* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Slide 1
ExxonMobil climate change controversy wikipedia , lookup
Climatic Research Unit documents wikipedia , lookup
Climate change adaptation wikipedia , lookup
German Climate Action Plan 2050 wikipedia , lookup
Climate change denial wikipedia , lookup
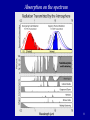
Climate change in Tuvalu wikipedia , lookup
Effects of global warming on human health wikipedia , lookup
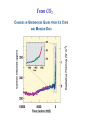
Climate governance wikipedia , lookup
Climate engineering wikipedia , lookup
Citizens' Climate Lobby wikipedia , lookup
2009 United Nations Climate Change Conference wikipedia , lookup
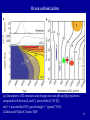
Economics of climate change mitigation wikipedia , lookup
Climate change and agriculture wikipedia , lookup
Media coverage of global warming wikipedia , lookup
Global warming controversy wikipedia , lookup
Climate change mitigation wikipedia , lookup
Climate sensitivity wikipedia , lookup
Economics of global warming wikipedia , lookup
Effects of global warming on humans wikipedia , lookup
Low-carbon economy wikipedia , lookup
Fred Singer wikipedia , lookup
Effects of global warming wikipedia , lookup
Instrumental temperature record wikipedia , lookup
United Nations Climate Change conference wikipedia , lookup
Climate change and poverty wikipedia , lookup
Effects of global warming on Australia wikipedia , lookup
Global warming hiatus wikipedia , lookup
Physical impacts of climate change wikipedia , lookup
Scientific opinion on climate change wikipedia , lookup
General circulation model wikipedia , lookup
Climate change, industry and society wikipedia , lookup
Attribution of recent climate change wikipedia , lookup
Global Energy and Water Cycle Experiment wikipedia , lookup
Climate change in the United States wikipedia , lookup
Surveys of scientists' views on climate change wikipedia , lookup
United Nations Framework Convention on Climate Change wikipedia , lookup
Climate change in Canada wikipedia , lookup
Carbon Pollution Reduction Scheme wikipedia , lookup
Mitigation of global warming in Australia wikipedia , lookup
Solar radiation management wikipedia , lookup
Global warming wikipedia , lookup
Public opinion on global warming wikipedia , lookup
Politics of global warming wikipedia , lookup
Climate change feedback wikipedia , lookup
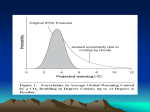
“Our Great Geophysical Experiment” 1 Questions to consider 1. The science of global warming. 2. The impacts of global warming on markets and environmental systems. 3. Why global warming poses such difficult problems for economic and environmental policy and the theory of stock global public goods. 4. The use of integrated assessment models to analyze trends and examine policies. 5. Alternative strategies for slowing climate change, especially cap and trade, the Kyoto Protocol, and carbon taxes. 2 Emissions: fossil fuel use generates CO2 The emissions -climateimpactspolicy nexus Carbon cycle: redistributes C around atmosphere, oceans, etc. Climate system: change in radiation warming, precip., ocean currents, etc.. Impacts on ecosystems, agriculture, diseases, skiing, golfing, … Policies: Measures to control emissions (limits, taxes, subsidies, …) 3 The Keeling curve of CO2 concentrations at Mauna Loa 4 The Greenhouse Effect: Fossil (C) fuel + O2 → Energy + CO2 CO2 has long atmospheric residence time as gas. CO2 is a “greenhouse” gas that retains surface heat. A CO2 Blanket 5 Energy balance of the earth 6 Radiative forcing and climate change 7 Absorption on the spectrum 8 Central notion of radiative forcings “The radiative forcing of the surface-troposphere system due to the perturbation (say, a change in greenhouse gas concentrations) is the change in net (down minus up) irradiance (solar plus long-wave in Wm-2) at the tropopause AFTER allowing for stratospheric temperatures to readjust to radiative equilibrium, but with surface and tropospheric temperatures and state held fixed at the unperturbed values.” IPCC Basic equation: ΔT = λ ΔF where T = mean surface temperature, F = forcings (W/m2), and λ is a feedback parameter. 9 From CO2 10 All GHGs, 2005 11 General Circulation Models - - These are the workhorses of climate change science. They are 3D computerized time-stepped simulation models of the atmosphere, oceans, cryosphere, and biosphere Based on fundamental physics (conservation, etc.), geography (where are oceans), and observations (initial conditions) Used to predict weather first, now climate, both historically and in the future Large ones are still very coarse grid (200 x 200 km) and require supercomputers (e.g., 8 TFLOP for GFDL). Because of complex physics, large remaining errors in and across GCMs (see next slide) 12 Ocean carbonization (a) Atmospheric CO2 emissions and changes in ocean pH and (b) projections compared with history(A and C), uncontrolled C/W (D); red + = uncontrolled WN; green triangle = “optimal” WN) Caldeira and Wickett, Nature 2003 13