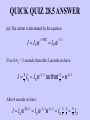* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Chapter 28 QQ
Schmitt trigger wikipedia , lookup
Galvanometer wikipedia , lookup
Integrated circuit wikipedia , lookup
Negative resistance wikipedia , lookup
Opto-isolator wikipedia , lookup
Power electronics wikipedia , lookup
Lumped element model wikipedia , lookup
Regenerative circuit wikipedia , lookup
Surge protector wikipedia , lookup
Transistor–transistor logic wikipedia , lookup
Index of electronics articles wikipedia , lookup
Power MOSFET wikipedia , lookup
Operational amplifier wikipedia , lookup
Valve audio amplifier technical specification wikipedia , lookup
Charlieplexing wikipedia , lookup
Zobel network wikipedia , lookup
Valve RF amplifier wikipedia , lookup
Two-port network wikipedia , lookup
Switched-mode power supply wikipedia , lookup
Surface-mount technology wikipedia , lookup
Resistive opto-isolator wikipedia , lookup
Current mirror wikipedia , lookup
Current source wikipedia , lookup
RLC circuit wikipedia , lookup
Rectiverter wikipedia , lookup
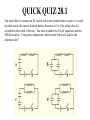
QUICK QUIZ 28.1 You would like to construct an RC circuit with a time constant that is equal to 1 second (in other words, the current from the battery decreases to 1/e of its initial value in 1 second after the switch is thrown). You have available two 0.5-mF capacitors and two 500-kW resistors. Using these components, which circuit below will achieve the desired results? QUICK QUIZ 28.1 ANSWER (b). Appropriate values for R and C to give you a 1-second time constant would be 1 MW and 1 mF. Therefore, you can combine the two 500-kW resistors in series to give you the 1 MW and you can combine the two 0.5-mF capacitors in parallel to give you 1 mF. QUICK QUIZ 28.2 A very large resistor is in parallel with a very small resistor. The equivalent resistance of this combination will be a) slightly greater than the resistance of the large resistor, b) slightly less than the resistance of the large resistor, c) slightly greater than the resistance of the small resistor, or d) slightly less than the resistance of the small resistor. QUICK QUIZ 28.2 ANSWER (d). An easy way to visualize this situation is to draw the two resistors side by side with the large resistor represented as a cylinder with a small cross sectional area and the small resistor represented as a cylinder with a large cross sectional area. The resistance is mainly determined by the small resistor since most of the current travels through it. The small additional cross sectional area provided to the current by the large resistor decreases slightly the total resistance to current flow. QUICK QUIZ 28.3 For the circuit shown, if you were to measure the voltage between the two points indicated you would measure a) 4 volts, b) 20 volts, c) 0 volts, or d) 6.67 volts. QUICK QUIZ 28.3 ANSWER (b). This is an example of an open circuit. Therefore, no current flows through the circuit. If no current flows through a resistor, then the voltage on each side of the resistor is the same. No voltage changes occur across any of the resistors. You have a 10-volt gain across the first battery and another 10-volt gain across the second battery, giving 20 volts between the terminals. QUICK QUIZ 28.4 You have available three 2-W resistors, each with a maximum power capacity of 16 W and an 8-volt battery capable of providing up to 4 A of current. You would like to build a circuit with these components using one of the resistors as a heater that will provide at least ten watts of power output. Which circuit below will achieve the desired result? QUICK QUIZ 28.4 ANSWER (d). In circuit a, the current will be I = DV/R = 8V/2W = 4 A, and the power dissipated in the resistor will be P = I2R = 32 W, beyond the resistor’s capacity. In circuit b, the current will be 8V/4W = 2A and the power dissipated in each resistor will be 8 W, neither resistor producing the desired power. Similarly in circuit c the power dissipated in each resistor will be 32/9 W, less than the desired power. In circuit d, the current from the battery will be 8V/3W = 8/3 A and the power dissipated in the lone resistor (not the two in parallel) will be 128/9 W, within the desired range. QUICK QUIZ 28.5 A certain RC circuit is used to charge a capacitor. Two seconds after the switch is thrown, the current in the circuit is 75% of its initial value, or 3Io/4. Four seconds after the switch is thrown, the current will be: a) Io/2 b) Io/4 c) 9Io/16 d) impossible to determine without knowing the values of R and C QUICK QUIZ 28.5 ANSWER (c). The current is determined by the equation I I 0 e t / RC I 0 e t / τ If we let t1 = 2 seconds, then after 2 seconds we have: I I0 I0 e 3 4 t1 / τ so that e-t1 / τ 3 4 After 4 seconds we have: I I0 e 2t1 / τ I0 e t1 / τ e t1 / τ I 3 3 0 4 4 9 16 I0