* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download God may be One, but Islam most definitely is not.”
Islamic democracy wikipedia , lookup
International reactions to Fitna wikipedia , lookup
Islam and Mormonism wikipedia , lookup
Soviet Orientalist studies in Islam wikipedia , lookup
Reception of Islam in Early Modern Europe wikipedia , lookup
Criticism of Islamism wikipedia , lookup
Succession to Muhammad wikipedia , lookup
Islam and violence wikipedia , lookup
Islam and secularism wikipedia , lookup
Islam and war wikipedia , lookup
Islam and Sikhism wikipedia , lookup
Morality in Islam wikipedia , lookup
Spread of Islam wikipedia , lookup
Medieval Muslim Algeria wikipedia , lookup
Islam in Iran wikipedia , lookup
Sources of sharia wikipedia , lookup
History of Islam wikipedia , lookup
Islam in Afghanistan wikipedia , lookup
Islam in Indonesia wikipedia , lookup
War against Islam wikipedia , lookup
Political aspects of Islam wikipedia , lookup
Usul Fiqh in Ja'fari school wikipedia , lookup
Islamic missionary activity wikipedia , lookup
Anti-Shi'ism wikipedia , lookup
Islam and modernity wikipedia , lookup
Imamah (Shia) wikipedia , lookup
Islamic culture wikipedia , lookup
Criticism of Twelver Shia Islam wikipedia , lookup
Origin of Shia Islam wikipedia , lookup
Islam and other religions wikipedia , lookup
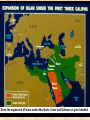
Development of the Muslim Empire Development of the Muslim Empire Click for Spread of Religions Watch the “Green” Quick Review What we know about Islam: People of the Book • Judaism • Christianity • Islam The Five Pillars of Islam 1) Shahada: The declaration of faith 2) Salat: Daily prayer (five times) 3) Zakat: Charity (almsgiving) 4) Sawm: Fasting from sunup to sundown during Ramadan 5) Hajj: A pilgrimage to Mecca at least once in a Muslim’s life John Green Review 1.Review the start of Islam for tomorrow’s quiz 2.What caused the Sunni- Shia split? Muhammad Dies Caliphate Established Islam Spreads under Abu Bakr/Umar/Uthman Division between Sunni and Shia Muaiwiya moves capital to Damascus Syria is center of Umayyad Muslim Empire (680-750) Abbasids Challenge Umayyad Leadership Umayyad State in Spain Baghdad is center of Muslim Empire (7501258) Draw the expansion of Islam under Abu Barkr, Umar and Uthman on your handout Quick Quiz: 1) What does Islam mean? Islam is an Arabic word meaning “submission to(God).” A Muslim is “one who submits to Allah’s will.” 2) Who? Where? When? Muhammad Mecca 610 – 632 CE 3) What is the Qur’an? The holy book of Islam, the Qur’an is the revealed word of Allah to Muhammad through the Angel Gabriel. 4) What are the two major branches of Islam? Which branch has more followers? Sunni: 85% of the Muslim World; Shia: 15% With more than 1.2 billion Muslims, Islam is the world’s fastest growing religion. Click for Review “God may be One, but Islam most definitely is not.” - Reza Aslan, No god but God It’s not the Western World versus the Muslim World. It’s the Muslim World vs. the Muslim World, an Islamic Reformation, and we’re caught in the crossfire. Sunni and Shia: The Split •Note: This is a very simplified version. •After Muhammad’s death (632), there was a dispute over who should succeed him as the next caliph (leader of the Muslim community). Sunni • As the most qualified was Abu Bakr was selected by the Muslim community at Medina. These followers became the Sunni, the main or “orthodox” branch of Islam. Shia • However, another group believed that Muhammad’s son-in-law, Ali (Muhammad’s cousin and husband of Muhammad’s daughter, Fatima), was the rightful successor. They became known as the Shiat Ali (“Party of Ali”), also know as the Shi’ites and Shia. Sunni vs. Shia • Ali became the fourth caliph, but he was murdered in 661 and his rival, Mu’awiya (Sunni), took over. “Before one embarks on a journey of revenge, he should dig two graves.” - Confucious •Ali’s son’s Hassan and Hussein continued to oppose the Sunni caliphs. Of course, Hassan eventually was poisoned (669) and Hussein died in battle (680). • The deaths of Ali, Hassan, and Hussein reinforced the Shia sense of betrayal and inspired the Shia devotion to martyrdom. • Shia became and remains the Islamic branch of the poor and oppressed waiting for deliverance. Shi’ism, Shia, Shi’ites, Shiat Ali • The Shias believe in divinelyappointed leaders (Imams) and await the return of the 12th Imam, Mohammed al-Mahdi, who disappeared in 878. Al-Mahdi’s return will reverse their fortunes and bring “a reign of divine justice.” Sunnis • The Sunnis reject leadership by Imams and follow the Sunna – the traditions of Muhammad composed in Hadith, the stories of the Prophet and his Companions. Basically, Hadith is what Muhammad said, did, agreed to, or condemned. Want to be more confused? • imam is a Sunni term used for the founding scholars of the four Sunni madhabs or schools of theological law. • Imam may also refer to the imams of the sciences related to Hadith. • Or to the heads of the Prophet's descendants in their times. In other words, "imam Ali" is a phrase used by both Shia and Sunni Muslims with different connotations. The Umayyads Ruled from 680-750 Moved capital to Damascus (Syria) Umayyad Empire stretched to Spain •Caliph appointed governors to rule provinces Spoils financed the govt. 3 level tax system •Muslim (least) •Converts •Non-Muslims (most) Trading Canals + irrigation Mosque Construction •Great Mosque of Damascus •Dome of the Rock Jerusalem Extravagant lifestyles of rulers Persians given secondary status Persian Abbasids revolted and took control Watch Islam Empire of Faith Dome of the Rock/Foundation Stone See page 261 in textbook Umayyad •Location- on Tigris near Euphratesexcellent for trade •Created standard code of law (Shariah) •Complete banking system using checks •Circular city protected by moat •Arcades filled with markets and shops Even more lavish living Some Muslim states separated from Abbasids (Muslim Spain) Fatimids-Sicily and Egypt Seliuq Turks gain control of caliphs (Start of the Crusades) Watch Islam Empire of Faith - Part 2 57 min (Baghdad) Baghdad Abbasid Caliph receiving embassy from Charlemagne Each Branch has Major Shariah – Schools of Theological Law Sunni Schools • Hanafi – Arab Middle East, India, Pakistan, parts of Afghanistan • Maleki – north, central, and west Africa and Egypt • Shafii – East Africa, Indonesia, and Southeast Asia • Hanbali – Saudi Arabia 12th Century school of astronomy and chemistry at Cordoba (Spain) Cordoba-grand city-500 mosques 300 baths70 Libraries •Control 80% by 711 •Invasion of France failed •Charlemagne could not drive Muslims from Spain Literature, Medicine, Law and agriculture Muslim Golden Age711-1492 Jews, Christians, + Muslims lived in peace Watch Islam Empire of Faith part 2 Cordoba Chapter 10 ---109 mins The Christian Reformation • Christianity took 1,500 years of bloodshed to reach its Reformation, including Europe’s Thirty Years’ War (1618-1648) between the Protestant Union and the Catholic League. Between 1/5 to 1/3 of the German population died.