* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Mendelian Genetics 4
Genetically modified crops wikipedia , lookup
Fetal origins hypothesis wikipedia , lookup
Gene therapy wikipedia , lookup
Medical genetics wikipedia , lookup
Polycomb Group Proteins and Cancer wikipedia , lookup
Gene desert wikipedia , lookup
Pharmacogenomics wikipedia , lookup
Pathogenomics wikipedia , lookup
Essential gene wikipedia , lookup
Population genetics wikipedia , lookup
Human genetic variation wikipedia , lookup
X-inactivation wikipedia , lookup
Epigenetics of neurodegenerative diseases wikipedia , lookup
Site-specific recombinase technology wikipedia , lookup
Dominance (genetics) wikipedia , lookup
Genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
Nutriepigenomics wikipedia , lookup
Genome evolution wikipedia , lookup
Genomic imprinting wikipedia , lookup
Behavioural genetics wikipedia , lookup
Ridge (biology) wikipedia , lookup
Gene expression programming wikipedia , lookup
Minimal genome wikipedia , lookup
Artificial gene synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Heritability of IQ wikipedia , lookup
History of genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
Epigenetics of human development wikipedia , lookup
Gene expression profiling wikipedia , lookup
Public health genomics wikipedia , lookup
Microevolution wikipedia , lookup
Quantitative trait locus wikipedia , lookup
Designer baby wikipedia , lookup
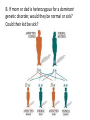
Finishing Up Mendelian Genetics AIM: How can our genes affect our health and how can the environment affect our genes? DO NOW: Handout HOMEWORK: Review sheet TEST ON TUESDAY, 2/15/11 Do Now 1. Which of the following crosses can never produce a child with blood type O? a) O x AB b) A x B c) A x O d) O x O Do Now 2. In squirrels, the gene for gray fur (G) is dominant over the gene for black fur (g). If 50% of a large litter of squirrels are gray, the parental cross that produced this litter was most likely a) GG x Gg b) GG x GG c) Gg x gg d) gg x gg Do Now 3. Some individuals with blood group A may inherit the genes for blond hair, while other individuals with blood group A may inherit the genes for brown hair. This can be explained by the principle of a) dominance b) multiple alleles c) independent assortment d) incomplete dominance I. Genetic Disorders What’s another way to say “two recessive traits”? A. If mom or dad is heterozygous for a recessive genetic disorder, would they be normal or sick? What would their kid be? Carriers – a parent that is heterozygous for a recessive genetic disorder B. If mom or dad is heterozygous for a dominant genetic disorder, would they be normal or sick? Could their kid be sick? 1. Huntington’s disease affects the nervous system and causes a gradual loss of brain function, uncontrollable movements, and emotional disturbances. There is no cure. Stop and think! Are there any carriers in dominant genetic disorders? Huntington’s Disease II. Sex-Linked Traits What genotype makes an organism male? What genotype makes an organism female? XY XX A. Men only get one X chromosome. If there happens to be a recessive gene on the X, men don’t have a dominant gene that can cancel it out. They are going to express it. B. Females have a far greater chance of having a dominant gene to hide the recessive one. C. Sex-linked traits – traits carried by either the X or the Y chromosome D. Sex-linked trait example: Color Blindness Color blindness is a gene located on the X-chromosome. Who would be more likely to be affected by this gene? Men or women? E. Sex-linked trait example: Hemophilia 1. Hemophilia – characterized by really slow clotting of the blood III. Polygenic Traits A. Most traits are the result of the action of many genes (One trait = many genes). ex. Skin color, hair color, and height depend upon the interaction of many independent genes. B. Polygenic traits are controlled by two or more genes. 1. They show a wide range of phenotypes III. Environmental Influences on Heredity Your genes are not the final answer! A. There is so much that can be influenced by the environment, including nutrition, exercise, and where you live. B. Genes + Environment = Phenotype Analyze the phrase, “Heredity loads the gun, but environment pulls the trigger” Ex. Diseases like diabetes or ulcers may be in a genetic code, but may never be seen in the phenotype if the person leads a healthy lifestyle. SUMMARY How can our genes affect our health? Give at least 3 examples. They can be from any class on genetics! How can the environment affect our genes? Give 3 examples (at least one not from class). Complete the summary worksheet