* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Meiosis and Genetics
X-inactivation wikipedia , lookup
Heritability of IQ wikipedia , lookup
Site-specific recombinase technology wikipedia , lookup
Public health genomics wikipedia , lookup
Pathogenomics wikipedia , lookup
Neocentromere wikipedia , lookup
History of genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
Hybrid (biology) wikipedia , lookup
Gene expression programming wikipedia , lookup
Nutriepigenomics wikipedia , lookup
Ridge (biology) wikipedia , lookup
Genome evolution wikipedia , lookup
Artificial gene synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Minimal genome wikipedia , lookup
Genome (book) wikipedia , lookup
Epigenetics of human development wikipedia , lookup
Gene expression profiling wikipedia , lookup
Genomic imprinting wikipedia , lookup
Designer baby wikipedia , lookup
Quantitative trait locus wikipedia , lookup
Biology and consumer behaviour wikipedia , lookup
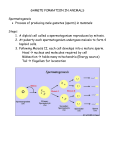
Meiosis and Genetics: • B = no baldness, b = bald. Segregation actually happens here during anaphase of meiosis I •What are the diploid and haploid numbers for this imaginary organism? Diploid (2n) = 2 Haploid (n) = 1 •Explain how this diagram of meiosis could relate to Mendel’s idea that two “factors” must control a trait. An individual has two genes or as Mendel called them “factors” for a trait. Each gene was inherited from a parent (in this case B and b). •How does this diagram relate to the law of segregation? When this individual makes gametes the alleles B and b must segregate into separate gametes. Genes are assorted randomly to gametes – assortment depends on how homologous pairs align in metaphase of meiosis I, alignment of maternal and paternal chromosomes is random