* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download File
Survey
Document related concepts
Seismic inversion wikipedia , lookup
Post-glacial rebound wikipedia , lookup
Large igneous province wikipedia , lookup
Ionospheric dynamo region wikipedia , lookup
Earthquake engineering wikipedia , lookup
Shear wave splitting wikipedia , lookup
Physical oceanography wikipedia , lookup
Seismic communication wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
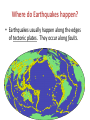
Seismology • Seismology is the branch of science devoted to studying Earthquakes. A seismologist is a scientist who studies earthquakes. Where do Earthquakes happen? • Earthquakes usually happen along the edges of tectonic plates. They occur along faults. What causes Earthquakes? • Plastic deformation (folding, bending) does not cause earthquakes… elastic deformation does. When the rock is stretched too far it will break. The breaking is what causes Earthquakes. Elastic Rebound • Sudden return of elastically deformed rock to its original shape is called elastic rebound. Energy is released and some of it travels as seismic waves. These cause the earthquake. Earthquake zones are places where a large number of faults are located. An examples is the San Andreas fault zone in CA. Earthquakes can happen along any type of plate boundary, and can also happen along faults in the middle of plates. How do earthquake waves travel? • Seismic waves are energy waves that travel through the earth. If they are inside the earth, they are called seismic body waves. • It they are at the earth’s surface, they care called seismic surface waves. • P Waves – Pressure or primary Waves that travel through solids, liquids, and gasses. They are the fastest, so they travel ahead. Moves back and forth. (body) • S Waves – Shear or secondary waves. Cannot travel through liquid and always arrive after P waves. Side to side. (body) • Surface Waves – Cause motion mostly in the upper few KM of earth’s crust. Travel more slowly and are more destructive than body waves. Can move up and down or side to side. Surface Wave