* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download The Egyptian Civilization
Survey
Document related concepts
Thebes, Egypt wikipedia , lookup
Index of Egypt-related articles wikipedia , lookup
Art of ancient Egypt wikipedia , lookup
Ancient Egyptian funerary practices wikipedia , lookup
Ancient Egyptian medicine wikipedia , lookup
Prehistoric Egypt wikipedia , lookup
Mastaba of Kaninisut wikipedia , lookup
Middle Kingdom of Egypt wikipedia , lookup
Ancient Egyptian race controversy wikipedia , lookup
Mastaba of Hesy-Re wikipedia , lookup
Military of ancient Egypt wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
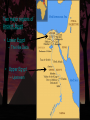
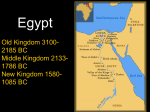
The Egyptian Civilization Two major regions of Ancient Egypt • Lower Egypt – The Nile Delta • Upper Egypt – Upstream The Nile River • Flows from south to north. • Boats could use the current to travel north… • Or use the winds to travel south. • Why is the Egyptian civilization known as the “gift of the Nile?” The Nile River • Flooded every summer – Left silt and rich soil on sides of the river. • Egyptians were relatively isolated from other civilizations. • These factors allowed the Egyptians to feel secure. – Had confidence in stability of their civilization. Egyptian Writing • Earliest writing was called hieroglyphics – Means “sacred writings” – Very complex – used pictures – Used on temple walls and in tombs. • Hieratic script is a simplified version of hieroglyphics. Three Major Periods • The Old Kingdom • The Middle Kingdom • The New Kingdom • These periods had… – Strong leadership – Freedom from invasion – Great building projects – Rich cultural activity The Old Kingdom • Lasted from 2700 B.C. to 2200 B.C. • Pharaoh – Title of Egyptian monarch – A God-King far from his people. • Also established a bureaucracy – An administrative organization • Built Pyramids – Buildings dedicated to the dead. – Build the Great Pyramid at Giza The Great Pyramid at Giza •Built for King Khufu in 2540 B.C. •Traditional story is that it took 100,000 Egyptians 20 years to build. The Great Pyramid at Giza The Great Pyramid at Giza The Great Sphinx at Giza •Body of a lion, head of a human. •Believed to be a likeness of Khufu’s son Khafre. •The sphinx is an important guardian of sacred sites. The Great Sphinx at Giza The Middle Kingdom • Lasted from 2055 B.C. to 1650 B.C. • Egypt begins to expand… – Invaded Nubia and SyriaPalestine. • Begins trading with… – Greece – Mesopotamia! • Invaded by Hyksos people in 1650 B.C. – They rule Egypt for 100 years. The New Kingdom • Lasts from 1550 B.C. to 1070 B.C. – In 1550 B.C., new pharaohs use new weapons to retake Egypt. • These new pharaohs become very powerful and wealthy. – Built many temples to show off wealth. • Examples: Hatshepsut and Tutankhamen Hatsheptsut • One of the first women to become pharaoh. Hatsheptsut • She builds a great temple near Thebes. Hatsheptsut Tutankhamen • Was only 8 or 9 years old when he became king. • Died at age 25 – his death remains a mystery. • His tomb was discovered in 1922 by Howard Carter. – Was the most intact and best preserved tomb ever discovered. Tutankhamen’s Tomb Tutankhamen’s Tomb Tutankhamen’s Tomb Tutankhamen’s Tomb Ramses II’s Tomb Ramses II’s Tomb Ramses II’s Tomb Ramses II’s Tomb Ramses II’s Tomb The New Kingdom • Collapses in 1070 B.C. • Egypt is then ruled by other civilizations for the next 1000 years. – Eventually becomes part of the Roman empire. • Which kingdom (Old, Middle, or New), do you consider to be Egypt’s Golden Age?











































![[5] Montague, D. Dictionary of Building and Civil Engineering](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/009004976_1-fc6389c636aacce74a2f42b6beed4fed-150x150.png)

