* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download a planet rotates on its own axis and revolves around
Outer space wikipedia , lookup
Equation of time wikipedia , lookup
Kepler (spacecraft) wikipedia , lookup
Rare Earth hypothesis wikipedia , lookup
Astrobiology wikipedia , lookup
History of astronomy wikipedia , lookup
Advanced Composition Explorer wikipedia , lookup
Nebular hypothesis wikipedia , lookup
Planets beyond Neptune wikipedia , lookup
Dialogue Concerning the Two Chief World Systems wikipedia , lookup
Definition of planet wikipedia , lookup
Crab Nebula wikipedia , lookup
IAU definition of planet wikipedia , lookup
Geocentric model wikipedia , lookup
Late Heavy Bombardment wikipedia , lookup
Planets in astrology wikipedia , lookup
Satellite system (astronomy) wikipedia , lookup
Aquarius (constellation) wikipedia , lookup
Extraterrestrial life wikipedia , lookup
Comparative planetary science wikipedia , lookup
Planetary habitability wikipedia , lookup
Tropical year wikipedia , lookup
Astronomical unit wikipedia , lookup
History of Solar System formation and evolution hypotheses wikipedia , lookup
Solar System wikipedia , lookup
Timeline of astronomy wikipedia , lookup
Formation and evolution of the Solar System wikipedia , lookup
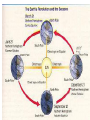
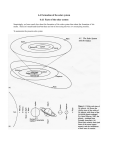
Solar System Formation and MOTION Process of Solar System Formation Solar Nebula The solar nebula is the name of the nebula that formed into our own solar system Nebula Gas and dust, very cold Two forces at work Gravity and pressure balance each other out to prevent nebula from collapsing or falling apart Birth of a Star The central part of the solar nebula contained so much mass and had become so hot that hydrogen fusion began. Outward pressure in the center balanced with the inward force of gravity that the gas stopped collapsing Our sun was born! Planets Gas giants (Jupiter, Saturn, Uranus, and Neptune) collected large amounts of dust in the cooler, outer solar nebula Closer to the sun, it was too hot for gases to remain, so these inner planets are made of rocky material (Mercury, Venus, Earth, Mars) Planetary Motion Everything in the solar system moves according to strict physical laws Each object follows different time frames and patterns for this to occur Rotation Rotation-Earth's spinning on its axis, which happens every 24 hours or a day. This is how day and night happen Revolution Orbit – a planet rotates on its own axis and revolves around the sun in a path Revolution- Earth completes an orbit around the sun which happens every 365.24 days or a year (leap years would be 366 days) This is how the seasons occur How were planetary orbits discovered? Johannes Kepler, German astronomer discovered this in 1601 Kepler's First Law of Motion Planets do not move in a circle around the sun, but in an elongated circle, or ellipse Distances in space Astronomical unit (AU) – represents the average distance between the Earth and the sun 1AU =149,597,817 km=92,955,807 mi Kepler's Second Law Kepler discovered that planets move faster when they are closer to the sun and slower when they are further away Kepler's Third Law If you know a planet's period of revolution, you can calculate its distance from the sun. Law of universal gravitation Developed by Newton, states that the force of gravity depends on the product of the masses of the objects divided by the square of the distance between them. Gravity is always working in the universe and it depends on the objects size, mass and location