* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Environmental Problems
Survey
Document related concepts
Hotspot Ecosystem Research and Man's Impact On European Seas wikipedia , lookup
Arctic ecology wikipedia , lookup
Polar ecology wikipedia , lookup
Physical oceanography wikipedia , lookup
Sea level rise wikipedia , lookup
Ocean acidification wikipedia , lookup
Marine biology wikipedia , lookup
Overdeepening wikipedia , lookup
Ice-sheet dynamics wikipedia , lookup
Arctic Ocean wikipedia , lookup
History of climate change science wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
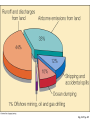
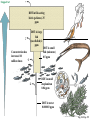
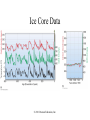
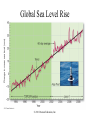
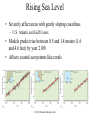
Environmental Problems • Pollution • Climate Change Marine Pollution • The introduction into the ocean by humans, substances that changes the physical, chemical or biological environment Plastic Pollution Video on the Problem: http://vimeo.com/21786927 One solution:: http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=cxVNhiBqGU&feature=related Fig. 15-27, p. 367 Each year 240 million gallons of used motor oil are dumped in storm drains…22x the amount spilled by Exxon Valdez Fig. 15-28, p. 368 Marine Pollution • Bioamplification – even small amounts of pollutants can have large effects • DDT example Stepped Art DDT in fish-eating birds (pelicans) 25 ppm DDT in large fish (needlefish) 2 ppm Concentration has increased 10 million times DDT in small fish (minnows) 0.5 ppm DDT in small zooplankton 0.04 ppm DDT in water 0.000003 ppm Fig. 15-32, p. 371 Marine Pollution • Eutrophication – Excess nutrients in water also lead to problems • HABs • Oxygen depletion Determining Causes of Earth’s Climate Change • Paleoclimatology • Proxy data – indirect evidence using natural recorders of climate variability – – – – – – Sea floor sediments Coral deposits Glacial ice rings Tree rings Pollen Historical documents © 2011 Pearson Education, Inc. Natural Causes of Climate Change • Solar energy changes, Variations in Earth’s Orbit, Volcanic eruptions, Movement of Earth’s Plates • Linked to Pleistocene Ice Age, Little Ice Age, Medieval Warm Period • Recent change unprecedented – More likely result of human activity than natural causes © 2011 Pearson Education, Inc. Global Warming: Causes • “Green house effect” Fig. 15-40, p. 378 Global Warming: Causes • Green house gases (chloroflourocarbons =CFCs, methane, CO2, water vapor) • Increasing CO2 – Deforestation & burning fossil fuels Table 16.01 Today – CO2 highest it has been in 10 million years Fig. 15-31, p. 326 Ice Core Data © 2011 Pearson Education, Inc. Global Warming • The 8 warmest years have occurred since 1998 • Earth’s surface temperature has risen 0.8°C (1.4°F) in last 140 years. © 2011 Pearson Education, Inc. Fig. 15-43, p. 380 Series of videos from National Science Foundation http://www.nsf.gov/news/special_re ports/degree/how_do_we_know.jsp Changes in the Oceans Changes in deep-water circulation • North Atlantic especially sensitive • Melting glaciers • Warmer surface waters © 2011 Pearson Education, Inc. Changes in the Oceans Polar Ice Melting • Arctic amplification • Loss of more than 2 million square kilometers (800,000 square miles) of Arctic sea ice in last decade • Loss of ice = enhanced warming due to lower albedo © 2011 Pearson Education, Inc. The North Pole 1996 Fig. 15-33, p. 327 Changes in the Oceans Polar Ice Melting • Arctic ice melting affects polar bear survival. • Food sources are dwindling for human Arctic dwellers. – Marine species migration © 2011 Pearson Education, Inc. Changes in the Oceans • Rising Sea Level – already occurring • Main contributors: – Melting of Antarctic and Greenland ice sheets – Thermal expansion of ocean surface waters – Melting of land glaciers and ice caps – Thermal expansion of deep-ocean waters © 2011 Pearson Education, Inc. Global Sea Level Rise © 2011 Pearson Education, Inc. The Maldives in the Indian Ocean – 80% pop. live only 1m above sea level Rising Sea Level • Severely affect areas with gently sloping coastlines – U.S. Atlantic and Gulf Coasts • Models predict rise between 0.5 and 1.4 meters (1.6 and 4.6 feet) by year 2100 • Affects coastal ecosystems like corals © 2011 Pearson Education, Inc. Coral Bleaching Linked to Increased Temperatures Fig. 14-15, p. 340 Changes in the Oceans Ocean acidity increase • Some atmospheric carbon dioxide dissolves in ocean water. – Acidifies ocean • Threatens calcifying organisms – – – – Coccolithophores Foraminifers Sea urchins Corals © 2011 Pearson Education, Inc. Organisms Threatened by Increased Marine Acidity © 2011 Pearson Education, Inc. Global Climate Change: Solutions? • Alternative energy Fig. 15-9, p. 355 Fig. 15-10a, p. 355 Fig. 15-10b, p. 355