* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download What is Genetic Testing?
Site-specific recombinase technology wikipedia , lookup
Artificial gene synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Cell-free fetal DNA wikipedia , lookup
Neuronal ceroid lipofuscinosis wikipedia , lookup
Heritability of IQ wikipedia , lookup
Human genetic variation wikipedia , lookup
Frameshift mutation wikipedia , lookup
Oncogenomics wikipedia , lookup
Gene therapy wikipedia , lookup
Epigenetics of neurodegenerative diseases wikipedia , lookup
Population genetics wikipedia , lookup
Point mutation wikipedia , lookup
History of genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
Pharmacogenomics wikipedia , lookup
Genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
DNA paternity testing wikipedia , lookup
Genealogical DNA test wikipedia , lookup
Medical genetics wikipedia , lookup
Designer baby wikipedia , lookup
Genome (book) wikipedia , lookup
Microevolution wikipedia , lookup
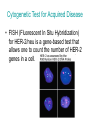
What is Genetic Testing? And what is its value? Sherri J. Bale, Ph.D., FACMG President and Clinical Director GeneDx Definition of Genetic Testing: • The analysis of human DNA in any of its forms or related products (chromosomes, RNA, proteins) Uses of Genetic Testing: • To detect disease-related genotypes, mutations, phenotypes, or karyotypes for clinical purposes More definitions • Genotype vs. Phenotype – The genetic make-up, as distinguished from the physical appearance • Mutation – A genetic change, usually one that is associated with a disease • Karyotype – A visual presentation of chromosomes Two Main Types of Genetic Tests • Constitutional – Tests for mutations that affect ALL CELLS in the body, and have been there since conception • Acquired – Tests for changes that affect only certain cells or cell types in the body, and that occurred later in life Genetic Tests for Constitutional Mutations • Molecular Tests • Cytogenetic Tests • Biochemical Tests Molecular Test: Example • Analysis of DNA sequence in patient with a rare inherited disease – Muscular Dystrophy – Gene: DMD – Clinical Picture • 1 in 3500 male births • progressive muscle weakness starting in early childhood • wheelchair by age 12 • death in 20s Molecular Test: Muscular Dystrophy • Obtain blood sample from child • Read the DNA sequence of the DMD gene • Identify the mutation that caused the disease How is this information useful? • Can test Mom – Is she an unaffected carrier of the mutation? Is she at risk to have more children with this disease? • Can test siblings of affected child • Can offer prenatal diagnosis in Mom’s next pregnancy OR • Can offer pre-implantation genetic diagnosis • Can provide information about prognosis Cytogenetic Test: Example • Karyotype – to examine the chromosomal complement of an individual including number, form, and size of the chromosomes. • Frequently used for children who present with multiple anomalies, developmental delay, autism Cytogenetic Test: Child with MCA and autism • Obtain a blood sample from baby • Look at chromosomes New type of Cytogenetic Test • Cross between a molecular and Cytogenetic test – arrayCGH- tests for presence/absence of genes at 1000s of positions on each chromosome. Much more sensitive than a karyotype How is this information useful? • Can determine exactly which genes are involved • Can test parents and siblings of affected child to see if they carry the abnormality • Can offer prenatal diagnosis in next pregnancy OR • Can offer pre-implantation genetic diagnosis • Can provide information about prognosis Biochemical Test • Analyzes the quantity of a downstream product of a gene (e.g. not looking directly at the gene, or the chromosome). • Example: Newborn Screening – Mandated in all 50 states – Twenty primary targets that all states do – Over 4 million newborns tested each year Biochemical Test: PKU • Phenylketonuria – Inherited metabolic disorder – If untreated, leads to mental retardation, seizures – Affects 1 in 20,000 newborns Missing enzyme: Phenylalanine Hydroxylase Measure amount of Phenylalanine in baby’s blood How is this information useful? • Can diagnose the baby in time to treat and avoid all clinical consequences of the disease Treatment: Restrict phenylalanine in the diet • Can test siblings of affected child to see if they are carriers for the disease (1 in 70 in the general population are carriers) Genetic Tests for Acquired Mutations • Molecular Tests • Cytogenetic Tests Tests for changes that affect only certain cells or cell types in the body, and that occurred later in life Molecular Test for Acquired Disease • KRAS gene test on tumor tissue from patients with colorectal cancer – Obtain tumor from patient – Extract DNA; treat with enzyme that allows visualization of the mutation How is this information useful? • Patients who’s colon tumors do not have a KRAS mutation are much more likely to respond to Cetuximab therapy • Identifies patients most likely to benefit from specific therapies • Allows choice of alternative therapies (and saves time and money) for patients unlikely to respond Cytogenetic Test for Acquired Disease: Example • Her-2/neu gene amplification in Breast Cancer – Occurs early in oncogenesis – Seen in up to 1/3 of breast cancers – Associated with poor prognosis – Responds to Herceptin (trastuzumab) treatment – Does not respond to Tamoxifen treatment Cytogenetic Test for Acquired Disease • FISH (Fluorescent In Situ Hybridization) for HER-2/neu is a gene-based test that allows one to count the number of HER-2 genes in a cell. How is this information useful? • Assists in selection of patients for chemotherapy, and which therapy to use • Predicts response to adjuvant therapy • Increases survival • Allows choice of alternative therapies (and saves time and money) for patients unlikely to respond Genetic Testing in the News Today Recreational Genetics – 23andMe, KnowMe, Navigenics Nutrigenomics – Sciona, Genelex, Market America, Suracell Ancestry Testing – African Ancestry,GeneTree,DNAPrint Skin and Hair Care – HairDx, Dermagenetics Canine Breed Analysis Summary • Constitutional genetic tests impact patients with inherited disorders and their families, by providing information about diagnosis, prognosis, treatment, and informing reproductive decisions • Genetic tests for acquired diseases impact patients with diseases like cancer, provide information about diagnosis and prognosis, and inform treatment decisions • Genetics and genetic testing impacts many phases of our lives, and will do so even more in the future