Run wikipedia , lookup
Battle of Roanoke Island wikipedia , lookup
Battle of New Bern wikipedia , lookup
Battle of Shiloh wikipedia , lookup
Battle of Lewis's Farm wikipedia , lookup
Battle of Harpers Ferry wikipedia , lookup
James Longstreet wikipedia , lookup
Battle of Malvern Hill wikipedia , lookup
Mississippi in the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
Battle of Chancellorsville wikipedia , lookup
Battle of Namozine Church wikipedia , lookup
Battle of Cedar Creek wikipedia , lookup
Second Battle of Corinth wikipedia , lookup
Western Theater of the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
Battle of Perryville wikipedia , lookup
Battle of Antietam wikipedia , lookup
Maryland Campaign wikipedia , lookup
Second Battle of Bull Run wikipedia , lookup
Battle of Fredericksburg wikipedia , lookup
Northern Virginia Campaign wikipedia , lookup
Battle of Stones River wikipedia , lookup
Chattanooga Campaign wikipedia , lookup
Battle of Gaines's Mill wikipedia , lookup
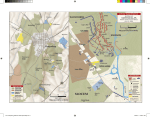
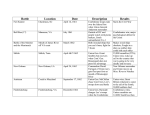
IX. The Tide Turns 1863 A. Lee Invades the North Part II • CSA on the move – – – – – Began June 3, 1863 With Jackson gone, Lee reorganizes the army I corps: James Longstreet (take Culpepper Courthouse II corps: Richard S. Ewell (drive off scattered Union forces III corps: A.P. Hill (moves northward with Lee) • Lee sets off northward on June 14, crosses the Potomac and heads east • J.E.B. Stuart’s mistake – Stuart was riding Lee’s right flank informing him of Union movements – Stuart believed he could ride around Hooker and get a better idea of Union movements – Union movement pushed Stuart farther east than anticipated and he was out of contact with Lee for 10 days B. Road to Gettysburg • Lee arrives in Pennsylvania with his army spread out because he believes the Union has not crossed the Potomac yet • June 28: Lee learns from Longstreet’s scout (Henry T. Harrison- actor) that the Union army is concentrated squarely on Lee’s flank in Frederick, MD • Lee moves south to the nearest defensible position just outside Gettysburg • Hooker is replaced by George G. Meade C. Battle of Gettysburg- Day 1 1) General Henry Heth, on a mission to find shoes, encounters Gen. John Buford’s dismounted cavalry- he attacks though ordered not to 2) Buford’s cavalry holds for several hours as Gen. John Reynolds and 3 corps of infantry arrive to reinforce 3) Reynolds is shot and killed 4) Lee orders A.P. Hill’s corps to attack 5) Gen. Ewell’s corps comes over the mountain and arrives on the field hitting the Union right flank hard 6) Union retreat through the town and occupy the high ground beyond 7) Union occupy Culp’s and Cemetery Hill. Lee orders Ewell to take the hill if practicable. Ewell refuses to take the hill and day 1 ends • Longstreet and Lee argue whether or not to stay and fight- Lee chooses to stay D. Day 2 8) Lonstreet’s artillery opens the battle on day 2- Hood takes the Devil’s Den but is wounded and loses his arm 9) Col. Joshua Lawrence Chamberlain commands the 20th Maine regiment on Little Round Top, the end of the Union line- he is ordered by Col. Vincent to hold to the last. Little Round Top • After resisting 4 charges by the 15th Alabama, Chamberlain reforms his line at a right angle • It is after a 5th charge that the 20th Maine are out of ammunition- Chamberlain orders his men to fix bayonets • As the 15th Alabama approaches, Co. B of the 20th Maine arises from behind a stone wall and fires into their side • Chamberlain orders a bayonet charge swinging down the hill like a gate 10) Longstreet moves on the peach orchard and wheat field smashing Gen. Dan Sickles line- Sickles loses his leg 11 & 12) Union re-patch the line as they are heavily attacked 13) Longstreet attacks the center where the Union and the 1st Minnesota repulse them 14 & 15) Generals Ewell and Early attack Cemetery & Culp’s Hill unsuccessfullyDay 2 ends • Longstreet begs Lee to allow him to flank the Union- Lee chooses to attack the center E. Day 3 16) Day 3 begins with an artillery barrage by Col. E. Porter Alexander 17) The barrage is accompanied by diversionary attacks on both flanks • Longstreet waits too long to begin his attack 18) General George Pickett leads a milelong, uphill, open ground charge against Gen. Winfield Scott Hancock and the Union center 19) CSA retreat after suffering massive casualties during Pickett’s Charge F. Captain’s Report • George Meade • 90,000 • 23,049 casualties • Robert E. Lee • 75,000 • 28,063 casualties Union Victory G. Vicksburg • Grant lays siege to Vicksburg and surrounding areas for 8 months • Gen. Pemberton was caught off guard and never got back on track against Grant • Grant traps Pemberton in Vicksburg and forces a surrender on July 4- Union now control the Mississippi River • Gettysburg falls on the 3rd, Vicksburg the 4th, and the tide has turned in favor of the North H. Chickamauga • Longstreet’s corps is transferred to the west to aid the Army of Tennessee in stopping the advancement of Rosecrans • Lee chose to rest his army and take up defensive positions in Virginia • Rosecrans moves on Chattanooga and opens the way for East Tennessee to be liberated by Ambrose Burnside in early September when he occupies Knoxville • Rosecrans pushes Bragg out of Chattanooga- Bragg stops @ Chickamauga & awaits reinforcements I. Battle of Chickamauga 1) Gen. Polk’s attacks fail to break though Gen. George H. Thomas’ line 2) Gen. Longstreet slams through a gap in the Union center 3) Panic sweeps through the Union flank as commanding officers flee including Gen. Rosecrans 4) Union avoids complete destruction as Gen. Thomas makes a stand on Snodgrass Hill 5) Gen. Grainger stops CSA charges as the Union retreats to Chattanooga J. Captain’s Report • William Rosecrans • 60,000 • 16,170 casualties CSA Victory • Braxton Bragg & James Longstreet • 67,000 • 18,454 causualties K. Aftermath of Chickamauga • Bragg handled his army poorly @ Chickamauga • Longsteet had saved the CSA from destruction during the battle • Bragg’s subordinates asked Davis to remove him- Bragg removed all his subordinates • Longstreet wrote Davis pleading for Bragg’s removal- Bragg attempted to remove Longstreet • Davis had to resolve the problem in person • Rosecrans was replaced by Gen. Thomas L. Chattanooga • Union forces move into Chattanooga after their defeat at Chickamauga • They receive reinforcements – Gen. Joseph Hooker (2 corps) from VA – Gen. William T. Sherman from Memphis • The armies of the Tennessee and the Cumberland are now concentrated in Chattanooga • Ulysses S. Grant is made overall commander of the western armies M. Battle of Chattanooga 1) Following the defeat @ Chickamauga, the Union retreat to a fortified Chattanooga 2) Grant creates a supply line through Brown’s Ferry 3) Nov. 23: Grant attacks and seizes Orchard Knob 4) Nov 24: Grant attacks both CSA flanks as Hooker attacks and captures Lookout Mt. 5 & 6) Sherman crosses the Tennessee River and aims for Tunnel Hill- he misses & entrenches on a nearby hill 7) Nov. 25: Sherman tries to take Tunnel Hill and fails 8) Grant orders Thomas to seize the foot of Missionary Ridge 9) Thomas’ men refuse to stop and they push Bragg off of the Ridge as the CSA retreat N. Captain’s Report • Ulysses S. Grant • 60,000 • 5,824 casualties Union Victory • Braxton Bragg • 46,000 • 6,667 casualties O. Occupation of Knoxville • Burnside was sent to take command of the Department of Ohio in March of 1863 • He was sent to occupy the city of Knoxville on September 2, 1863 to “liberate East Tennessee” of the CSA presence- Lincoln believed that by taking East Tennessee, he would have the CSA by the throat • Jefferson Davis had to make a trip to Chickamauga to settle the dispute between Bragg & Longstreet- Davis sends Longstreet to Knoxville • Longstreet moved his men on November 2 toward Knoxville- due to the condition of the trains, he did not arrive in Sweetwater until November 13 • Burnside’s fortifications surrounded the city of Knoxville • Longstreet began his siege of Knoxville on Nov. 17 • Longstreet made his headquarters in Bleak House owned by Robert Armstrong (located today on Kingston Pike not far from Neyland Dr.) P. The Battle of Knoxville • Longstreet determined that the best point of attack was on Ft. Sanders • Longstreet believed this to be the weakest point of Burnside’s defenses- the fort was deceiving • The fort was surrounded by a ditch 6-8 feet deep and appeared to be only 3-4 feet deep. Some planks had been placed across it and, from distant Confederate observation posts, troops were observed crossing easily -- but they were using the planks. • The earthen walls were 13 feet high in most places, and had cotton bales piled on top to protect the riflemen and were wrapped in rawhide to prevent fire. • Water had been poured down the side of the earthen fort. It froze overnight and created ice on its sides and in the ditch. • For perhaps 30 to 80 yards in front of the northwest bastion that was selected for the assault, there were 18-inch tree stumps between which the engineers had stretched telegraph wire to trip and delay the attackers. • Longstreet ordered a short artillery barrage by Gen. E.P. Alexander, afterwards, 3 brigades charged the fort • The telegraph wires and the now apparent 12 ft. wide ditch slowed the CSA down under considerable musket fire • The CSA did enter the ditch, but without scaling ladders • The battle lasted 20 minutes and resulted in a devastating defeat for the CSA • Lonstreet retreated to Jefferson County for the winter- a record cold winter P. Captain’s Report • Gen. Ambrose Burnside • 23,000 • 100 casualties Union Victory • Gen. James Longstreet • 15,000 • 800 casualties