* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Dr Yaser Gad
Onchocerciasis wikipedia , lookup
Eradication of infectious diseases wikipedia , lookup
Rocky Mountain spotted fever wikipedia , lookup
African trypanosomiasis wikipedia , lookup
Sexually transmitted infection wikipedia , lookup
Sarcocystis wikipedia , lookup
Trichinosis wikipedia , lookup
Hepatitis C wikipedia , lookup
Marburg virus disease wikipedia , lookup
Leptospirosis wikipedia , lookup
Traveler's diarrhea wikipedia , lookup
Anaerobic infection wikipedia , lookup
Hepatitis B wikipedia , lookup
Human cytomegalovirus wikipedia , lookup
Gastroenteritis wikipedia , lookup
Dirofilaria immitis wikipedia , lookup
Clostridium difficile infection wikipedia , lookup
Schistosomiasis wikipedia , lookup
Antibiotics wikipedia , lookup
Carbapenem-resistant enterobacteriaceae wikipedia , lookup
Neisseria meningitidis wikipedia , lookup
Coccidioidomycosis wikipedia , lookup
Oesophagostomum wikipedia , lookup
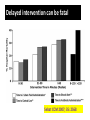
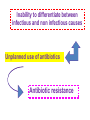
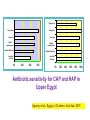
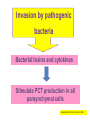
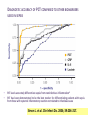
رب اجعل هذا بلدا آمنا وارزق أهله من الثمرات من امن منهم باهلل و اليوم اآلخر Clinical Implication of Serum Procalcitonin in Sepsis and pneumonia Lecturer of chest diseases, Assuit faculty of medicine The most common cause of death in intensive care units Mortality rate up to 50% depending on severity. Early diagnosis and intervention markedly reduce the mortality INFECTION SOURCE IN SEVERE SEPSIS 10.8% 6.0% 8.0% 44.0% 2.2% 6.6% 8.6% 9.1% Respiratory Bacteremia GU Abdomen Soft tissue Device CNS Endocarditis Other 17.3% Angus DC et al. Crit Care Med. 2001; 29:1303 The major infection-related cause of death in developed countries 10 to 20% admitted to the intensive care unit 20 to 50% of them will ultimately die Fight as much as you can Early diagnosis and intervention Differentiate between infectious and non infectious case of systemic inflammation Early diagnosis is essential to : Administer the correct treatment Avoid unnecessary antibiotic use Reducing the morbidity, mortality And decrease care-related costs. Cantürk et al., Turk J Med Sci 2008; 38 (2): 139-144 Delayed diagnosis • • • • Delays treatment Increases hospital length-of-stay Increases costs Increased mortality Delayed intervention can be fatal Sebat CCM 2007; 35: 2568 It is very important to differentiate between infectious and non infectious case of systemic inflammation Inability to differentiate between infectious and non infectious causes Unplanned use of antibiotics Antibiotic resistance 70% are infectious in origin . 20–30% related to bacteria detected by sputum culture viruses are detected in >50% of exacerbations Bacteria are isolated from the respiratory tract of only 50% of patients Dauben et al., BMC Infect Dis. 2008; 8: 145. Chen et al, 2008 Chinese Medical Journal, 2008, Antibiotics were found to have been prescribed in 85% of patients admitted for AE-COPD to 360 hospitals throughout the USA Drug costs accounted for more than 70% of the total costs AECOPD Chen et al, 2008 Chinese Medical Journal, 2008, 100% 80% 60% 40% 20% 0% Aminoglycosides Clindamycin 1st&2nd cephalosporins. Ca vu lin at e e im Lincomycin 0% 10% 20% 30% 40% 50% 60% Am ox ici llin Ce fip es id Ma cr ol ac in lox Le vo f Mo xif l ox ac in Tetracyclines Antibiotic sensitivity for AECOPD in Upper Egypt Agamy et al., Egyp.J. Ch.dises. And tub. 2011 Erythromycin Tetracyclines Tetracyclines Lincomycin Lincomycin 1st&2nd cephalosporins. 1st&2nd cephalosporins. Ampicilin-Sulbactam Ampicilin-Sulbactam AmoxicillinClavulinic AmoxicillinClavulinic 0% 20% 40% 60% 0% 20% 40% 60% 80% 100% Antibiotic sensitivity for CAP and HAP in Upper Egypt Agamy et al., Egyp.J. Ch.dises. And tub. 2011 Acute phase reactants Capable of demonstrating the inflammation differentiate between bacterial and nonbacterial inflammation CRP and leukocyte count do not have sufficient specificity in differentiating between bacterial infections, non-infectious systemic inflammations or viral infections. Cantürk et al., Turk J Med Sci 2008; 38 (2): 139-144 Because most microbiological test results are not available for 24 h, a sensitive and specific marker of systemic infection would be useful. Hausfater et al, 2002. Clinical Infectious Diseases Volume 34, Issue 7Pp. 895-901 Reimer et al. Clinical Microbiol Rev 1997; 10:444-65. We are in need for a simple and rapid laboratory method to: Guide antibiotic use Predict the prognosis Predict mortality Differentiate between infectious and non infectious causes of systemic inflammation (PCT) levels appears to be useful in order to minimize this problem. The sensitivity and specificity of PCT in bacterial infections were found to be 92.6% and 97.5% Cantürk et al., Turk J Med Sci 2008; 38 (2): 139-144 Invasion by pathogenic bacteria Bacterial toxins and cytokines Stimulate PCT production in all paraynchymal cells Adapted from Christ-Crain et al. 2005 22 VALUES OF PROCALCITONIN IN INFECTION 23 1- PCT LEVEL INCREASE = INCREASED SIGNIFICANCE OF BACTERIAL INFECTION 2 ng/ml 0.5 ng/ml 0.05 ng/ml Healthy Individuals Local Infections Systemic Infections (Sepsis) Severe Sepsis Septic Shock 24 Differentiates between bacterial contamination and real bacterial infection 2- PCT may help discriminate blood stream infections from blood culture contamination due to coagulase-negative staphylococci Schuetz P. et al., Infection 2007;35 (5): 352-5 25 3- Predicts bacteremia PCT measurement demonstrated the potential to reduce the number of blood cultures Muller et al. CHEST July 2010 26 4- PROCALCITONIN CORRELATES TO THE SEVERITY OF THE INFECTION Sepsis Pneumonia Harbarth S et al. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 2001, 164: 396-402 Meisner M et al., Critical Care 1999, 3(1): 45-50 Krüger S. et al., Eur Respir J 2008; 31: 349–355 27 5- Evaluates the prognosis Mortality by PCT level 12% PCT 10% ≥ 0.1 Mortality, % 8% 6% 4% < 0.1 2% 0% 0 5 10 15 20 25 30 Day PCT • Low PCT levels identify patients presenting in the ED that have a low risk for mortality Huang, et.al., Annals of Emergency Medicine, Vol 51, March 2008 28 6- Evaluates patient response to antibiotics • Decreasing PCT levels indicate effective treatment of the underlying infection • Persistently elevated PCT levels indicate a possible treatment failure Stueber, F. University of Bonn, Lecture at ISICEM, Brussels 2001 29 PCT GUIDANCE IN ANTIBIOTIC USAGE EFFECTS ON LENGTH OF STAY • Effect of PCT-guided management in patients with sepsis on ICU length of stay Nobre V. et alAM Resp Crit Care Med 2008: 177:498-505 30 7- Sort out the etiology of the fever in patients with the fever of unknown origin (FUO) syndrome • PCT levels do not increase in some of the disease entities that cause the FUO syndrome, e.g., Still's disease, systemic lupus erythematosus, and inflammatory bowel disease 31 PCT levels are not affected by the patient's use of nonsteroidal antiinflammatory agents or glucocorticoids PCT levels remain a valuable marker of the host inflammatory response even when nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs and corticosteroids are used 32 DIAGNOSTIC ACCURACY OF PCT COMPARED TO OTHER BIOMARKERS USED IN SEPSIS • • PCT levels accurately differentiate sepsis from noninfectious inflammation* PCT has been demonstrated to be the best marker for differentiating patients with sepsis from those with systemic inflammatory reaction not related to infectious cause Simon L. et al. Clin Infect Dis. 2004; 39:206-217. 33 False negative results Low PCT levels in the presence of bacterial infection may occur: • Early course of infection: Re-measure in 6-12hrs • Subacute Endocarditis • Localized infections 34 False positive results Cirrhosis Pancreatitis Mesenteric infarction (ischemic bowel) Cardiogenic shock, and hypotension during surgery Burns Pulmonary edema and pulmonary aspiration 35 PCT is usefull to diffrentiate between bacterial and non bacterial infection Differentiates between bacterial contamination and real bacterial infection Predicts bacteremia 36 PCT level correlates with the severity of infection in sepsis and pneumonia Evaluates the prognosis Evaluates patient response to antibiotics Sort out the etiology of the fever in patients with the fever of unknown origin (FUO) syndrome 37 Never ever forget to love those dearest to you 38