* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Daughter cells are
Non-coding DNA wikipedia , lookup
Artificial gene synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Polycomb Group Proteins and Cancer wikipedia , lookup
Nucleic acid analogue wikipedia , lookup
Cell-free fetal DNA wikipedia , lookup
Population genetics wikipedia , lookup
Designer baby wikipedia , lookup
Site-specific recombinase technology wikipedia , lookup
Cre-Lox recombination wikipedia , lookup
Extrachromosomal DNA wikipedia , lookup
No-SCAR (Scarless Cas9 Assisted Recombineering) Genome Editing wikipedia , lookup
Neocentromere wikipedia , lookup
Primary transcript wikipedia , lookup
Deoxyribozyme wikipedia , lookup
Genome (book) wikipedia , lookup
X-inactivation wikipedia , lookup
Genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
Vectors in gene therapy wikipedia , lookup
Point mutation wikipedia , lookup
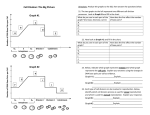
Heredity Asexual & Sexual Reproduction RNA & DNA Mitosis & Meiosis Genetics Asexual & Sexual Reproduction • Asexual Reproduction: – Only involves single parent cell – No variation – Very rapid – 4 types: • • • • Budding Vegetative propagation Spore formation Binary fission Sexual Reproduction • • • • Female gamete – egg (ovum) Male gamete – sperm (spermatozoan) Fertilization = joining of sperm and egg Fertilized egg called zygote (then embryo, then fetus) • Know these terms for plants: – Pollen, stamen, pistil, seed, ovary, fruit, germination DNA & RNA • Building block of DNA/RNA = nucleotide (see diagram) • DNA: ATCG • RNA: AUCG • Structure of DNA: double helix (see diagram) • Complementary base pairing DNA • Replication • Transcription • Translation Mitosis • Interphase • Mitosis – Prophase – Metaphase – Anaphase – Telophase Identify the Stages of Mitosis Meiosis Meiosis • Reduction division Mitosis # divisions # daughter cells Chromosome # in daughters Daughter cells are Purpose Meiosis Genetics • • • • • • • • Dominant Recessive Codominance Incomplete Dominance Genotype Phenotype Heterozygous Homozygous Punnet Squares • Homozygous tall X Homozygous short Punnet Squares • Homozygous tall X Heterozygous tall Punnet Squares • Heterozygous tall X Heterozygous tall Genetic Engineering • Mutation is the ultimate source of variation • Gene splicing (transformation) – DNA from one organism is transferred into another Genetic Diseases • • • • Mutation – change in the DNA sequence Point mutations Frame shift mutations Chromosome mutations – Deletions, insertions, inversions, translocations, nondisjunction Genetic Diseases • Phenylketonuria (PKU) • Cystic Fibrosis • Huntington’s • Hemophilia • Color blindness • Which type of compound is NOT part of DNA? – Deoxyribose; nitrogen base; phosphate; protein • Color blindness results form the expression of a single recessive sex-linked allele. Therefore, the disorder occurs in males when the allele is – Missing on both the X & Y; present on both the X & Y; present on the X; present only on the Y • In humans, brown eyes, B, are dominant to blue eyes, b. What is the genotype and phenotype of a person who is heterozygous for this trait? – bb blue; Bb brown; Bb blue; BB brown • Which represents mitosis? – Sexual cellular reproduction; the division of genetic material of a cell to produce a zygote; the splitting of a cell to produced 2 daughter cells identical to the parent; the splitting of a cell to produce 2 gametes with ½ the chromosome number as the parent • Which is an advantage of sexual reproduction over asexual reproduction? – Fewer opportunities for genetic errors occur, thereby ensuring a more durable population; sexual reproduction eliminates the need for more than one organism if reproduction is to occur; species using sexual reproduction will be better assured of the ability to adapt to changing environmental conditions; the genetic material of the parent will be copied exactly • Which of the following would NOT result in an abnormality in offspring? – Extra chromosomes in a gamete; failure of chromatids to separate; formation of a polar body during gamete production; genetic mutation • Gregor Mendel, in his study of the characteristics of pea plants, developed an understanding of the role of hereditary expression of plant traits. His work led to the development of the branch of biology called – Botany; genetics; microbiology; plant physiology • If a human cell reproduces itself through mitosis, what is the correct number of chromosome PAIRS present in each daughter cell? – 12; 23; 46; 92 • What structure contains both the genetic material for a new plant and a stored food supply? – Fruit; pistil; seed; spores • A bee aids in the assurance of genetic variation of flowering plants by contributing to the process of – Cross pollination; germination; self pollination; vegetative propagation • During which phase of mitosis do the chromosomes divide and move to opposite poles of the cell? – Prophase; metaphase; anaphase; telophase • A zygote is produced from which of the following processes? – Fertilization; germination; meiosis; mitosis • Choose the best definition form ovum. – A cell produced by the union of male and female sex cells; a female sex cell; a male sex cell; the organ responsible for the production of reproductive cells • One strand of DNA has the following arrangement of nucleotides: ACTGA. What would be the nucleotide arrangement on the complementary strand? • Which of the following disorders is NOT a result of a genetic abnormality? – Down Syndrome; hemophilia; pneumonia; sickle cell anemia • Which of the following is the male structure of a flower? – Pistil; ovary; stigma; stamen • Meiosis results in the formation of – Cells with a haploid number of chromosomes; cells with a diploid number of chromosomes; cells with the same number of chromosomes as the parent cell; cells with only one chromosome