* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download LS ch. 8 surgeon_brooks
Gene therapy of the human retina wikipedia , lookup
Epigenetics of neurodegenerative diseases wikipedia , lookup
Genetic testing wikipedia , lookup
Genetic code wikipedia , lookup
Neuronal ceroid lipofuscinosis wikipedia , lookup
Genome evolution wikipedia , lookup
Hybrid (biology) wikipedia , lookup
Human–animal hybrid wikipedia , lookup
Site-specific recombinase technology wikipedia , lookup
Human genetic variation wikipedia , lookup
Quantitative trait locus wikipedia , lookup
Tay–Sachs disease wikipedia , lookup
Oncogenomics wikipedia , lookup
Koinophilia wikipedia , lookup
Public health genomics wikipedia , lookup
Heritability of IQ wikipedia , lookup
Behavioural genetics wikipedia , lookup
Medical genetics wikipedia , lookup
Population genetics wikipedia , lookup
History of genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
Genome (book) wikipedia , lookup
Genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
Designer baby wikipedia , lookup
Frameshift mutation wikipedia , lookup
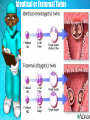
Surgeon Brooks Your Subtitle Goes Here Genetic Changes Life Science Chapter 8 Mutations 1. Mutation = any change in genetic material. Example: Albinism - pigment 2. Mutations happen any time, randomly 3. Mutations are mostly harmful 4. Lethal mutations – cause death before or after birth Albinism Types of Mutations 1. Gene Mutation = changes in the sequence of bases A. Produces wrong code in RNA B. Sometimes no effect – eye color mutates in a skin cell C. Sometimes minor effect – mole D. Sometimes lethal E. Example of a screw falling into a clock! Somatic & Germ mutations 1. Somatic Mutation = mutation in a body cell - cells that do not make gametes 2. Germ Mutation = occur in gametes or cells that form gametes A. Do not effect organism, but can effect offspring B. Most are recessive C. After several generations, possible to get mutated trait Chromosomal Changes 1. Defined: mutation involving the number of chromosomes. 2. Small or large effect on organism 3. 2 set of chromosomes = diploid 4. Unusual number = ploidy mutations 5. Down’s syndrome = ploidy mutation. They have three sets on the 21st chromosomes. (47 instead of 46) Down’s Syndrome Seedless Watermelon Japan’s Square watermelon? Facets of Genetics: Human Disorders 1. Carrier = has gene but does not express the trait 2. Queen Victoria & hemophilia =bleeder’s disease, found in 1 in 10,000 males (sexlinked) 3. Duchene = type of muscular dystrophy (sex-linked) 4. Cystic Fibrosis = affects mucous and sweat glands (recessive) 5. Tay Sachs =lack enzyme that breaks down fatty substances (recessive) 6. Malignant hyperthermia – high fever under anestheia (dominant gene) 7. Achondroplasia = arms and legs do not grow properly (dominant) Tay Sachs Disease Malignant Hyperthermia Scientist experiment on a dog to help humans Duchene’s Disease Cystic Fibrosis 8B Applied Genetics 1. Some produce unusual traits that are beneficial 2. We then will breed to preserve the trait 3. Example Ancon sheep & Mink Mink Ancon Sheep Your subtopic goes here Applied Genetics 1. Selection – Jacob’s flock in OT A. Selective breeding Breed selected traits (plants – corn example, p.114) B. Inbreeding is mating an organism with its close relatives – goal is for pure breed with desirable traits (Animal – chickens, Plant = selfpollination) C. Many new breeds began from plants or animals that mutated Cross Breeding 1.Involves breeding individuals with different traits to produce offspring different from both parents 2. Hybrid vigor = offspring stronger than parents. 3. Hybrids produce different offspring 4. Takes many years to get hybrids to produce offspring alike (ex: shorthorn cattle – good meat, Brahams cattle – like cold) 5. Sometimes with breed organisms from different groups a) doesn’t work with animals b) successful w/ plants (tangelos) Tangerine + Grapefruit = Tangelo The New Genetics 1. Genetic engineering = use of special techniques to control the genetic makeup We… A. Isolate genes and transfer them to other cells B. create super crops like frost resistant tomatoes C. could form a disease that could destroy many things Tomatoes…. Human Genetic Engineering 1. Human genetics – 2 views A. We are made in the image of God, precious creation. B. We have the God-given ability to learn and direct our lives. 2. Not good or bad alone 3. Is science qualified to answer the moral questions that genetic engineering raises? 4. Would a genetically engineered human race solve our problems? Facets of Genetics 1. Human Genome Project = map all human genes! We did it! 2. Identical twins = sperm + ovule = zygote. Zygote then divides and forms two identical individuals. (Clones) 3. Fraternal Twins = 2 sperm + 2 ovules = 2 zygotes. Born at the same time but genetically different. Can be 2 girls or 2 boys, or one of each! Identical or Fraternal Twins Identical Twins Identical Twins Your subtopic goes here Fraternal Twins Your Topic Goes Here Your subtopic goes here Transitional Page Transitional Page Your Topic Goes Here Your subtopic goes here Your Topic Goes Here Your subtopic goes here Elements www.animationfactory.com