* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Electric Circuits
Survey
Document related concepts
Giant magnetoresistance wikipedia , lookup
Nanogenerator wikipedia , lookup
Lumped element model wikipedia , lookup
Electric charge wikipedia , lookup
Superconductivity wikipedia , lookup
Power electronics wikipedia , lookup
Galvanometer wikipedia , lookup
Nanofluidic circuitry wikipedia , lookup
Operational amplifier wikipedia , lookup
Switched-mode power supply wikipedia , lookup
Opto-isolator wikipedia , lookup
Surge protector wikipedia , lookup
Power MOSFET wikipedia , lookup
Two-port network wikipedia , lookup
Electrical ballast wikipedia , lookup
Resistive opto-isolator wikipedia , lookup
Rectiverter wikipedia , lookup
Current source wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
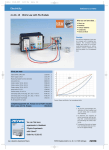
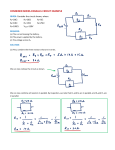
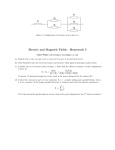
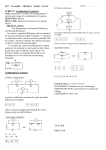
Electric Circuits Current: Current: I = Δq Δt ⇒ Current flows because a potential difference across a conductor creates an electric field which exerts a force on free electrons in the circuit. Conventional current: the “hypothetical” flow of positive charge (it is really electrons flowing in opposite direction) Electromotive force or emf: the maximum difference in electrical potential between the terminals of a battery Ohm’s Law: Ohm’s law: R = ΔV = constant I Ohm’s law is more commonly stated as: V = IR or I = V R Resistance and Resistivity: Resistance of a wire is given by: R = ρL A Resistivity depends upon temperature: ρ = ρ 0 [1 + α (T − T0 )] Power: Power: P = IV P = I 2R = applies to any circuit element 2 V R applies only to resistors Resistors in series: Resistors in parallel: Current is the same through each resistor Voltage is the same across each resistor Voltage is split among individual resistors Current is split among the individual resistors Req = R1 + R2 + R3 + ... 1 1 1 1 = + + + ... Req R1 R2 R3