* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download CHANGES IN DNA CAN PRODUCE VARIATIONS
Zinc finger nuclease wikipedia , lookup
United Kingdom National DNA Database wikipedia , lookup
Mitochondrial DNA wikipedia , lookup
Genetic code wikipedia , lookup
Population genetics wikipedia , lookup
Polycomb Group Proteins and Cancer wikipedia , lookup
Genealogical DNA test wikipedia , lookup
Nutriepigenomics wikipedia , lookup
Epigenomics wikipedia , lookup
Molecular cloning wikipedia , lookup
Primary transcript wikipedia , lookup
DNA supercoil wikipedia , lookup
Nucleic acid double helix wikipedia , lookup
DNA vaccination wikipedia , lookup
DNA damage theory of aging wikipedia , lookup
No-SCAR (Scarless Cas9 Assisted Recombineering) Genome Editing wikipedia , lookup
Nucleic acid analogue wikipedia , lookup
Genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
Cancer epigenetics wikipedia , lookup
Microsatellite wikipedia , lookup
Site-specific recombinase technology wikipedia , lookup
Cre-Lox recombination wikipedia , lookup
Genome (book) wikipedia , lookup
Non-coding DNA wikipedia , lookup
Therapeutic gene modulation wikipedia , lookup
Extrachromosomal DNA wikipedia , lookup
Genome editing wikipedia , lookup
Designer baby wikipedia , lookup
Deoxyribozyme wikipedia , lookup
Cell-free fetal DNA wikipedia , lookup
Helitron (biology) wikipedia , lookup
Oncogenomics wikipedia , lookup
Artificial gene synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Frameshift mutation wikipedia , lookup
Vectors in gene therapy wikipedia , lookup
History of genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
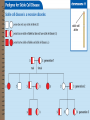
CHANGES IN DNA CAN PRODUCE VARIATIONS • DNA sequences can change (mutation) • Mutations can cause genetic disorders (like sickle cell anemia & cystic fibrosis) • Cancer is a genetic disorder that affects the cell cycle DNA sequence can change • Each human cell, with 46 chromosomes, has 6 billion base pairs in its DNA. • 99.9% of DNA in cells of 2 different humans is same. Just 0.1% variation in DNA makes you unique & different from others. (about 1 base in every thousand). • Only 5% of the billions of base pairs of DNA are in the GENES that code for RNA and proteins Differences in genes affect height, color of eyes, hair, skin, etc. Skin color comes from protein (melanin). The more melanin their skin cells are programmed to make, the darker their skin color DNA sequence can change • Exposure to ultraviolet radiation, x-rays, & toxins can damage DNA. Any change in DNA is called a MUTATION. • Cells have different ways to repair mistakes (through enzymes). • If a mutation occurs in a gene (the 5% of DNA that’s the coding region) the wrong amino acid may be placed in the amino-acid chain. 3 possible outcomes if mutation occurs in a gene (coding region) • MUTATION CAUSES NO EFFECT: there are 2 sets of DNA (1 from each parent) so if 1 gene isn’t working, the other may still code for enough of the protein to let the cell function normally • EFFECT OF MUTATION IS MINOR: a change in the genes may only produce a slight change in appearance (the amount of melanin produced for skin or hair color) Possible outcome if mutation occurs in coding region of DNA • EFFECT OF MUTATION IS GREAT: can be good (plant has increased resistance to disease) or bad, causing genetic disorder or disease. • If mutation occurs in the 95% of DNA that doesn’t code , no effect will occur; it is neutral MUTATIONS CAN CAUSE GENETIC DISORDERS • Genetic disorder results from mutations that affect the normal functioning of a cell. • Some are inherited (passed on from parent to offspring; like Tay-Sachs, Sickle-cell , and cystic fibrosis) • Others are results from mutations within a person’s own lifetime (cancers) • Sometimes a “tendency” for getting a disease (like diabetes, glaucoma, alzheimers) is inherited and a person’s behavior can bring on or prevent the disease. GENETIC DISORDERS • Sickle Cell disease occurs from a mutation where one amino acid is replaced by another. Since it is recessive, both alleles must be inherited to cause it (abnormally shaped red blood cell decreasing oxygen and damaging tissue). • Sickle cell protects against malaria, so allows people to survive with it and pass it on (occurs in Africa, parts of India and Middle East). • A PEDIGREE (diagram of family relationships that include 2 or more generations) can show how the sickle cell allele is passed on through generations of a family. Cancer is a genetic disorder that affects the cell cycle • Cancer is a group of disorders, all characterized by uncontrolled division of cells. • Cancer cells spread quickly & invade other tissues; become “immortal” dividing indefinitelywhile normal cells have a definite life span and die. • Most cancers due to mutations to DNA over a person’s life. Some from mistakes during replication, but many from harmful chemicals (carcinogens). • Cancer involves series of mutations; some people inherit 1 step in the series or a “tendency” for it.