* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download PP4 (Ch.12-25)DNA
Survey
Document related concepts
Eukaryotic DNA replication wikipedia , lookup
DNA sequencing wikipedia , lookup
Zinc finger nuclease wikipedia , lookup
DNA repair protein XRCC4 wikipedia , lookup
Homologous recombination wikipedia , lookup
DNA profiling wikipedia , lookup
DNA replication wikipedia , lookup
DNA polymerase wikipedia , lookup
Microsatellite wikipedia , lookup
DNA nanotechnology wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
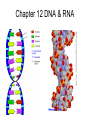
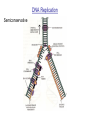
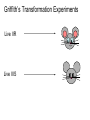
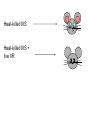
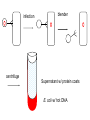
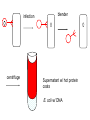
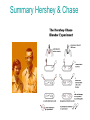
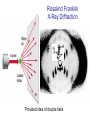
Chapter 12 DNA & RNA DNA’s Structure Purines: A & G - small name big molecule Pyrimadines: T & C - big name small molecule Monomer = building block One Nucleotide is a monomer = nucleic acid + deoxyribose + phosphate (Nitrogenous Base) DNA’s Structure 3’ has OH - hydroxide 5’ has Phosphate Molecule •Directional Structure •Anti-parallel to each other •Always builds 5’ to 3’ •DNA Polymerase can only add to the 3’ end If DNA were synthesized in the 3' to 5' direction, the energy for the process would come from the 5' end of the growing strand rather than from free nucleotides. If the 5' nucleotide needed to be removed this triphosphate end would be lost, losing the energy source required to add a new nucleotide to the end. DNA’s Structure nm = 1 Billionth of a meter DNA Replication Semiconservative Chromosome Structure Key Terms: Histone = the protein Nucleosome = A cluster of histones Chromatin = DNA + Protein in an uncoiled form Chromosome = condensed chromatin Chromatid = each side of a chromosome Centromere = point of attachment of sister chromatids Evidence for DNA as Genetic Material • Griffith - 1928 – transformation • Avery, MacLeod, and McCarty - 1944 – Proves DNA is the transforming agent using enzymes • Hershey & Chase -1952 – Reproves Avery’s evidence using bacteriophage Time Line • • • • • • 1866 Mendel publishes paper 1900 Mendel’s paper rediscovered 1902 chromosome theory of inheritance 1905 the term “genetics” coined 1950 base pairing discovered 1953 Watson & Crick deduce the structure of DNA Griffith’s Transformation Experiments • Diplococcus pneumoniae – two strains: IIR & IIIS – two differences in genotype • R = rough, avirulent; S = smooth, virulent Griffith’s Transformation Experiments Live IIR Live IIIS Heat-killed IIIS Heat-killed IIIS + live IIR Live IIR Heat-killed IIIS Live IIR Heat-killed IIIS Explanations? • IIR cells mutated to S? • Serotype was changing • IIR were changing into IIIS • 2 mutations? • Only happened when IIR and dead IIIS mixed • Non-living component of IIIS cells changing genetics of IIR cells Avery, MacLeod and McCarty heat-killed IIIS + IIR removed polysaccharide coat heat-killed IIIS + IIR removed protein Avery, MacLeod and McCarty heat-killed IIIS + IIR removed RNA heat-killed IIIS + IIR removed DNA Avery, MacLeod and McCarty • DNA is the transforming principle • DNA could change IIR bacteria into IIIS – Now know bacteria may pick up pieces of exogenous DNA and incorporate them into their own chromosomes = transformation Hershey and Chase • Studied bacteriophage – virus which attacks E. coli • Ran two side-by-side studies – labeled DNA of phage w/ 32P in one study – labeled protein of phage w/ 35S in second • In which study does radioactivity end up in E. coli? 32P labeled DNA 35S labeled protein Hershey and Chase • • • • • Mix phage and bacteria Allow infection Shear off what’s on outside - blender Centrifuge Look for radioactivity in pellet (bacteria) infection blender centrifuge Supernatant w/ protein coats E. coli w/ hot DNA infection centrifuge blender Supernatant w/ hot protein coats E. coli w/ DNA Summary Hershey & Chase Chargaff’s Rules 1947 Provided base pairing and hydrogen bonding Rosalind Franklin 1920-1958 (1951) Rosalind Franklin X-Ray Diffraction Provided idea of double helix Nobel Prize (1962) Made Model 1953 Frederick Wilkins James Watson Francis Crick