* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Hereditary Traits and Pedigrees
Pharmacogenomics wikipedia , lookup
Vectors in gene therapy wikipedia , lookup
Gene therapy of the human retina wikipedia , lookup
Neuronal ceroid lipofuscinosis wikipedia , lookup
History of genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
Genome evolution wikipedia , lookup
Genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
Nutriepigenomics wikipedia , lookup
Therapeutic gene modulation wikipedia , lookup
Epigenetics of human development wikipedia , lookup
Hardy–Weinberg principle wikipedia , lookup
Site-specific recombinase technology wikipedia , lookup
Gene therapy wikipedia , lookup
Gene expression profiling wikipedia , lookup
Public health genomics wikipedia , lookup
Skewed X-inactivation wikipedia , lookup
Gene desert wikipedia , lookup
Gene nomenclature wikipedia , lookup
Genomic imprinting wikipedia , lookup
Neocentromere wikipedia , lookup
Dominance (genetics) wikipedia , lookup
Saethre–Chotzen syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Quantitative trait locus wikipedia , lookup
Y chromosome wikipedia , lookup
Gene expression programming wikipedia , lookup
Artificial gene synthesis wikipedia , lookup
X-inactivation wikipedia , lookup
Microevolution wikipedia , lookup
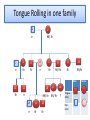
Pedigree Charts • Pedigree charts allow us to work out: – Which traits are recessive and which are dominant – The genotypes of individuals • we can see the phenotype, e.g. whether someone can roll their tongue or not, but not always the underlying genotype. – E.g. Tongue rolling is a dominant gene • The tongue rolling phenotype has two possible genotypes- RR and Rr • There non-rolling phenotype has only one possible genotype- rr. • Where do we need to dig deeper to find the genotype? Tongue Rolling in one family 1 2 rr RR/ Rr 7 3 4 8 5 9 6 rr Rr Rr rr Rr RR/ Rr Rr 10 RR/Rr Male 11 12 16 Rr rr RR/ Rr 13 14 15 rr Rr Rr 17 RR/ Rr 18 ? Tongue roller Nonroller Female Sex-linked traits • The chromosomes which determine sex are of uneven length. • The X chromosome contains many more genes than the Y chromosome. These chromosomes code for sex but also for other characteristics • For a female child (XX), genetic inheritance from this chromosome follows a normal pattern- one allele from mother and one from father. • For a male child (XY) the genetic inheritance is different. Here there are many genes only encoded on the X chromosome, so the male child will inherit the mother’s gene, with none from the male. • About 50 known diseases are inherited this way (eg. Haemophaelia) Haemophaelia • Haemophaelia is carried only on the X gene, and it is recessive • For a female child, an X will be inherited from mother and an X from father. Even if one chromosome carries the gene for haemophaelia, it will be overridden by normal blood clotting gene from the other parent (genotype XHXh). • As a result it is unlikely for a female to suffer from haemophaelia, but she can carry the disease • For a male child, and X will be inherited from the mother and Y from the father. The Y does not have a gene coding for blood clotting, so the male child takes on the gene of the mother. A male with haemophaelia has genotype XhY • If the mother is a carrier, XHXh, what is the chance of her son having haemophaelia? • If a female was a haemophaelia sufferer, what would the genotypes of her parents be?