* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download chromosome - Rossignols.net
Survey
Document related concepts
Epigenetics of human development wikipedia , lookup
Site-specific recombinase technology wikipedia , lookup
Gene therapy of the human retina wikipedia , lookup
Y chromosome wikipedia , lookup
Epigenetics in stem-cell differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Microevolution wikipedia , lookup
Artificial gene synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Designer baby wikipedia , lookup
Polycomb Group Proteins and Cancer wikipedia , lookup
Vectors in gene therapy wikipedia , lookup
X-inactivation wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
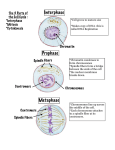
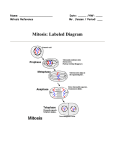
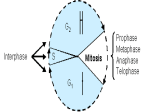
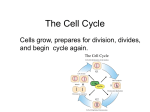
Cell Division: MITOSIS Genes and Chromosomes • Humans have 46 chromosomes in all body cells (somatic cells) • You have 23 pairs of homologous chromosomes – The two chromosomes in the pair look similar and contain genes which affect the same characteristics (2 different alleles) • All of your somatic cells are diploid—they have chromosomes which are in homologous pairs • Some cells don’t have any DNA at all – Red blood cells Anatomy of a Chromosome Check your Understanding • • • • • • • • How many chromosomes do human cells have? How many pairs of chromosomes do human cells have? What are somatic cells? You have one gene for blue eyes and one gene for brown eyes. – Where did these genes come from? – What are the 2 forms of this gene called? What does diploid mean? What are the two halves of a single chromosome called? What structure holds the chromatids together? What is a gene? How Eukaryotic Cells Divide • Cell spends most of its time in interphase –not dividing, just doing its job – DNA is stretched out into long, thin chromatin strands • Before division, each chromosome is copied exactly—replication • Nucleus divides and each daughter cell gets a full set of chromosomes – This is called mitosis Stages of Mitosis • Prophase – Chromosomes become visible as they coil up and get shorter and thicker – Nuclear membrane disappears – Centrioles move to opposite sides of the cell – Spindle fibers appear and shoot out from centrioles • Metaphase – Chromosomes line up in center of cell – Spindle fibers attach to each chromosome • Anaphase – Sister chromatids are pulled apart – Chromatids are reeled to opposite sides of the cell by spindle fibers • Telophase – Nuclear membrane appears around each set of chromosomes – Chromosomes unwind and go back to being chromatin Cytokinesis • Whole cell divides in half • Each daughter cell has an exact duplicate of the DNA • Each daughter cell has 46 chromosomes • Each daughter cell is diploid—23 pairs of chromosomes Check your Understanding • How are the terms DNA, chromatin, chromosome, and genes related? • What is the name of the process by which DNA is copied? • Name, in order, the 6 stages of the cell cycle, starting with the phase cells are in most of the time • Name the phase of the cell cycle where: – – – – – – Chromosomes line up in the middle of the cell Chromosomes first become visible Spindle fibers first appear Spindle fibers attach to sister chromatids Centrioles move to opposite sides of the cell Sister chromatids get pulled apart Still checking… – – – – Nuclear membrane disappears Nuclear membrane reappears Entire cell divides in half No chromosomes are visible • How many daughter cells are created from one parent cell? – How many chromosomes does each daughter cell have? – How many pairs of chromosomes does each daughter cell have? – What is the ploidy of the daughter cells? 1: interphase 2: late interphase / beginning prophase 3: early prophase 4: mid prophase 5: late prophase 6: metaphase 7: late metaphase / early anaphase 8: anaphase 9: early telophase 10: late telophase / cytokinesis VOCABULARY TERMS Somatic Homologous Alleles Diploid Centromere Gene Chromatid chromosome Interphase Chromatin Replication Daughter cells Mitosis cytokinesis