* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download World War II European Front
Consequences of Nazism wikipedia , lookup
Battle of the Mediterranean wikipedia , lookup
World War II by country wikipedia , lookup
Allied plans for German industry after World War II wikipedia , lookup
Appeasement wikipedia , lookup
New Order (Nazism) wikipedia , lookup
Economy of Nazi Germany wikipedia , lookup
Foreign relations of the Axis powers wikipedia , lookup
Technology during World War II wikipedia , lookup
Home front during World War II wikipedia , lookup
Western betrayal wikipedia , lookup
Allies of World War II wikipedia , lookup
Naval history of World War II wikipedia , lookup
Invasion of Normandy wikipedia , lookup
End of World War II in Europe wikipedia , lookup
American Theater (World War II) wikipedia , lookup
Diplomatic history of World War II wikipedia , lookup
Causes of World War II wikipedia , lookup
Consequences of the attack on Pearl Harbor wikipedia , lookup
War Front: Turning Point wikipedia , lookup
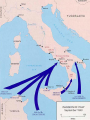
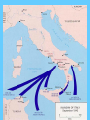
WORLD WAR II World War II • World War II –Dictators ruling Europe –Hitler in Germany –Mussolini in Italy –Stalin in Russia Europe on the brink of war (AGAIN) 1933- Germany has rearmed and rebuilt their industry 1936- Germany and Italy allied forming Axis Power alliance 1936 Japan and Germany agree to work together to stop spread of Communism • Germanys’ aggression in Europe • Germany annexed Austria • France and Great Britain took no action • Another violation of Treaty of Versailles –What might have happened if they took some action against the aggression? World War II • Sudetenland part of Czechoslovakia –Hitler believed it was part of Germany • 3 million Germans lived there Hitler threatened to invade Sudetenland to protect German citizens from harm. • France and Great Britain take action –Is it a military confrontation? –No •1938 Munich Conference September 29, 1938 Britain and France agreed to allow Hitler and Germany to annex the Sudetenland Was this a good decision? Appeasement Policy of accepting demands of an aggressor in an attempt to avoid war • Neville Chamberlain –“Peace in our Time” • France would not protect Czechoslovakia –March 1939 Invasion of Czechoslovakia and Lithuania –Mussolini invaded Albania • Stage is set for war –Britain and France prepare •Hitler aware of the problem of a two front war signs a –NON AGRESSION PACT –With Stalin and Russia • Germany and Russia started secret talks while Germany was negotiating with Great Britain and France. –Terms of Non Aggression pact: –Will not attack each other – Will remain neutral if either is attacked • What was not announced to the world: Hitler and Stalin agreed to divide parts of Eastern Europe Germany – Western Poland Soviets - Eastern Poland, Baltic countries WORLD WAR II What advantage did Germany gain from the Neutrality of Russia? WORLD WAR II • Invasion of Poland –Port city of Danzig –Was under joint Polish and German control WORLD WAR II • September 1, 1939 annexed city –At same time massive attack on Poland •Air •Land •Blitzkrieg WORLD WAR II • Luftwaffe German Air Force –Bombed Poland –Land forces invaded Poland • Luftwaffe destroyed all of Poland’s old aircrafts • Disrupted railroads WORLD WAR II • Poland fell in three weeks WORLD WAR II • Britain reacts WORLD WAR II • Appeasement • Munich Conference • Czechoslovakia • “Peace in our time” • Neville Chamberlin • Poland • Blitzkrieg • Winston Churchill • Non-Aggression Pact http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=8ha0qKq uG2E WORLD WAR II • German Aircraft –Stukas Bombed Poland Airfields WORLD WAR II • Britain and France honored agreement to protect Poland • September 3, 1939 Britain and France declare war on Germany after Germany refused to answer ultimatum from England WORLD WAR II WORLD WAR II WAR EXPANDS • Hitler’s invasion of Poland introduced new warfare • Blitzkrieg (Lightning war) • Great speed along with Great force WORLD WAR II • Poland surrendered within a month • Elsewhere in Europe there was troop movement • But little else WORLD WAR II • Blockades but not much fighting • On western front • Newspaper dubbed it “Phony War” • There was hope that war could be avoided WORLD WAR II • Soviets then invaded Eastern Poland • Poland again disappeared from map • Soviets then attacked Finland WORLD WAR II • Finland fought hard but fell to the Soviets in 1940 • Next on Germany attack list was Norway and Denmark • They fell to Germany in a single day WORLD WAR II • Germany now had complete access to Atlantic Ocean • U-Boats again put British shipping in danger • France also was in danger of losing merchant ships WORLD WAR II WORLD WAR II • In Britain Winston Churchill replaced Neville Chamberlain as Prime Minister WORLD WAR II • He was outspoken against appeasement • By end of May 1940 Hitler controlled –Netherlands Luxembourg –Belgium WORLD WAR II • Hitler is in position to surround France WORLD WAR II st •1 TURNING POINT OF WORLD WARII •RESCUE AT DUNKIRK WORLD WAR II • British forces were in France • German tanks drove toward the English Channel • British forces retreated from French city Dunkirk WORLD WAR II • Germany made a mistake by not attacking the retreating forces • 330,000 troops retreated back to England • With Germany not attacking the troops it gave England a chance to regroup WORLD WAR II FALL OF FRANCE • France stood alone after British evacuation • France was expecting same type of warfare as World War I • Hitler attack on France was aggressive air and land WORLD WAR II • France had no chance in defeated Germany • Italy now declared war on France and England • June 14, 1940 Germany enters France WORLD WAR II Fall of France • France could not defend their country • France surrendered • France signed a treaty with Germany WORLD WAR II • Germany would occupy France • France paid the cost of occupation • France disarmed • Government of France was moved out of Paris to Vichy WORLD WAR II • The Vichy Government cooperated with the Germans • Résistance –Charles de Gaulle –Led the Free French Government WORLD WAR II • Headquarters were in London • Inside France underground • Groups fought called marquis –They used acts of sabotage –Blowing up bridges –Wrecking trains as they crossed WORLD WAR II • Cutting communication lines –Were they terrorists, patriots or guerilla or freedom fighters? WORLD WAR II • They did not defeat Germans but caused havoc WORLD WAR II ND •2 TURNING POINT OF WORLD WAR II •BATTLE OF BRITAIN BATTLE OF BRITAIN • France has fallen –Hitler began bombing England –Hitler offered Churchill a settlement –He refused –Luftwaffe bombed Britain WORLD WAR II • This was to soften Britain for invasion across the English Channel Luftwaffe stationed airplanes in France and Belgium Closer to England WORLD WAR II • Attacked – Military targets – Railroads – Industry – Civilians Raids became known as “Battle of Britain” WORLD WAR II • Hitler believed the constant bombardment of London and other cities in England would destroy Britain’s will to fight • Britain held on WORLD WAR II • And the RAF began to repel attacks • Radar help give Britain warning that an attack was coming • Britain air defense inflicted damage to the German Luftwaffe WORLD WAR II • The Luftwaffe seemed invincible –The loss of air supremacy and stopped Germany from crossing the English Channel WORLD WAR II • The air war continued and Hitler increased the blockade of England • He thought he could “starve” England into surrendering • Roosevelt and Churchill met in August 1941 WORLD WAR II • They agreed to the Atlantic Charter • The United States involvement was short of a declaration of war on Germany WORLD WAR II • U.S. agreed to send supplies to England • U.S. supported England short of going to war • Hitler had suffered a setback with the inability to defeat Britain quickly as he had defeated all of Western Europe WORLD WAR II • Hitler still had his master plan and needed the Soviet Union for there abundance of natural resources and million of acres of land for his expansion plans Rescue at Dunkirk Battle of Atlantic WORLD WAR II RD •3 TURNINGPOINT OF WORLD WARII •ATTACK ON PEARL HARBOR Pearl Harbor • Japan –Aggressive in China and Southeast Asia –America –Isolationist Pearl Harbor • Tension building in 1930’s between United States and Japan Pearl Harbor • Economic Unbalance in China • Open Door Policy threaten with Japan invasion of China Pearl Harbor • Japan and Nanking • Reign of terror on China Pearl Harbor • 1940 Japan signed Tri-Partite Treaty Germany, Italy and Japan were now allied Pearl Harbor • Apparent that this policy must be changed • Granted diplomatic recognition to Russia • Initally America wanted to be neutral Pearl Harbor • Japan and United States negotiations failed during summer of 1941 Pearl Harbor • December 7, 1941 • Japan attacked United States • Pearl Harbor Pearl Harbor • Surprise attack on Pacific Fleet • Planned on delivering a fatal blow to United States ability to fight Pearl Harbor • Attack was devastating • However it failed two major objectives • United States aircraft carriers were not at Pearl Harbor • Japanese planes failed to destroy fuel depots behind airport Pearl Harbor Pearl Harbor Franklin D. Roosevelt Franklin D. Roosevelt Franklin D. Roosevelt Pearl Harbor Pearl Harbor Pearl Harbor Pearl Harbor Pearl Harbor Pearl Harbor Pearl Harbor • Next day Roosevelt declared war on Japan • Germany then declared war on United States Pearl Harbor • United States was now involved in the conflict World War II • United States fighting a three front war • European theater • Pacific theater Home front HOME FRONT WORLD WAR II HOME FRONT WORLD WAR II • December 8, 1941 • United States entered World War II • Roosevelt Speech • “Day that will in infamy” HOME FRONT WORLD WAR II HOME FRONT WORLD WAR II • War Powers Act • December 18,1941 • Gave Roosevelt overall • authority of everything in WWII HOME FRONT WORLD WAR II • 1941 –War Production Board –Awarded Defense contracts –Managed scarce resources HOME FRONT WORLD WAR II • Ended the Great Depression • Economy doubled HOME FRONT WORLD WAR II • Office of Price Administration –Froze prices and rents –Charge of overall economy HOME FRONT WORLD WAR II • Preparing for all out industrial war production • All factories converted to military equipment • Automobile factories to tanks and planes HOME FRONT WORLD WAR II • Soft drink company converted from filling soda bottles to shells with explosives • Pencil factory to bomb parts HOME FRONT WORLD WAR II • Ship yards expanded • Labor • Women to the rescue • 6 million • 60% of what men earned HOME FRONT WORLD WAR II •Worked in factories •Took the place of men fighting HOME FRONT WORLD WAR II • Rosie the Riveter • http://www.darksideoflight.com/totebagpics/totes/rosieriveter.JPG HOME FRONT WORLD WAR II • War was popular • Common enemies –Japan and Germany HOME FRONT WORLD WAR II • Mobilization of armed forces –1935 –1945 200,000 8,000,000 HOME FRONT WORLD WAR II • Home Front • Selective Service • Recruiting offices jammed • 5 million who volunteered were not enough HOME FRONT WORLD WAR II • Two front war needed another 10 million soldiers • Japanese Americans joined • African Americans joined –Limited at first to non combat roles HOME FRONT WORLD WAR II • 1943 finally saw action • Segregated from white troops HOME FRONT WORLD WAR II Tuskegee Airmen HOME FRONT WORLD WAR II • Scientific community • OSRD Office of Scientific Research and Development –radar –Sonar HOME FRONT WORLD WAR II • Penicillin • Wonder drug • 1942 also started Manhattan project HOME FRONT WORLD WAR II • Economic Conditions –Price controls –Wage controls –Rationing –Fuel –Metals rubber goods Plastics HOME FRONT WORLD WAR II • War bonds to raise money HOME FRONT WORLD WAR II • WPD –Organized paper drives nationwide –Scrap iron Total effort for war HOME FRONT WORLD WAR II • Culture • Propaganda movies –Evils of Fascism –Heroic War Movies HOME FRONT WORLD WAR II • War Cartoons • Bugs Bunny HOME FRONT WORLD WAR II • Japanese Internment • All Japanese were bad • Some Germans were good • Italians same HOME FRONT WORLD WAR II • Americans saw the Japanese as a threat • Hearst Newspapers demanded protection for spies HOME FRONT WORLD WAR II • Executive order 9066 • was the instrument that allowed military commanders to designate areas "from which any or all persons may be excluded." Under this order all Japanese and Americans of Japanese ancestry were removed from Western coastal regions to guarded camps in the interior. : HOME FRONT WORLD WAR II • West Coast was vulnerable • War Department Plan –Internment camps set up away from west coast HOME FRONT WORLD WAR II • Supreme Court • Upheld • Hirabayshi v United States • Korematsu v United States HOME FRONT WORLD WAR II HOME FRONT WORLD WAR II HOME FRONT WORLD WAR II HOME FRONT WORLD WAR II HOME FRONT WORLD WAR II HOME FRONT WORLD WAR II Japanese Internment Camps Tule Lake, CA World War II European Front WORLD WAR II EUROPEAN FRONT • Churchill and Roosevelt met to discuss war plans • Europe and Hitler were more of threat than Japanese WORLD WAR II EUROPEAN FRONT • Plan was to defeat Hitler first and fight a defensive war in Pacific • Europe first WORLD WAR II TH •4 TURNINGPOINT OF WORLD WARII •BATTLE OF THE ATLANTIC World War II European Front • BATTLE OF ATLANTIC World War II European Front • Allies: • War not going well • Atlantic Ocean • Industry could not replace ships fast enough World War II European Front Germany produced 6 times as many U-Boats as were sunk Many United States ships were lost off coast of United States World War II European Front • Germany was victorious in the early years of the war • Tide turns World War II European Front • Technical advancements • Sonar • http://www.liverpoolmuseums.org.uk/maritime/exhibitions/boa/defendingthelifeline.asp World War II European Front • Advancements in depth charges World War II European Front • ENIGMA • German coding machine and code book was captured World War II European Front • Now allies knew where UBoats were and could steer away or escort ships could be increased World War II European Front • Atlantic was now more secured supplies could be delivered WORLD WAR II • Also US was building ships at a fast pace Tide turned in the Atlantic in 1943 keeping supply lines opened to Europe WORLD WAR II TH •5 TURNINGPOINT OF WORLD WAR II •Battle of Stalingrad WORLD WAR II • EASTERN FRONT • OPERATION BARBAROSSA – Hitler ordered military plan for invading USSR – Included not only military conquest but “ethnic cleansing” – He was going to rid USSR of their Jews and intellectuals World War II • Hitler postponed attack on Russia because of an uprising in Yugoslavia WORLD WAR II • Hitler planned on a quick strike and conquest • Hitler needed land and resources for his Master Race • June 22,1941 Germany invaded USSR WORLD WAR II • His Blitzkrieg was slowed after initial success • USSR did not have good roads and the mechanized divisions were slowed WORLD WAR II • Soviets were routed early and used scorched earth policy in their retreat • Moscow and Leningrad (formerly St. Petersburg) WORLD WAR II • Hitler expected quick surrender but Soviets fought to last man • Hitler plan for early surrender Were dashed by what? WORLD WAR II • Soviet winter • German army was within miles of Moscow • Never was able to take over city WORLD WAR II • Stalingrad –Needed to be taken by Germany •At all costs •Oil reserves for army and Third Reich WORLD WAR II • Soviets were to defend Stalingrad at all costs • Another turning point of the war • Symbol of the war for Soviets WORLD WAR II • Germany fought and Soviets defended for six months • Street fighting house to house fighting in Stalingrad • Germany tried to starve Stalingrad WORLD WAR II • Eventually Soviets launched counter attack and surrounded German army • The German army surrendered to the Soviets World War II • First land defeat of the German Army World War II TH •6 TURNING POINT OF WORLD WARII •North African Campaign World War II • North Africa • Allied Supreme commander • Dwight D. Eisenhower • Great administrator and Battle planner little command experience World War II • Operation Torch WORLD WAR II • Campaign in North Africa –Italy first attempted to control North Africa –Were not successful –Hitler sent Rommel “Desert Fox” World War II European Front • War in North Africa • Important to Allies • Needed to reclaim Europe • Attack “soft underbelly” of German control World War II European Front • Suez Canal was critical to both Axis and Allies Held by Axis • Egypt and Malta were held by Allies World War II European Front German commander Erwin Rommel Desert Fox World War II European Front World War II European Front • Allied Commanders • Montgomery = Britain World War II European Front • Became a war of armor • General Montgomery Britain • General George S Patton World War II • Rommel Afrikakorps • Rommel drove to • El Alamein and were defeated by Allies • Rommel retreated and ambushed Allied troops at Kasserine Pass World War II • Kasserine Pass • Rommel was able to break through weak allied defenses World War II • Air Power 3 to 1 superiority by Allies • Allies outnumbered Axis tanks • Rommel countered inflicted heavy losses on Allies World War II • Kasserine Pass • Caused Allies to rethink Allied command • Appointed George Patton World War II European Front World War II • Rommel was short on supplies but continued to fight • Allies broke Germans defense World War II • Rommel wanted to withdraw and regroup • Hitler ordered him to continue • Rommel withdrew unable to hold on World War II • Morocco –Allies needed to control Mediterranean Sea –Could attack Hitler from soft underbelly World War II • Invasion of Morocco • Naval concentration • Intense fighting Allies were able to drive off Germans WORLD WAR II • Patton from the east • Montgomery from the west • pushed Rommel and Germans out of North Africa WORLD WAR II • Allies then concentrated on Italy in 1943 • Sicily was first World War II • Sicily was stepping stone for allied attacks in Europe • Operation Husky amphibious attack on Sicily • July 1943 World War II • Surprised Italians • A storm blew many of first invaders off course • Allied planes were mistaken for German planes and shot down World War II • Despite setbacks German response was quick and punishing • Almost drove allies out of Sicily World War II • Allies were able to defeat Germans gained control of Sicily World War II • Russia then would deploy troops to attack Germany • Weakening the German army in the east World War II Battle of Salerno Germany defended Salerno Battle was going in Germany Favor Reinforced allied troops World War II • Plus Germany too thin and stretched unable to add reinforcements • After severe fighting Salerno was secured • Next Naples World War II • Winter Line Campaign • Naples was captured after defeating German resistance World War II • Allies did not enough troops to defeat Germans • Experienced troops were sent to England to prepare for invasion of France • Battle continued with no end until 1945 World War II • Battle of Anzio • Allies invaded and Germany reinforced troops • Anzio was a stalemate until late 1944 World War II • At a cost tens of thousands of lives Anzio was finally in Allied hands • Cassino next • Allies under extreme German defense took control World War II • Rome was taken and became the first major city liberated from Germany World War II • All the time Battles for Italy • bombing of Germany was underway • Carpet bombing of German cities depleted Germany ability World War II • To wage war because of heavy damage to industrial cities • Unsung heroes of WWII • Tuskegee Airman World War II • African American pilots pursuit squadron • Highly successful protecting U.S. bombers th 99 th •7 turning point of World War II •D-Day WORLD WAR II • Invasion of Europe and Liberation of France Operation Overlord • Invasion of Northern France • June 6, 1944 D-Day • Patton used as deception at Calais • Germany believed that Calais was where the Allies would attack • Allies attacked on June 6 1944 • Utah, Omaha, Gold, Juno, Sword all beachheads attacked • http://www.britannica.com/dday/art-40543 WORLD WAR II • Omaha Beach • Invasion of Beach head caused many casualties • Omaha was the largest assault • It covered a stretch of over 6 miles • A third of the beach was defended by a 10 foot high seawall and was over-looked by cliffs that were 170 foot high in places. • Meet tremendous resistance • Finally allied troops broke through and secured beaches • American casualties 2,400 • Allies continued assault finally on August 25, 1944 entered Paris WORLD WAR II • Battle of the Bulge • Or the ARDENNES OFFENSIVE • December 16, 1944 • 1.5 million troops fought • German and Allied Forces • Winter Battle WORLD WAR II WORLD WAR II WORLD WAR II • Germans wanted to surround Allies and force a settlement • Largest land battle of World War II • The battle lasted until January 1945 WORLD WAR II Allies rallied to defeat the Germans Germany had expended air power trying to eliminate air power of Allies They failed and the Battle of the Bulge was a victory for Allies WORLD WAR II WORLD WAR II WORLD WAR II • Yalta Conference –Roosevelt –Churchill –Stalin • Big 3 Meet in Yalta WORLD WAR II WORLD WAR II • Met to discuss post war Europe • Reestablished Poland borders • Some thought Roosevelt appeased Stalin • Roosevelt was extremely ill World War II • Poland • United States and England wanted a free Poland • Stalin insisted on a Communist Government WORLD WAR II • Poland had either invaded Russia or Poland was used to invade Russia • Stalin did not want that to happen again WORLD WAR II • Roosevelt and Churchill agreed reluctantly • Also Russia would control for a short period of time Hungary • Czechoslovakia Albania • WORLD WAR II • Stalin promised free elections in these countries if he had temporary control of these countries WORLD WAR II • Soviets agreed to enter war within 3 months of end of war in Europe • IMPORTANT to the invasion of Japan • more on that later World War II • Germany would be divided into 4 parts with each of the allies and France getting a portion • United States, Great Britain, France, and the Soviet Union World War II • Stalin wanted German reparations • Churchill and Roosevelt refused to agree and tabled issue for later discussion WORLD WAR II • The three also agreed to try Germany of War Crimes • Nuremburg Trials accomplished this • Yalta last agreement • Russia due to the heavy causalities in the war was allowed to take Berlin over Patton objections • U. S. forces went south as Russia took Berlin • Hitler believed he would be treated better if U.S. forces were allowed to take Berlin WORLD WAR II • April 12, 1945 • Warm Springs Georgia after Yalta • Death of President Roosevelt WORLD War II Harry S Truman is President WORLD WAR II • By end of April Germany surrendered to Allies in Italy • Army was weakened and could not defend Berlin • Stalin was allowed to take Berlin WORLD WAR II • As Russian troops advancing to Berlin • Hitler, Eva Braun and close associates committed suicide in his bunker WORLD WAR II • May 8, 1945 Germany surrenders WORLD WAR II • Victory in Europe • War was over in Europe but not in Pacific Holocaust Holocaust • Hitler invasion of Europe and Soviet Union was part of Master Plan • “New World Order” • Europe would be under Hitler’s Holocaust • Needed living space for Master Race • To have master race ethnic and religious cleansing was necessary Holocaust • Ayrian race was superior • Russia would supply Third Reich with food and natural resources including oil • Russians were inferior Holocaust • Hitler scapegoat was the Jewish population • He first tried to deport Jews out Germany • Not many countries accepted the large number of immigrants • Passed Nuremberg Laws Holocaust • (a) to clarify the requirements of citizenship in the Third Reich, • (b) to assure the purity of German blood and German honor and • (c) to clarify the position of Jews in the Reich. These three laws, passed on September 15, 1935, and the numerous auxiliary laws which followed them are called the Nuremberg Laws. Holocaust • Second isolation of Jews in Ghettos • Finally the Jewish problem was to be eliminated • Final Solution Holocaust • First they shot the Jews • Not efficient • Messy and too public Holocaust • 1942 Wannese Conference –Set up concentration camps –Germany • Dachau • Buchenwald Holocaust • Dachau Holocaust Holocaust • BUCHENWALD Holocaust • Poland • Auschwitz • Treblinka Holocaust • As they were led into camps • Sorted into groups • Old, infirmed, or unable to work were sent to “showers” • In reality they were Gas chambers Holocaust • Those not killed –Worked forced labor –Starved –Lived under brutal conditions –Disease Holocaust • Killed millions • Deposed of bodies in crematory after mass graves proved ineffective • Some people in Germany and other countries tried to help Holocaust • There was not enough uprisings to stop killing • Denmark did help • Raoul Wallenberg saved thousands Holocaust Holocaust • WHITE ROSE • Anti Nazi group of students and was secret Holocaust • Ultimately 6 million people Jews, Gypsy Slavs • And those who did not confirm to Nazism Auschwitz Belzec Bergen-Belsen Buchenwald Chelmno Dachau Ebensee Flossenbürg Gurs Gusen Majdanek Mauthausen Neuengamme Plaszow Ravensbrück Rivesaltes Sachsenhausen Stutthof Theresienstadt Treblinka Trzebnia (sub-camp of Auschwitz) Vught Westerbork Holocaust • Henrich Himmler Holocaust • Adolph Eichman Holocaust • Jewish specialist • Assigned to eliminate Jews • Following orders • After no gassing order he continued to eliminate Jews Holocaust • Convicted and executed in 1962 • In Israel Holocaust Holocaust Holocaust Holocaust • Warsaw Ghetto Uprising • Holocaust Holocaust Holocaust WORLD WAR II PACIFIC FRONT • Early victories for Japan • Singapore • Philippines • Guam • Midway WORLD WAR II PACIFIC FRONT • Wake Island • Hong Kong • Malaya • Bataan WORLD WAR II PACIFIC FRONT • Bataan Death March • 65 mile march • prisoners were denied food water • Thousands died on march WORLD WAR II PACIFIC FRONT • Thousands more died in the camp • One of the most brutal and devastating events in war WORLD WAR II PACIFIC FRONT st •1 Turning point of World War II Pacific Front •Doolittle Raids WORLD WAR II PACIFIC FRONT • Doolittle Raids • 16 B-25 • http://www.digitalcurriculum.com/ WORLD WAR II PACIFIC FRONT WORLD WAR II PACIFIC FRONT • Col Jimmy Doolittle • Doolittle Raids April 18th WORLD WAR II PACIFIC FRONT • Bombed three Japanese cities • Tokyo • Yokohamma • Kobe WORLD WAR II PACIFIC FRONT WORLD WAR II PACIFIC FRONT • More of a psychological victory • Japan seemed invincible with early victories • Put some doubt in Japanese defense WORLD WAR II PACIFIC FRONT • Japan feeling that they divinely protected • That was shattered WORLD WAR II PACIFIC FRONT • Did not know where the planes came from • Damage was not great but caused Japan to strengthen to defend island WORLD WAR II PACIFIC FRONT • AXIS or Japanese Plan • 3 step attack of Japan • Air control of Coral Sea • Then to occupy Midway • Then Aleutian islands WORLD WAR II PACIFIC FRONT • Wanted to lure United States Navy into a sea battle • Intent to destroy the entire Pacific fleet WORLD WAR II PACIFIC FRONT • Third Step • New Caledonia • Fiji • And Samoa WORLD WAR II PACIFIC FRONT • Isolating Australia • 1st step Battle of Coral Sea • 2nd step Battle of Midway • 3rd Step never happened WORLD WAR II PACIFIC FRONT nd •2 Turning point of World War II Pacific Front •Battle of Coral Sea WORLD WAR II PACIFIC FRONT BATTLE OF CORAL SEA WORLD WAR II PACIFIC FRONT • May 3 and May 8 • 1st Battle in history that a naval battle where ships did not fire on each other • Commandeer WORLD WAR II PACIFIC FRONT • Japanese Force • 7 transports, • 5 five destroyers, • 1 light aircraft carrier, Shoho, • 2 fleet carriers Shokaku and Zuikaku • • • • • • WORLD WAR II PACIFIC FRONT United States Ships 13 destroyers, 8 cruisers, 4 light cruisers and 2 aircraft carriers, USS Lexington and USS Yorktown WORLD WAR II PACIFIC FRONT • Air battle • Both sides had trouble locating ships • United States had radar • Unknown to Japanese WORLD WAR II PACIFIC FRONT • Carrier Yorktown damaged • Lexington damage and sunk • Japan lost 43 aircraft and aircraft carrier Shoho Lexington • Shokaku_Bombed WORLD WAR II PACIFIC FRONT • Japanese losses were less • But were not able to advance in the Pacific • Australia was safe • Plan to invade Port Moresby were dashed by Coral Sea victory • Turning point of World War II Pacific Front • Battle of Midway rd 3 WORLD WAR II PACIFIC FRONT • Strategic victory for United States • Aircraft carrier had now replaced battleship as the backbone of Navy WORLD WAR II PACIFIC FRONT • BATTLE OF MIDWAY • June 4-7 1942 • Japan planned to invade Midway Island WORLD WAR II PACIFIC FRONT • United States had the Japanese codes and knew of the attack • Carrier battle and air battle WORLD WAR II PACIFIC FRONT • Effective dive bombers of United States WORLD WAR II PACIFIC FRONT • Three Japanese carriers were sunk • Akagi, Kaga, and Soryu WORLD WAR II PACIFIC FRONT • Japanese submarines sunk the Yorktown WORLD WAR II PACIFIC FRONT • United States losses • Yorktown and Hammann sunk • Planes: About 150 lost in action or damaged beyond repair. 92 officers and 215 men. WORLD WAR II PACIFIC FRONT • Four carriers sunk: Akagi, Kaga, Soryu, Hiryu, with the loss of all their planes and many of their personnel. Estimated 275 planes, 2400 men. WORLD WAR II PACIFIC FRONT • Results of Battle of Midway • End of the Japan’s offensive movement by their Navy • United States was able to built up their Navy while Japan could not WORLD WAR II PACIFIC FRONT • Japan and her Naval advantage was now gone WORLD WAR II PACIFIC FRONT th •4 Turning Point of World War II Pacific Front •Battle of Gudalcanal WORLD WAR II PACIFIC FRONT • Battle of Guadalcanal • First offensive land attack of Pacific campaign • Began the reclamation of captured Japanese Territories WORLD WAR II PACIFIC FRONT • August 7 1942 to February 9, 1943 WORLD WAR II PACIFIC FRONT • Important for shipping of supplies • Vicious fighting for months • Japanese supplies were cut by Allied bombings WORLD WAR II PACIFIC FRONT • Battle was the first United States and Allied victory on land and was a critical victory for planned Island Hopping Campaign WORLD WAR II PACIFIC FRONT • Island Hopping continued • Solomon Islands, Gilbert Islands, Marshall Islands WORLD WAR II PACIFIC FRONT • Battle of Philippine Sea • Needed to recapture Philippine Islands • United States devastated Japan airfields thus limiting the effect of air attacks WORLD WAR II PACIFIC FRONT • Japan also lost a majority of their aircraft Another devastating defeat for Japan and her Navy WORLD WAR II PACIFIC FRONT • Led to the recapture of Philippines and airfields to • Launch air bombings of Japanese mainland WORLD WAR II PACIFIC FRONT • Cities in Japan were firebombed Tokyo, Kawasaki, • Yokohama WORLD WAR II PACIFIC FRONT th •5 Turning point of World War II Pacific Front •Battle of Leyte Gulf WORLD WAR II PACIFIC FRONT Battle of Leyte Gulf October to November 1944 Considered the largest naval battle in history First use of Kamikaze planes by Japanese WORLD WAR II PACIFIC FRONT • Series of Naval Battles • • • • • • Palawan Passage Surigao Strait Battle of Sibuvan Sea Battle of Sumar Battle of Cape Engano Battle of Ormac Bay WORLD WAR II PACIFIC FRONT • The United States inflicted heavy losses again on the Imperial navy of Japan th •6 Turning Point of World War II •Battles of Iwo Jima and Okinawa WORLD WAR II PACIFIC FRONT • Okinawa and Iwo Jima • Battle of Iwo Jima • February 16, March 16, 1945 WORLD WAR II PACIFIC FRONT • Vicious fighting • Japanese held out to last man • Needed for its location for bombing of Japan mainland • Emergency landing strip for US aircraft WORLD WAR II PACIFIC FRONT WORLD WAR II PACIFIC FRONT • Taken by Joe Rosenthal WORLD WAR II PACIFIC FRONT • Okinawa • Last major land battle of the war • Needed to launch invasion of Japan WORLD WAR II PACIFIC FRONT • Operation Downfall • Journalist and war reporter Ernie Pyle was killed on island WORLD WAR II PACIFIC FRONT • Tremendous loss of life WORLD WAR II PACIFIC FRONT –JAPANESE • 76,000+ soldiers killed and 27,000 civilians killed, 7,455 surrendered/captured WORLD WAR II PACIFIC FRONT • United States causalities • 18,900+ killed, • 38,000 wounded + • 33,096 non combat wounded, • 763 planes shot down WORLD WAR II PACIFIC FRONT • Last major step before invasion of Japan WORLD WAR II PACIFIC FRONT • June 20, 1945 Japanese surrendered • Potsdam Conference • Finalized plan to Divide Germany End of WORLD WAR II World War II Pacific Front th •7 Turning Point of World War II •Decision to drop Atomic Bomb End of WORLD WAR II • Manhattan Project • Building and testing of Atomic Bomb End of WORLD WAR II • Robert Oppenheimer • Developed project in complete secrecy • Vice-President Truman did not know of project End of WORLD WAR II • Bomb was tested July 16, 1945 in New Mexico • Test was successful End of WORLD WAR II • Decision to drop bomb: • Next step in Pacific was invasion of Japan • Truman and military leaders feared Japan would fight to last man, woman and child End of WORLD WAR II • Soviets were to enter into war in Pacific 3 months after surrender of Germany • Stalin stalled on entering war End of WORLD WAR II • 3 paths Truman considered –drop the bomb over Pacific to Japanese what they could expect –Invade Japan –Drop bomb on Japan End of WORLD WAR II • Decided to drop Atomic bomb on Japan • August 6, 1945 • Fat Man and Little Boy End of WORLD WAR II • Enola Gay End of WORLD WAR II • August 6, 1945 • Hiroshima End of WORLD WAR II • Hiroshima 100,000 deaths from initial explosion • Many more died from radiation poisoning • 60,000 died at Nagasaki End of WORLD WAR II End of WORLD WAR II End of WORLD WAR II End of WORLD WAR II • August 9, 1945 • Nagasaki bombed End of WORLD WAR II • Japan offered to surrender August 10, 1945 • The Emperor in the first radio broadcast told Japanese people that Japan was surrendering End of WORLD WAR II • First time ever Japanese people actually heard their Emperor speak End of WORLD WAR II • Japan surrendered on • September 2, 1945 • Unconditional except Emperor was allowed to stay End of WORLD WAR II • World War II was over