* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download home address
Survey
Document related concepts
Deep packet inspection wikipedia , lookup
Asynchronous Transfer Mode wikipedia , lookup
SIP extensions for the IP Multimedia Subsystem wikipedia , lookup
Wake-on-LAN wikipedia , lookup
Distributed firewall wikipedia , lookup
Computer network wikipedia , lookup
Piggybacking (Internet access) wikipedia , lookup
Network tap wikipedia , lookup
Airborne Networking wikipedia , lookup
List of wireless community networks by region wikipedia , lookup
Recursive InterNetwork Architecture (RINA) wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
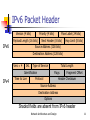
Advanced Issues in Internet Protocol (IP) IPv4 Network Address Translation (NAT) IPV6 IP Security (IPsec) Mobile IP IP Telephony Network Architecture and Design 1 Challenges to IP Addresses needed for 21st century Internet devices will be more numerous, and not adequately handled by NATs Estimated 20 billion people Multiple interfaces/node Multiple addresses/interface mobile phones cards residential servers The solution: IPv6 Network Architecture and Design 2 IPv6 IPv6 Address: 128 bits 3,4x10^38 different addresses Allows: multiple interfaces per host multiple addresses per interface Advanced routing functions unicast multicast anycast Network Architecture and Design 3 IPv6 Notation X:X:X:X:X:X:X:X where X is Hex values of 16 bits, e.g. FEDC:BA98:7654:3210:FEDC:BA98:7654:3210 Skip one sequence of zero words, e.g. FEDC:0000:0000:0000:9876:0000:0000:ABCD = = FEDC::9876:0000:0000:ABCD Network Architecture and Design 4 IPv6 Address Types According to the prefix there are 5 types of addresses Local use: Provider-based (global): Prefix:010 Link local: Prefix: 1111 1110 10 Site local: Prefix: 1111 1110 11 Multicast: Prefix: 1111 1111 Reserved unspecified, loop back, IPv6 with embedded IPv4 addresses: Prefix: 0000 0000 Network Architecture and Design 5 IPv6 Address Types Global Site-Local Link-Local Global - Forwarded anywhere Link Local – Not forwarded outside the link Site Local – Not forwarded outside the site Network Architecture and Design 6 IPv6 Provider Based Address Registry Provider Subscriber 010 0 0 ID ID ID 3 5 16 8 24 8 Subnet ID 16 Interface ID 48 Forwarded anywhere Network Architecture and Design 7 IPv6 - Link Local Address 1111 1110 10 10 bits 0 Interaface ID n bits 118-n bits Not forwarded outside the link Network Architecture and Design 8 IPv6 - Site Local Address 1111 1110 11 10 bits 0 Interaface ID n bits 118-n bits Not forwarded outside the site Network Architecture and Design 9 IPv6 – Multicast Addresses 1111 1111 8 bits Scope 4bits Group ID 112 bits Flag: 000T Flags 4 bits T=0 for permanent address T=1 for transient address Scope: 1: Node Local 2: Link Local 8: Org Local Network Architecture and Design 10 IPv6 Packet Header Version (4 bits) Priority (4 bits) Payload Length (16 bits) IPv6 Flow Label (24 bits) Next Header (8 bits) Hop Limit (8 bits) Source Address (128 bits) Destination Address (128 bits) Vers = 4 IHL Type of Service Identification IPv4 Time to Live Total Length Flags Protocol Fragment Offset Header Checksum Source Address Destination Address Options Shaded fields are absent from IPv6 header Network Architecture and Design 11 IPv6 Extension Headers Options field of IPv4 is replaced by extension headers, used for special purposes: Extension headers are chained together IPv6 Header TCP Header + Data Next Header = TCP IPv6 Header Routing Header Next Header = Routing Next Header = TCP TCP Header + Data IPv6 Header Routing Header Fragment Header Fragment of TCP Next Header = Routing Next Header = Fragment Next Header = TCP Header + Data Network Architecture and Design 12 IPv6 Header Types Header Types Hop-by-Hop = 0 Routing Header = 43 Fragment Header = 44 Authentication Header = 51 Encrypted Payload = 52 TCP =6 UDP =17 Network Architecture and Design 13 IPv6 Flow Label Header Field IPv6 header gives the ability of labeling traffic flow (24 bits) Flow label indicates that packets need special handling: Real time service Special QoS Network Architecture and Design 14 IPv6 – Priority Header Field 4 bit priority field Enables source to identify the desired delivery priority of it’s packets relative to other packets from the same source Two ranges 0 through 7 specifies priority of packets (no real time) 8 through 15 specify priority of real time packets Network Architecture and Design 15 IPv6 Vs IPv4 Expanded addressing capabilities Simplified header format Reduction in processing cost Flow labeling Support for authentication and privacy Support for improved options and extensions Support of all IPv4-based mechanisms IPsec – diffserv – QoS features Network Architecture and Design 16 IPv6 and IPv4 Co-existence IPv4 and IPv6 will exist together As time goes by: Devices support only IPv4 Devices support IPv4 and IPv6 Devices support only IPv6 Coexistence using: Dual stack approach Tunneling approach Applications choose version to use Encapsulation of IPv6 in IPv4 packets Translation approach Extended NAT techniques for translating IPv6 to IPv4 Network Architecture and Design 17 Advanced Issues in Internet Protocol (IP) IPv4 Network Address Translation (NAT) IPV6 IP Security (IPsec) Mobile IP IP Telephony Network Architecture and Design 18 IP Security (IPsec) Advantages Provides seamless security to application and transport layers (ULPs) Allows per flow or per connection security and thus allows for very fine-grained security control Disadvantages More difficult to exercise on a per user basis on a multi-user machine Network Architecture and Design 19 IPsec Services Connectionless integrity Data origin authentication Assurance that traffic is sent by legitimate party or parties Confidentiality (encryption) Assurance that received traffic has not been modified Integrity includes anti-reply defenses Assurance that user’s traffic is not examined by nonauthorized parties Access control Prevention of unauthorized use of a resource Network Architecture and Design 20 IPsec Protocols IPsec = AH + ESP + IPcomp + IKE Authentication Header (AH) Provides authenticity guarantee for packets, by attaching strong crypto checksum to packets Ensures: The packet was originated by the expected peer The packet was not generated by impersonator The packet was not modified in transit Network Architecture and Design 21 IPsec Protocols Encapsulating Security Payload (ESP) Provides confidentiality guarantee for packets, by encrypting packets with encryption algorithms Ensures The packet was not wiretapped in the middle Network Architecture and Design 22 IPsec Protocols IP payload compression (IPcomp) Provides a way to compress packets before encryption by ESP Internet Key Exchange (IKE) AH and ESP needs shared secret key between peers IKE provides ways to negotiate keys in secrecy Network Architecture and Design 23 IPsec Example (Tunnel) A single IPSec gateway secures multiple site networks Simplicity, High Performance, Flexibility and Compatibility IP clear text IP clear text payload encrypted ESP new IP header IPSec ESP header IP IP payload payload IPSec gateway clear text IPSec gateway Internet IPSec “tunnel” LAN LAN Network Architecture and Design 24 IPsec Example (Transport) Bulk data in clear text, but sensitive information encrypted Privacy, Transparency, Flexibility and High Performance IP clear text encrypted IPSec host ESP payload IP IPSec ESP header IPSec ESP header encrypted sensitive information ESP payload router clear text encrypted IPSec host router Internet LAN clear text LAN IP IP payload payload clear text bulk data Network Architecture and Design clear text 25 Advanced Issues in Internet Protocol (IP) IPv4 Network Address Translation (NAT) IPV6 IP Security (IPsec) Mobile IP IP Telephony Network Architecture and Design 26 Mobile IP – The Problem Home Network Mobile node Foreign Network A mobile host must be assigned a new address when it moves outside of the home network Host address must be preserved regardless of a hosts location Network Architecture and Design 27 Mobile IP – Basic Entities Mobile Node (or Mobile Host) Home Agent (HA) Foreign Agent (FA) The agent of the foreign network where the mobile node may be found Home Address (HA) The agent of the network where the mobile node belongs (Home Network) The mobile node’s permanent address Care-of Address (CA) The mobile node’s temporary address assigned in the foreign network Network Architecture and Design 28 Mobile IP – Basic Entities A mobile node keeps its home address inside the home network, but in a foreign network it borrows a care-of address Agents: Take care of all issues related to the mapping of the care-of address to the home address Agents are: Routers Advanced servers Network Architecture and Design 29 Mobile IP Mechanism Advertising care-of address Registration Tunneling Network Architecture and Design 30 Mobile IP Advertising Care-of Address Home and foreign agents periodically broadcast agent advertisements (ICMP messages) to mobile nodes Messages contain: If (Network Prefix IP Source Address advertisement = Network Prefix Home Address) then mobility agent address care-of addresses mobile node is in the home network Else Move detection Registration required Network Architecture and Design 31 Mobile IP Advertising Care-of Address Foreign Agent Home Agent Internet Agent Addr: 169.17.8.29 Agent Addr: 132.5.3.2 Care-of Addr: 169.17.8.11 Care-of Addr: 132.5.3.8 132.5.3.69 132.5.3.74 This node requires registration This node is in the home network Network Architecture and Design 32 Mobile IP - Registration Internet Foreign Ag. relays request to Home Ag. Host requests service For. Ag. relays status to Host Home Ag. accepts or denies After registration: Both, host and agents know the host’s new location Home agent knows the host’s state-of address Network Architecture and Design 33 Mobile IP - Tunneling How packets from sources are delivered to host? Home agent (router) intercepts packets destined to host Home agent tunnels (encapsulates) packets to sate-of address Foreign agent decapsulates packets and delivers them to mobile host Network Architecture and Design 34 Mobile IP - Tunneling Mobile Host Home Address: 148.6.8.2 Mobile Host State-of Address: 134.2.5.7 Mobile Host Foreign Agent Home Agent Source Internet Packets to Host Dest. Addr. Data 148.6.8.2 Header Payload Dest. Addr. Dest. Addr. 134.2.5.7 148.6.8.2 Data Outer Header Inner Header Payload Network Architecture and Design Dest. Addr. Data 148.6.8.2 Header Payload 35 Mobile IP: NAT issues The problem: The Care-of address is a private address. This address is not reachable from outside the private network. Two Mobile Nodes in different private networks may happen to have the same private address as Care-of address. The solution: draft-ietf-mobileip-nat-traversal-05.txt Use IP in UDP tunnels. Use the source IP address and source port of Registration Request messages to locate the Mobile Node. Add an option to registration messages to inform of UDP tunneling capability. Network Architecture and Design 36 Advanced Issues in Internet Protocol (IP) IPv4 Network Address Translation (NAT) IPV6 IP Security (IPsec) Mobile IP IP Telephony Network Architecture and Design 37 IP Telephony Since today PSTN and Internet were two different networks Need of integration Solution: Voice over IP (VoIP) New devices IP Telephones Gatekeepers Network Architecture and Design 38 IP Telephony IP Phone IP Network PSTN Gatekeeper Switch PC Phone Network Architecture and Design 39 IP Telephony Vs Pure Telephony Pure Telephony: End to End QoS No delay Isolated from new IP services IP telephony Variable QoS Delay Integrated with other services Problems will be solved in the future Network Architecture and Design 40 IP Telephony Features Data Transport : Signalling: RTP IETF SIP protocol suit ITU-T H.323 protocol suit Quality of Service: RSVP Network Architecture and Design 41 IP Telephony Protocol Stack Network Architecture and Design 42 First Intermediate Report NAT Mobile IP Klaoudatou Mavrogenis Mobile IP: NAT issues Doukas Kikilis Lizos Deadline: 15/03/04 Network Architecture and Design 43 First Intermediate Report IPv6 IPsec Baliotis Panoutsakopoulos IPv6 and IPv4 coexistence Kolovou Barbarousis IP telephony Ratsiatos Rekleitis Plataniwtis Deadline: 16/03/04 Network Architecture and Design 44 First Intermediate Report Structure Overview of examined technology Focus on open research points Related to open points works - State of the art behind open points Your own interests - Ideas Conclusions References Network Architecture and Design 45 First Intermediate Report Report (soft and hard copy) A related presentation (about twenty minutes). Network Architecture and Design 46 Basic Grid Functions Services Data Publication and Subscription Toolkits Instrument Management Toolkits Collaboration Toolkits Visualization Toolkits Applications Application Codes Grid Layers Grid Enabled Libraries Resource Brokering Data Management: replication and metadata Resource Discovery Fault Management Scheduling and Access to Computing Workflow Management Uniform Data Access Encapsulation as Web Services Accounting Monitoring and Events Grid Communication Functions transport services security services Communications Internet space-based networks optical networks ... Distributed Resources Tertiary Storage On-Line Storage national supercomputer facilities CPUs clusters Network Architecture and Design Condor pools of workstations Scientific Instruments 47 Emulator of distributed resources We need this emulator in order to perform Resource discovery and resource distribution tasks http://www.samos.aegean.gr/icsd/gkorm/ Network Architecture and Design 48