* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Important Genetic Disorders
Survey
Document related concepts
Medical genetics wikipedia , lookup
Tay–Sachs disease wikipedia , lookup
Dominance (genetics) wikipedia , lookup
Cell-free fetal DNA wikipedia , lookup
Polycomb Group Proteins and Cancer wikipedia , lookup
Neuronal ceroid lipofuscinosis wikipedia , lookup
Epigenetics of neurodegenerative diseases wikipedia , lookup
Genome (book) wikipedia , lookup
Skewed X-inactivation wikipedia , lookup
Y chromosome wikipedia , lookup
X-inactivation wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
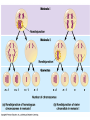
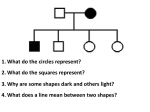
Important Genetic Disorders Bio Definitions • Autosomes- any chromosome that is not a sex chromosome. Not the “X” or “Y” • Sex-linked- genes located on the sex chromosome. Usually on the “X” • Nondisjunction- A chromosome mishap in meiosis A Karyotype is a photograph of the chromosomes of a single cell. Another view Huntington’s Disease • Symptoms: Gradual Brain tissue loss in middle age. • Defect: Inhibitor of brain cell metabolism • Autosomal/somatic dominate • 1/10,000 Cystic Fibrosis • Symptoms: Mucus clogs lungs, liver, pancreas • Defect: Failure of chloride ion transport mechanism • Autosomal recessive • 1/2080 whites most common disorder Sickle Cell Anemia • Symptoms: impaired blood circulation, organ damage • Defect: Abnormal hemoglobin molecules – RBC’s • Autosomal Recessive • 1/500 African Americans -If heterozygous will not get malaria Tay-Sachs Disease • Symtoms: deterioration of CNS in infancy. • Defect: Defective form of enzyme hexosaminidase A (Hex A) • Autosomal recessive • 1/1600 Jews of European desent Phenylketonuria (PKU) • Symptoms: Failure of brain to develop in infancy; if untreated causes death. • Defect: defective form of enzyme phenylalanine hydroxylase • Autosomal recessive • 1/18,000 urine test, treated by diet until puberty. Hemophilia • Symptoms: failure of blood to clot • Defect: defective form of blood-clotting agent. • X-linked recessive • 1/7,000 Muscular Dystrophy • Symptoms: wasting away of muscles; short life expectancy • Defect: muscle fiber degenerate • X-linked recessive • 1/10,000 “Jerry’s Kids” Down’s Syndrome • Symtoms: Mental retardation with abnormal physical features. • Defect: extra “X” chromosome • Non-disjunction of the 21st pair of chromosomes • Somatic chromosome • Also called Trisomy 21 Klinefelter’s • Symptoms: only in males, sterile, do not develop 2nd sex characteristics. Below normal intelligence • Defect: extra “X” in 23 pair of chromosomes • Meiosis error- genotype XXY Turner’s • Symptoms: only in females, appear normal at birth, become stockier & shorter than other females- large necks, sex organs & breasts do not develop- sterile • Defect: missing “X” chromosome in 23rd pair • Non-disjunction of sex chromosome • Genotype XO