* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download collocations
Preposition and postposition wikipedia , lookup
Lithuanian grammar wikipedia , lookup
Navajo grammar wikipedia , lookup
Georgian grammar wikipedia , lookup
Comparison (grammar) wikipedia , lookup
Old English grammar wikipedia , lookup
Swedish grammar wikipedia , lookup
Transformational grammar wikipedia , lookup
Modern Hebrew grammar wikipedia , lookup
Kannada grammar wikipedia , lookup
Japanese grammar wikipedia , lookup
Macedonian grammar wikipedia , lookup
Serbo-Croatian grammar wikipedia , lookup
Compound (linguistics) wikipedia , lookup
Spanish grammar wikipedia , lookup
Zulu grammar wikipedia , lookup
Arabic grammar wikipedia , lookup
Old Irish grammar wikipedia , lookup
Portuguese grammar wikipedia , lookup
Chinese grammar wikipedia , lookup
Italian grammar wikipedia , lookup
Latin syntax wikipedia , lookup
Ancient Greek grammar wikipedia , lookup
Russian grammar wikipedia , lookup
Scottish Gaelic grammar wikipedia , lookup
French grammar wikipedia , lookup
Yiddish grammar wikipedia , lookup
Determiner phrase wikipedia , lookup
Polish grammar wikipedia , lookup
Esperanto grammar wikipedia , lookup
Turkish grammar wikipedia , lookup
Basque grammar wikipedia , lookup
Malay grammar wikipedia , lookup
English grammar wikipedia , lookup
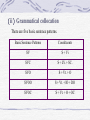
The Importance of Teaching English Collocations Students: Frank (黃國桓 M94C0215) Advisor:Professor Shaohua Zchang I. Introduction *Collocational competence is a key to language fluency and accuracy. .* Collocational errors are completely caused by differences between the mother tongue of the students and the target language they are learning. II. Literature Review: (Types of Collocations) Collocations are strung together in a linear word to some grammatical relationships. The restrictions on how words are used together are called collocations. Collocations are divided into two major types—lexical collocation and grammatical collocation. (i)Lexical collocation Lexical collocations are further divided into free collocation and fixed collocation. a) Free collocation The most frequent collocates are almost made with some of the most common words in English, such as good, bad, big, small, old, new, combine with almost any noun. Adjective+Noun:heavy rain (*big rain) Verb+Noun:kick the ball (*kick the idea) Verb+Adverb:appreciate sincerely (*cry sincerely) Adverb+Adjective:badly-dressed (*poorly-dressed) Noun+Verb:The machine will work. (*The stone will work.) b) Fixed collocation An idiom, phrase or proverb is a sequence of words operated as a single semantic unit. They must be considered as one single lexical item meaning. 1) Idioms: to rob Peter to pay Paul (挖東牆補西牆) 2) Phrases: to have an eye for (鑑賞) under the rose (秘密進行地) to break through (突破) 3) Proverbs:Where there is a will, there is a way.(有志者、事竟成) Fish become stink with the head.(上樑不正、下樑歪) (ii)Grammatical collocation There are five basic sentence patterns. Basic Sentence Patterns Constituents SV S+Vi SVC S+LV.+SC. SVO S+Vt.+O SVOO S+Vt.+IO+DO SVOC S+Vt.+O+OC a) S+Vi Birds fly away. b) S+LV.+SC. I am a graduate student. c) S+Vt.+O I like English. d) S+Vt.+IO+DO Father gave me a new watch. e) S+Vt.+O+OC Joy makes our room cheerful. However, syntactic restrictions operate between two lexical items, a verb and a noun. * The idea sleeps. * Sincerity admired the teacher. * The student eats frankness. (iii)Grammaticalization Definition: Grammaticalization is defined as the development from lexical to grammatical forms or from a less grammatical to a more grammatical status, because the development of grammatical forms depends on the constructions to which they belong. An Example of Grammaticalization be going to : I am going to visit Joy. (1) Be Ving (正在):I am now on my way to Joy’s house (2) Future(表未來):I intend to visit Joy. Grammaticalization of the common verbs, such as “ have”, “give”, “make”, “do”, “ take” can be seen in the following expressions: have fun give a visit to sb. make an appointment make a phone call take a shower do the dishes do the cooking