* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Evolution-Part2
Behavioural genetics wikipedia , lookup
Koinophilia wikipedia , lookup
Quantitative trait locus wikipedia , lookup
Epigenetics wikipedia , lookup
Behavioral epigenetics wikipedia , lookup
Non-coding DNA wikipedia , lookup
Vectors in gene therapy wikipedia , lookup
Therapeutic gene modulation wikipedia , lookup
Polymorphism (biology) wikipedia , lookup
Heritability of IQ wikipedia , lookup
Genetic testing wikipedia , lookup
Site-specific recombinase technology wikipedia , lookup
Group selection wikipedia , lookup
Public health genomics wikipedia , lookup
Artificial gene synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Deoxyribozyme wikipedia , lookup
Nutriepigenomics wikipedia , lookup
Genetic drift wikipedia , lookup
Genome (book) wikipedia , lookup
Designer baby wikipedia , lookup
Gene expression programming wikipedia , lookup
Human genetic variation wikipedia , lookup
Genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
History of genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
Natural Selection
Variation
Natural Selection
Variation
Heredity
Natural Selection
Variation
Heredity
Differential Survival
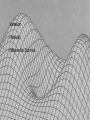
Fitness Landscape
Sewell Wright
(1899-1988)
4
Multi-dimensional spaces
{x,y,z}
Generalize to:
{x,y,z,a,b,c,d,e}
Multi-dimensional spaces
{x,y,z}
Generalize to:
{x,y,z,a,b,c,d,e}
Show K-means model
Fisher’s Fundamental Theorem
Ronald Fisher
(1890-1962)
R. A. Fisher's so-called fundamental theorem of natural selection:
"The rate of increase in fitness of any organism at any time is equal to its genetic variance in fitness at that time."[1]
Or, in more modern terminology:
"The rate of increase in the mean fitness of any organism at any time ascribable to natural selection acting through
changes in gene frequencies is exactly equal to its genetic variance in fitness at that time".[2]
7
Information and Matter
Natural history
Evolvability
Modularity: Evo Devo
Evolution of Cooperation/Eusociality
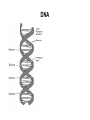
DNA
DNA
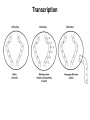
Transcription
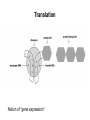
Translation
Notion of “gene expression”
Epigenetics
From Wikipedia:
“Epigenetics is the study of heritable changes in gene
expression or cellular phenotype caused by mechanisms
other than changes in the underlying DNA sequence.”
http://www.pbs.org/wgbh/nova/body/epigenetics.html
Is epigenetics why cloned animals don’t fare well?
Genetic regulation
Genetic Switches (in “non-expressed” regions)
Lac Operon
http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=oBwtxdI1zvk
Genetic Regulatory Networks
Random Boolean Networks
as models of genetic regulatory networks