* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Presentation
Sanghyang Adi Buddha wikipedia , lookup
Buddhist ethics wikipedia , lookup
Buddhist art wikipedia , lookup
Buddhism and sexual orientation wikipedia , lookup
Pre-sectarian Buddhism wikipedia , lookup
Triratna Buddhist Community wikipedia , lookup
Enlightenment in Buddhism wikipedia , lookup
History of Buddhism wikipedia , lookup
Buddhism and Western philosophy wikipedia , lookup
Women in Buddhism wikipedia , lookup
Buddhism and Hinduism wikipedia , lookup
History of Buddhism in India wikipedia , lookup
Silk Road transmission of Buddhism wikipedia , lookup
Greco-Buddhism wikipedia , lookup
Buddhism in Myanmar wikipedia , lookup
Decline of Buddhism in the Indian subcontinent wikipedia , lookup
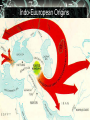
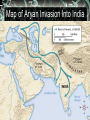
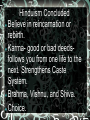
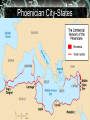
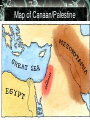
Indo-Europeans Migrate Indo-Europeans were seminomadic people who came from a dry grassland called the steppe. Herded sheep goat and cattle. Historians can tell where these people settles by the language they spoke. Indo-Euuropean Origins Unexpected Migration Migration is the movement of people from one region to another. Lands where animals grazed may have dried up. Human or animal population got too large to feed. Escaping invaders. Hittites Build an Empire Hitties were Indo-Europeans who occupied Anatolia. Rich resources-Timber/minerals Hittite city-states come together and form an empire. Conquer Babylon, but struggle for control of northern Syria. Hittite Empire Hittite Technology/Adaption Borrowed ideas such as government, art, law, politics, and language from the Babylonian. Hittite chariots are light and easy to manuver. First in the region to smelt iron. Chariots Iron Weapons Fall of the Hittites/Rise of Aryans Hittites fall to a wave of invaders from the north in 1190 B.C. Aryans were Indo-Europeans entered the Indus Valley around 1500 B.C. What we know about them comes from their literature. Map of Aryan Invasion Into India Aryans Sacred Literature Caste System Develops Aryans were different in many ways to those already living in this region. Aryans were divided into three social classes. Determine your role. Closer contacts with nonAryans. Caste Syste Caste System Concluded Born into your caste for life. Fourth class- Non-Aryans. Skin color was the distinguishing feature of this system. Ritual purity. Untouchables-Outside the Caste. Aryan Kingdom Arises Aryans extend their power eastward. Chiefs were elected by tribes in the beginning, but minor kings set up territorial kingdoms. Magadha emerges as the major kingdom. Move south. Aryan Kingdoms Mahabharata Reflects the Aryans struggles into Southern India. At 106,000 verses, it is the longest single poem in the world. Violence and confusion leads many to speculate about people and gods in the world. Rise of Hinduism in India As Aryans and non-Aranys intermingled, beliefs blended. People began to question themselves and the world. This mixture produced Hinduism. The religion has no founder. Origins and Beliefs of Hinduism Hinduism is a collection of beliefs that developed over a long period of time. Upanishads are written dialog between teacher and student. Moksha or a state of perfect understanding of all things. Hinduism Concluded Believe in reincarnation or rebirth. Karma- good or bad deedsfollows you from one life to the next. Strengthens Caste System. Brahma, Vishnu, and Shiva. Choice. The World's Soul and its Personalities Jainism Believed everything has a soul and should not be harmed. Founded by Mahavira. Work in trade and commerce. Have not sent out missionaries. Jian Monks Buddhism Siddharata Gautama is the founder of Buddhism. Leaves home at age twentynine to seek enlightenment or wisdom. Achieves an understanding of the cause of pain and suffering. Siddharata Gautama- Buddha Buddhist Beliefs To achieve enlightenment one must follow the Four Noble Truths and master the Eight Fold Path. Goal was to be released from selfishness and pain- nirvana. Rejects Caste system. Hinduism similarities. Buddhist Way to Enlightenment Buddhist Community Three Jewels- Buddhist, non Buddhist, and the Buddha. Reluctantly admitted woman to the religious order. Monks and nuns live life of poverty. Spread their beliefs. Places of learning develop. Sacred Literature of Buddhism Buddhism Concluded Message is spread by missionaries throughout Southeast Asia. Traders play bigger role in spreading the Buddha's message. Does not spread throughout India. Minoans Seafaring people who lived on the island of Create. Capital of Knossos. Civilization is named after King Minos. Athletic people who loved nature. Map of Minoan Civilization Minotaur Minoan's Concluded Great Mother Earth Goddess was worshiped. Bull- leaping. Natural disasters of 1470 B.C. brought this civilization to an end. Phoenicians Sea faring traders from the area of present day Lebanon. Great shipbuilders and seafarers. Never created an empire. City-states were about thirty miles apart from one another. Phoenician City-States Phoenicians Concluded Developed a writing system that used symbols to represent sounds. Modern alphabet. Eastern city-states captured by the Assyrians, Babylonians, and the Persians. Phoenician Alphabet Judaism Beginnings The Area of Palestine called Canaan was home to the Hebrews. Jews. The Philistines were the other people in this area. Canaan was the land God had promised to the Hebrew people. Map of Canaan/Palestine Judaism Continued The Hebrews early history is found in the first five books of the Hebrew Bible-Torah. God chose Abraham to be the father of the Hebrews. Lives in Ur, but is commanded to go to Canaan. Egypt. God of Abraham The Hebrew God is called Yahweh. Believed in one and only one God. Yahweh promise to protect the Hebrews if they obeyed him. Covenant or agreement. Let My People Go Hebrews go to Egypt because of drought and famine. Are enslaved. Moses frees the Hebrews. Delivers Ten Commandments. Second Covenant or agreement. Moses Land and People of the Bible After the death of Moses, Hebrews return to Canaan. Become stable. Organized into twelve tribes and united in times of trouble. God raised judges to unite the tribes in times of trouble Deborah Hebrew Law Hebrew woman's duty was to raise her children. Ten Commandments regulated social and religious behavior. Laws interpreted by messengers-prophets. Ethical monotheism. Kingdom of Israel Hebrews expand north and south. Judah only tribe that remainsJews. Unite under three kings. Kingdom would be called Israel. Three Kings Saul drives the Philistines out of the central hills of Palestine. David unites the tribes, established Jerusalem as the capital, starts a dynasty. Solomon Most powerful of all the kings. Builds great temple.. Saul, David, and Solomon Kingdom Divides Kingdom splits after the death Solomon. High taxes and forced labor. Jews in the northern part of the kingdom revolt. Becomes Judah. Kingdom Conquest Northern kingdom of Israel falls to the Assyrians. Southern kingdom of Judah falls to the Babylonians under Nebuchadnezzar. Persians conquer the Babylonians. Rebuild the Temple.