* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Resonant Circuit
Integrating ADC wikipedia , lookup
Spark-gap transmitter wikipedia , lookup
Distributed element filter wikipedia , lookup
Schmitt trigger wikipedia , lookup
Superheterodyne receiver wikipedia , lookup
Mathematics of radio engineering wikipedia , lookup
Josephson voltage standard wikipedia , lookup
Power MOSFET wikipedia , lookup
Power electronics wikipedia , lookup
Operational amplifier wikipedia , lookup
Opto-isolator wikipedia , lookup
Surge protector wikipedia , lookup
Crystal radio wikipedia , lookup
Switched-mode power supply wikipedia , lookup
Electrical ballast wikipedia , lookup
Current source wikipedia , lookup
Two-port network wikipedia , lookup
Phase-locked loop wikipedia , lookup
Resistive opto-isolator wikipedia , lookup
Radio transmitter design wikipedia , lookup
Nominal impedance wikipedia , lookup
Wien bridge oscillator wikipedia , lookup
Regenerative circuit wikipedia , lookup
Standing wave ratio wikipedia , lookup
Rectiverter wikipedia , lookup
Network analysis (electrical circuits) wikipedia , lookup
Valve RF amplifier wikipedia , lookup
Index of electronics articles wikipedia , lookup
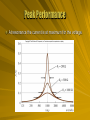
Resonant Circuit Series Behavior The behavior of the series i R RLC circuit is governed by the impedance. • Magnitude and phase v L 1 Z R 2 L C C 1 L C arctan R 2 Perfect Match There is special behavior when XC = XL. • Vectors cancel • Impedance only from resistor VL=IXL VR=IR This is called resonance. VC=IXC Resonant Frequency The requirements for XC X L 1 0 L 0C 1 LC 2 0 0 1 LC 0 1 f0 2 2 LC resonance come from the reactances. There is a resonant frequency 0 associated with the circuit. • Angular frequency • Can be converted into frequency f in Hz Vector Sum The total impedance is the magnitude of Z. XC XL Z The phase between the current and voltage is the angle between Z and the x-axis. R Z R2 X L X C 2 1 2 Z R L C 2 X L XC tan R 1 L C arctan R Peak Performance At resonance the current is at maximum for the voltage. Circuit Example Find the resonant frequency in the following circuit in Hz. The problem requires the formula for the frequency f. f0 1 2 LC 100 W Only the inductance and capacitance matter. 10 V 250 mH 0.1 mF • 1/2 (0.25 H 10-7 F)1/2 = 1 kHz Circuit Example The behavior of the series 100 W RLC circuit is governed by the impedance. • Magnitude and phase 10 V 250 mH 0.1 mF 1 Z R 2 L C 1 L C arctan R 2 Resonant Reactance In the preceding circuit the voltage across each component can be found. • Current due to resistor only The voltage across the inductor has an amplitude of 158 V. • So does the capacitor I V / R 0.1A VL 2f 0 IL 158 V I VC 158 V 2f 0C They are each 90° out of phase and cancel out. next