* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download History of Astronomy
Chinese astronomy wikipedia , lookup
Outer space wikipedia , lookup
De revolutionibus orbium coelestium wikipedia , lookup
Archaeoastronomy wikipedia , lookup
Planets beyond Neptune wikipedia , lookup
Lunar theory wikipedia , lookup
Theoretical astronomy wikipedia , lookup
Aquarius (constellation) wikipedia , lookup
International Ultraviolet Explorer wikipedia , lookup
IAU definition of planet wikipedia , lookup
Observational astronomy wikipedia , lookup
Solar System wikipedia , lookup
Tropical year wikipedia , lookup
Definition of planet wikipedia , lookup
Astrobiology wikipedia , lookup
Rare Earth hypothesis wikipedia , lookup
Late Heavy Bombardment wikipedia , lookup
Planets in astrology wikipedia , lookup
Satellite system (astronomy) wikipedia , lookup
Formation and evolution of the Solar System wikipedia , lookup
Comparative planetary science wikipedia , lookup
Planetary habitability wikipedia , lookup
History of Solar System formation and evolution hypotheses wikipedia , lookup
History of astronomy wikipedia , lookup
Extraterrestrial life wikipedia , lookup
Astronomical unit wikipedia , lookup
Copernican heliocentrism wikipedia , lookup
Ancient Greek astronomy wikipedia , lookup
Hebrew astronomy wikipedia , lookup
Geocentric model wikipedia , lookup
Dialogue Concerning the Two Chief World Systems wikipedia , lookup
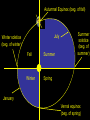
The History Of Astronomy Ancient times (Before 3000 B.C): • People believed that the earth is Flat and that astronomical bodies pass beneath Earth at night • Some cultures were interested in astronomical events, as evidenced by stone structures that were designed to match up with solstices (Carnac, Newgrange Tomb, Stonehenge, Giza Pyramids & Sphynx) Newgrange Tomb, Ireland Stonehenge, England Babylonians (3000 BC) • Mathematical theory rather than just observations • Motions of the sun and moon • Provided the first evidence that the earth is round • Developed basic constellations and astrology • Introduced the 24 hour day • Developed a lunar calendar Aristotle (384 BC – 322 BC) Geocentric Theory • Proved that the earth is spherical • Believed that the earth is the center of the solar system and that everything revolves around it • Believed that all stars are fixed points which rotate on a single celestial sphere 6 Aristotle believed there were only a few basic Substances 1. Earthly Realm – Air, Earth, Fire, and Water 2. Heavenly Realm – Quintessence (Not found on Earth) Aristotle agreed that the Earth is spherical BUT didn’t believe that the earth moved. 1. No Rotation- NO sense of motion...no strong winds…..No displacement of thrown object. 2. No Revolution – No measureable stellar parallax, BUT the stars were too far away to measure stellar parallax back then. They needed better equipment. The soul passing into quintessence Stellar Parallax – Aristotle said that if the earth revolved, the closer stars should shift among the background of further stars. They actually do shift but not enough for ancient astronomers to detect. 9 Aristarchus (310-230 B.C.) • 1st to place the sun at the center of the universe, but his ideas were to radical for anyone to accept. • 1750 years BEFORE Copernicus! Eratosthenes (276 - 195 B.C.) • 1st person able to measure the circumference of the Earth Hipparchus (190-120 B.C.) • Compiled first star catalog • Developed a scale for star brightness • Accurately calculated distance from Earth to the moon! Ptolemy (90 – 168 AD) • Earth-centered model which included a complex system of Epicycles and perfect circles for the orbits of planets, sun, and moon around Earth • Assumed that the imperfect Earth was surrounded by perfect heavenly spheres Ptolomy’s model worked so well, it was not challenged for 1300 years! Copernicus (1473-1543, Poland) • Popularized the suncentered, “heliocentric” model of universe • Stated that the earth spins once per day on its axis and revolves around the sun in one year • Published in Des Revolutionibus in 1543 (on his death bed) The Heliocentric Model • Sun at center of universe • Planets orbit sun in perfect circles • Stars on a huge fixed sphere (the firmament) More Copernicus • • • • • • Explained retrograde motion using passing orbits Correctly ordered planets, and calculated their distances! Correctly calculated time for planets to orbit sun Explained apparent motion of stars and sun using Earth’s rotation and orbit Explained why Mercury and Venus are always seen near the Sun Invented idea of Astronomical Unit (A.U.) – Distance of Earth from the Sun (About 93 million miles) Distances of Planets from the Sun Planets Copernicus Modern Mercury Venus Earth Mars Jupiter Saturn 0.38 0.72 1.00 1.52 5.22 9.18 0.387 0.723 1.00 1.52 5.20 9.54 Distances Measured In Astronomical Units (A.U.) 15 Tycho Brahe (Teeko Bra-hay) (1546 - 1601) • • • • • • • A Danish nobleman Believed in geocentric model of solar system designed and built accurate and powerful instruments to observe the stars used these instruments to chart the positions of planets and other celestial objects with great precision disproved many of the commonly held notions of planetary and stellar motion Difficult to work with. He wasn’t very nice :-\ Died of a burst bladder (yukko!) Johannes Kepler (1571- 1630) • Worked with Tycho Brahe and kept his equipment and notes • Proposed that orbits of planets are ellipses, not circles • Developed 3 simple laws to explain planetary motion in 1609 ** 1st law- Orbit of all planets are ellipses with the sun at one focus ** 2nd law – Law of Equal Areas which defines planetary speed as they go around the Sun ** 3rd law – As planet distance from the Sun increases, orbital period increases Kepler’s 1st Law of Planetary Motion • The orbit of a planet is an ellipse, with the sun at one focus. Kepler’s 2nd Law of Planetary Motion • When a planet is nearer the sun in its orbit (perihelion), it moves faster. When it’s farther from the sun (aphelion), it moves slower. Autumnal Equinox (beg. of fall) July Winter solstice (beg. of winter) Fall Summer Winter Spring Summer solstice (beg. of summer) January Vernal equinox (beg. of spring) Kepler’s 3rd Law of Planetary Motion • The larger the planet’s orbit, the longer it takes. Planet, etc. Mercury Venus Distance 0.39 AU 0.72 AU Period 88 days 225 days Earth Mars Jupiter 1.00 AU 1.5 AU 5.2 AU 365 days 687 days 11.9 years Saturn 9.5 AU Halley’s Comet ~ 17 AU 29.4 years 76 years Galileo Galilee (1564–1642, Italy) • Father of observational astronomy • 1st to publish in Italian…Not Latin! • While he did not invent the telescope, he was the first to use the telescope for astronomy Galileo’s Astronomical Accomplishments • Redesigned the telescope to be suited for observing the sky (only 14X magnification) • Discovered that there were many stars not visible to the naked eye More Galileo • • Discovered mountains, craters, and plains on Moon Discovered phases of Venus similar to the moon And More Galileo • Discovered sunspots on Sun Still More Galileo • Discovered 4 moons orbiting Jupiter Progress at Personal Cost • Placed under house arrest by Catholic Church and made to confess “vainglorious ambition” and mistakes of “pure ignorance” (aka – renounce Copernicanism) • Not all religious: some political and personal rivalries, too • Worked on laws of motion and falling bodies until his death (8 years later) Phases of Venus….Evidence for a Heliocentric Solar system Isaac Newton (1642-1727, England) • • • Not expected to live over a few hours…instead lived 84 years and 3 months Served as England’s “Master of the Mint” Knighted in 1705 Newton’s Contributions • • • Invented calculus (at age 23!) Realized that “white light” can be broken down into colors of rainbow using a prism (age 30) Invented reflecting (mirror-based) telescope, a great improvement over Galileo’s refracting (lens-based) telescope More Newton Mathematically derived Kepler’s 3 Laws. • Calculated the existence of other planets due to orbital anomalies of outer known planets • Law of Gravity: • Gravity exists between any 2 objects that have mass • Gravity is always attractive, never repulsive • Gravity increases with increasing mass • Gravity decreases with increasing distance • 3 Laws of Motion • Newton’s 1st law applied to Planets Albert Einstein (1879 – 1955 A.D.) Came up with many theories which expanded our understanding of the universe a. Space and time are not separate units but rather one unit called space-time b. Gravity is the curvature of space-time. The more massive the object, the greater the curvature. (This is the basis of Einstein’s General Relativity Theory) *** Einstein explained the true nature of gravity. • That it’s not a force but a pathway that a mass takes around more massive objects. This theory was proven correct by the deflection of starlight observed during a 1919 eclipse. c. Most Famous for the Equation E=mc2 which led to the development of the atomic bomb Einstein’s Theory of Relativity Edwin Hubble (1889 - 1953) • determined that so-called “spiral nebulae” were, in fact, other galaxies, proving that the Universe extends well beyond our own galaxy. • showed that these other galaxies were moving away at speeds proportional to their distances away form us. Georges Lemaître : (1894 – 1966): • Belgian priest, astronomer and physics professor • proposed the theory of the expansion of the Universe, widely misattributed to Edwin Hubble. • derived what is now known as the Hubble's law and made the first estimation of what is now called the Hubble constant which he published in 1927, two years before Hubble's article. • proposed what became known as the Big Bang theory of the origin of the Universe Stephen Hawking (1942 - ): • Combined the theories of general relativity and quantum physics to prove that black holes emit radiation • Has written several books that explain complicated subjects in astronomy, physics, and cosmology to the general public. • Completely paralyzed due to ALS, yet his computer generated voice is very famous.