* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download evolution ppt
Unilineal evolution wikipedia , lookup
Catholic Church and evolution wikipedia , lookup
Sociobiology wikipedia , lookup
The Descent of Man, and Selection in Relation to Sex wikipedia , lookup
Sexual selection wikipedia , lookup
Population genetics wikipedia , lookup
Evidence of common descent wikipedia , lookup
Paleontology wikipedia , lookup
Evolving digital ecological networks wikipedia , lookup
Natural selection wikipedia , lookup
Evolutionary history of life wikipedia , lookup
Evolutionary mismatch wikipedia , lookup
Inclusive fitness wikipedia , lookup
Theistic evolution wikipedia , lookup
Saltation (biology) wikipedia , lookup
Hologenome theory of evolution wikipedia , lookup
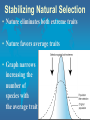
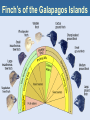
Evolution Essential ?s • How & why have species changed with time? • What is the benefit & value of evolution? • How can the theory of evolution be applied to today? • What evidence & thought have contributed to the theory of evolution? Evolution Change in genetic make-up over time Process by which modern organisms have descended from ancient organisms The History of the Development of Evolutionary Thought st 1 Hypothesis Use & Disuse Jean – Baptiste Lamark 1809 French naturalist • Tendency Towards Perfection & Complexity • organisms continually change to become better adapted to their environment & improve survival • Use & Disuse of Organs • structure that are used frequently will become larger and be more developed during a lifetime • structures not used will become weaker or disappear (vestigial organs) during a lifetime • Inheritance of Acquired Traits • newly acquired traits can be passed on to offspring Evaluation of Lamark’s Theory • Incorrect because….. • acquired traits (those gained during an organisms lifetime) are NOT inherited • acquired behaviors CANNOT develop heritable characteristics • Correct because…. • organisms adapt to their environment overtime to increase survival nd 2 Hypothesis Natural Selection Charles Darwin 1831 Voyage on the H.M.S. Beagle The Trip around the World • Observed many various organisms • Researched their patterns of diversity • Studied living organisms & fossils • Concluded that the earth is constantly changing The Galapagos Islands • Most influential location to Darwin’s development of the theory of evolution • 13 small islands off the West coast of South America by Ecuador • Close proximity • Extremely diverse climates & environments • Isolated from each other • Organisms on each island vary greatly in characteristics to be specialized & better adapted to their diverse environments Darwin’s Theory of Evolution Published in 1931 “The Origin of Species” Natural Selection • Organisms varying in inheritable characteristics (mechanics of genetics was unknown at this time!) • Large population size causes competition for resources & restricts survival rate Natural Selection • Organisms with traits that are better “fitted” or adapted to their environment survive and reproduce more successfully passing on their superior genes to the next generation • Fitness • resulting adaptations that increase the survival of an organism • Adaptations • any inherited characteristic that increases an organism’s survival “Survival of the Fittest” Descents with Modification • Over many successive generations: • pressures of natural selection • change traits of a population • increase overall fitness of the population • Species evolve: • differences in structures & niches • resulting in the formation of a new species • remaining related to each other by a common ancestor 3 Types of Natural Selection Stabilizing Natural Selection • Nature eliminates both extreme traits • Nature favors average traits • Graph narrows increasing the number of species with the average trait Directional Natural Selection • Nature eliminates only 1 extreme trait • The other extreme trait is favored • Graph & population diversity shifts toward favored trait Distributive Natural Selection • Nature eliminates the average trait & favors the extreme traits • Graph & population diversity shifts towards the 2 extreme traits • Possibly leading to creating 2 new species Finches of the Galapagos Islands Darwin’s most famous discoveries came from his observations on the variations of finch species on the Galapagos Islands which had extremely diverse and extensive gene pools, supporting his theory of evolution • All of the Finches from the Galapagos Island evolved from the same founder species • The Finches were separated to different islands over several years • On each island they experience different natural pressures • Finches on each island developed variations to make them better adapted to their different environments of each island • Eventually the Finches became specialized and different from each other becoming separate & new species on each island Finch’s of the Galapagos Islands