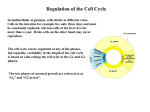
* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Evolution by natural selection - BioGeoWiki-4ESO
Polymorphism (biology) wikipedia , lookup
Deoxyribozyme wikipedia , lookup
Genomic imprinting wikipedia , lookup
Genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
Ridge (biology) wikipedia , lookup
Group selection wikipedia , lookup
Site-specific recombinase technology wikipedia , lookup
Quantitative trait locus wikipedia , lookup
Oncogenomics wikipedia , lookup
Adaptive evolution in the human genome wikipedia , lookup
Artificial gene synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Epigenetics of human development wikipedia , lookup
Gene expression profiling wikipedia , lookup
Genome (book) wikipedia , lookup
Designer baby wikipedia , lookup
Population genetics wikipedia , lookup
Genome evolution wikipedia , lookup
Point mutation wikipedia , lookup
Minimal genome wikipedia , lookup
History of genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
Biology and consumer behaviour wikipedia , lookup
Evolution by natural selection Introduction • Natural selection happens when individuals of a population have differing characteristics caused by their genes (heritable) • Differences between individuals mean that some individuals are better adapted to their environment than others Why do individuals of the same species have variations in their characteristics? •Because of differences in their genes. •Genes are made up of DNA and are found in every cell of your body •The genetic code is a set of instructions for making an entire organism with each gene coding for a specific protein. Where does variation in the genes come from? • When cells divide or gametes are formed the DNA is replicated (copied) • Sometimes errors occur in the copying called mutations. Mutations are random • These mutations change the code for making an organism. • Most of the time this has no effect or a negative effect on the organisms survival chances • But sometimes these mutations can be beneficial What will happen to the survival chances of better adapted individuals? More likely to survive and have more offspring than less well adapted individuals. What effect does this have on the gene pool? •When organisms reproduce they pass on their genes •Organisms with beneficial characteristics are more likely to pass on their genes •The frequency of the genes that cause these beneficial characteristics will increase from generation to generation Darwin’s finches These finches are found on different islands of the Galapagos How are they similar? How are they different? Why? Darwin’s finches There are at least 13 different species of finch found in the Galapagos Similar because they share a common ancestor Different because of differing selection pressures on different islands Example of natural selection leading to speciation. Can no longer interbreed Is evolution just a theory? What evidence is there to support it? •Fossil record provides evidence for evolution •Incomplete needs certain conditions to delay decay e.g. low temperature, low oxygen, highly acidic soil •Often only hard parts e.g. skeleton are well preserved Artificial selection Is evolution still happening? Can you think of any examples? •Antibiotic resistant bacteria •Insecticide resistance Are acquired characteristics heritable? How do we know? Why is evolution such a controversial topic?