* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download CRS_Ch11 - earthjay science
Survey
Document related concepts
Human impact on the nitrogen cycle wikipedia , lookup
Entomopathogenic nematode wikipedia , lookup
Soil horizon wikipedia , lookup
Canadian system of soil classification wikipedia , lookup
Soil erosion wikipedia , lookup
Surface runoff wikipedia , lookup
Plant nutrition wikipedia , lookup
Soil respiration wikipedia , lookup
Crop rotation wikipedia , lookup
Terra preta wikipedia , lookup
Soil salinity control wikipedia , lookup
Soil compaction (agriculture) wikipedia , lookup
No-till farming wikipedia , lookup
Soil food web wikipedia , lookup
Sustainable agriculture wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
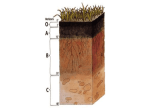
Living with Earth 1st Edition Classroom Response System Questions Chapter 11 © 2011 Pearson Education, Inc. 11.01 Amongst the roles that soil plays in the environment are: A. B. C. D. E. recycling waste. transferring matter among Earth systems. cleaning water. All of the above A and C © 2011 Pearson Education, Inc. 11.01 Amongst the roles that soil plays in the environment are: A. B. C. D. E. recycling waste. transferring matter among Earth systems. cleaning water. All of the above A and C ANSWER: D, [p. 329] © 2011 Pearson Education, Inc. 11.02 Humus is known to be: A. B. C. D. weathered parent material. soil found in the zone of accumulation. organic matter. coarsely chopped up bedrock. © 2011 Pearson Education, Inc. 11.02 Humus is known to be: A. B. C. D. weathered parent material. soil found in the zone of accumulation. organic matter. coarsely chopped up bedrock. ANSWER: C, [p. 333] © 2011 Pearson Education, Inc. 11.03 Why is bacteria in soil critical to its health and fertility? A. Because the bacteria support vegetable growth. B. Because the bacteria fight off diseases that the soil might undertake. C. Because the bacteria eat all of the carbon that can ruin the plants. D. Because the bacteria undergoes photosynthesis which helps the life of the soil. © 2011 Pearson Education, Inc. 11.03 Why is bacteria in soil critical to its health and fertility? A. Because the bacteria support vegetable growth. B. Because the bacteria fight off diseases that the soil might undertake. C. Because the bacteria eat all of the carbon that can ruin the plants. D. Because the bacteria undergoes photosynthesis which helps the life of the soil. ANSWER: A, [p. 340] © 2011 Pearson Education, Inc. 11.04 Soil is most susceptible to erosion __________. A. B. C. D. wherever bacteria exhaust all of the carbon wherever vegetation cover is removed wherever there is too much life in the soil None of the above because soil cannot be eroded © 2011 Pearson Education, Inc. 11.04 Soil is most susceptible to erosion __________. A. B. C. D. wherever bacteria exhaust all of the carbon wherever vegetation cover is removed wherever there is too much life in the soil None of the above because soil cannot be eroded ANSWER: B, [p. 342] © 2011 Pearson Education, Inc. 11.05 Pesticides and herbicides have major effects on: A. B. C. D. E. soil biodiversity. health of small animals, only. quality of water. health of people, animals, and plants. All of the above © 2011 Pearson Education, Inc. 11.05 Pesticides and herbicides have major effects on: A. B. C. D. E. soil biodiversity. health of small animals, only. quality of water. health of people, animals, and plants. All of the above ANSWER: E, [p. 346] © 2011 Pearson Education, Inc.