* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Risk factors for heart disease
Survey
Document related concepts
Cardiac contractility modulation wikipedia , lookup
History of invasive and interventional cardiology wikipedia , lookup
Heart failure wikipedia , lookup
Antihypertensive drug wikipedia , lookup
Electrocardiography wikipedia , lookup
Quantium Medical Cardiac Output wikipedia , lookup
Arrhythmogenic right ventricular dysplasia wikipedia , lookup
Mitral insufficiency wikipedia , lookup
Management of acute coronary syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Artificial heart valve wikipedia , lookup
Coronary artery disease wikipedia , lookup
Heart arrhythmia wikipedia , lookup
Lutembacher's syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Dextro-Transposition of the great arteries wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
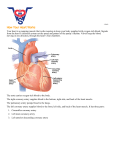
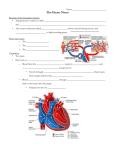
anatomy The heart is a hollow , 4 chambered muscular organ which lies in the mediastinal cavity between the right and left lungs just behind the body of the sternum A pointy blunt section of the heart points to the left side of the heart and it is called he apex of the heart. 2/3 of its mass is to the left of the midline and 1/3 is to the right The average heart is 5 inches long and 31/2 inches wide. The primary function of the heart is to supply the body with enough blood to meet its metabolic demands. A normal heart beats 60-100 times per minute. Pumping an average of 5.5 liters per minute. What is the primary function of the heart? a) to supply the body with blood to meet the metabolic needs. b) to help with insulin production c) to produce RBC's d) to help create increased metabolism How many times does the heart beat per minute? a) 40-60 b) 60-80 c) 60-100 d) 90-120 How many chambers are there in the human heart? a) one b) three c) four d) six Heart layers Pericardium: outermost layer Myocardium: middle muscular layer Endocardium; inner layer THE MIDDLE MUSCULAR LAYER OF THE HEART IS CALLED WHICH OF THE FOLLOWING? a) ENDOCARDIUM b) PERICARDIUM c) EPICARDIUIM d) MYOCARDIUM Heart surfaces Anterior surface Posterior surface Inferior surface Lateral surface Heart chambers 2 upper chambers right and left atrium 2 lower chambers right and left ventricles The 2 atrium are divided by the interatrial septum.the 2 lower chambers are divided by the interventricular septum The right heart receives deoxygenated blood from the body and sends it to the lungs for oxygenation. The left heart receives oxygenated blood and sends it to the body. Each heart beat =2 and ½ ounces. What side of the heart receives deoxygenated blood? a) right side b) left side valves The tricuspid valve separates the right atrium from the right ventricle. Mitral valve separates the left atrium and ventricle. Called AV valves(atria and ventricles) What valve seperates the right atrium from the right ventricle? A) tricuspid valve b)Mitral valve c) bicuspid valve d) pulmanary valve The valves have cusp or leaflets which are connected to papillary muscles in the ventricles called chordae tendineae Incomplete closure of the valves creates a murmur. What creates a heart murmur? a) the normal opening and closing of the valves b) incomplete closure of the valves c) arteriosclorosis d) PDA The aortic and pulmonary valve (semilunar) valves prevent back flow into the ventricle from the pulmonary artery and aorta The lub dup sound of the heart beat is the valves opening and closing. Blood flow The right atrium receives unoxygenated blood from the superior and inferior vena cava, and the coronary sinus. The tricuspid valve opens and the blood fills the right ventricle . The right ventricle now contracts ejecting the blood through the pulmonary valve into the lungs via the pulmonary artery. Where does the right atrium receive blood? a) coronary sinus b)Superior vena cava c) inferior vena cava d) all of the above In the lungs the blood picks up oxygen and releases carbon dioxide. The left atrium receives the oxygenated blood from the lungs via the pulmonary veins.as the left atrium fills with blood the pressure increases and the mitral valve opens allowing blood to flow into the left ventricle. The left ventricle contracts and ejects the blood through the aortic valve into the aorta where it is distributed to the rest of the body. The right and left side side are working simultaneously. Where does the blood pick up oxygen and release carbon dioxide? a) heart b) coronary sinus c) capillaries d) lungs Discection film Risk factors for heart disease Heredity Gender Age Hypertension Hyperlipidemia Diabetes Smoking Diet Lack of exercise Obesity stress Disease process The coronary arteries supply oxygen rich blood to the heart muscle. Arteriosclerosis is a thickening and hardening of the wall which causes a loss of elasticity resulting in decreased blood flow. A lack of blood flow to the heart results in an oxygen and nutrient deficit called ischemia. Angina Lack of blood flow to the heart will cause chest pain. S&S are the same as a heart attack S&S: tightening band, or a crushing sensation., burning sensation like indigestion it may radiate to the left jaw or arm, SOB, anxiety, light-headedness Myocardial infarction When an artery is totally occluded and blood flow is blocked or shut off tissue death occurs. Muscle death is a heart attack. S&S similar to angina only more severe and longer may also be N/V and diaphoresis Diagnostic treatments Cardiac catherization:A tube is inserted into the femoral artery and feed up to the heart chambers. The patient is awake but sedated. Angiogram: during the cardiac catherization A dye is injected into the coronary arteries in order to detect blockages in the artery. Percutaneous transluminal coronary angioplasty PTCA is a tx for blocked arteries that can be performed upon completion of the angiogram.A catheter with a balloon ath the end is placed in the artery at the site of the blockage. As the balloon is inflated and enlarges the diameter of the artery. This increases blood flow TEE Transesophageal echocardiography ; A flexible tube about the size of your index finger is inserted in your mouth and down your esophagus at the tip of the tube is a small probe that produces sound waves.they bounce off the heart and make a picture on a screen. Coronary artery bypass graft CABG: open heart surgery: blood vessels from other parts of the body are removed and (harvested) they are sewn into the aorta and then into the coronary artery beyond the blockage. These harvested vessels bypass the blockage Cardioversion ; defibrillation External electrical shocks are applied to a patient in order to correct ventricular tachycardia or ventricular fibrillation Implanted cardiac defibrillator ICD s small defibrillator implanted into a patients chest that will automatically detect tachycardia. Implanted cardiac defibrillator ICD s small defibrillator implanted into a patients chest that will automatically detect tachycardia. echocardiogram A test that uses ultrasonic waves to obtain a picture of the chambers, valves, and walls of the heart. This test can also detect abnormalities of the heart valves and walls pacemaker A surgically implanted device used in patients whose heartbeat is too slow. drugs Streptokinase and tissue plasminogen activator are meds called thrombolytic agents which dissolve clots. Aspirin also thins the blood Coronary circulation There are 2 coronary arteries that provide blood supply to the heart. The right and left coronary sinus. Cardiac cells The heart consists of electrical cells and myocardial cells. The electrical cells are responsible for impulse formation. The electrical cells generate and conduct electrical impulses that result in contraction and relaxation of the myocardial cells. These electrical impulses are generated by a flow of positively charged ions back and forth across the cardiac cell membrane creating and electrical current which results in depolarization (electrical activation) Contraction and repolarization(recovery) electrolytes Each cardiac cell is surrounded by and filled with a solution that contains positively charged ions. And negatively charged ions. Potassium is the intracellular ion and sodium is the extracellular ion. In the resting state of the cell the inside of the cell membrane is considered negatively Charged. While the outside is considered positively charged. Once an electrical impulse is generated sodium moves into the cell and K Begins to exit converting the electrical forces inside the cell to a positive charge. The cell is then depolarized. As soon as the cell is depolarized K re-enters the cell and Na exits returning the inside to a resting neg charge. Electrical conduction SA node =60-100 bpm AV node= 40-60 Ventricular pacemaker 30-40 EKG The hearts electrical activity is represented on the EKG monitor as 3 waveforms P wave QRS complex and T wave Ekg :practice session