* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Unit 3- Section 2
Cancer epigenetics wikipedia , lookup
Nutriepigenomics wikipedia , lookup
Genomic imprinting wikipedia , lookup
Epigenetics of neurodegenerative diseases wikipedia , lookup
Vectors in gene therapy wikipedia , lookup
Nucleic acid analogue wikipedia , lookup
Genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
Gene expression profiling wikipedia , lookup
Expanded genetic code wikipedia , lookup
Koinophilia wikipedia , lookup
Gene expression programming wikipedia , lookup
Saethre–Chotzen syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Skewed X-inactivation wikipedia , lookup
Deoxyribozyme wikipedia , lookup
Y chromosome wikipedia , lookup
No-SCAR (Scarless Cas9 Assisted Recombineering) Genome Editing wikipedia , lookup
Population genetics wikipedia , lookup
Therapeutic gene modulation wikipedia , lookup
Genome evolution wikipedia , lookup
History of genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
Site-specific recombinase technology wikipedia , lookup
Epigenetics of human development wikipedia , lookup
Polycomb Group Proteins and Cancer wikipedia , lookup
Neocentromere wikipedia , lookup
Genome editing wikipedia , lookup
Helitron (biology) wikipedia , lookup
X-inactivation wikipedia , lookup
Oncogenomics wikipedia , lookup
Designer baby wikipedia , lookup
Genetic code wikipedia , lookup
Artificial gene synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Genome (book) wikipedia , lookup
Frameshift mutation wikipedia , lookup
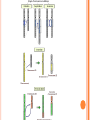
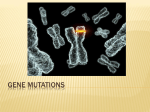
Unit 3: Molecular Genetics Section 2-Mutations I. Chromosomes a. b. c. Made of tightly wound DNA. Most of the code is useless Useful code=genes Genes code for proteins b. EX: Melanin a. d. Each person has different forms of genes=alleles Everyone has gene for melanin b. Some produce more than others a. II. Mutation a. b. c. A change in the DNA or RNA sequence Caused by mistakes in mitosis and meiosis Caused by mutagens-UV light, carcinogens III. Two types a. Germline Occurs in germ cells-egg and sperm b. Passed on to next generation a. b. Somatic Occurs in typical body cells b. Not passed on a. IV. Chromosomal Alterations a. Occurs when mistakes are made in mitosis and meiosis Deletion-A portion of the chromosome is lost and the information is lost with it. Duplication-A portion from the homologous chromosome is added Inversion- A portion is added but it attaches in the reverse direction Insertion- additional information is added Translocation-A portion of a chromosome attaches to a different chromosome, completely messing up the genetic code. V. Other mutations a. Point mutations One nitrogenous base is changed b. Affects the resulting protein by one amino acid a. b. Frameshift mutations A nitrogenous base is added or deleted b. Affects the whole amino acid sequence a. VI. Effects of mutation a. Genetic disorders Proteins are assembled incorrectly b. Sickle-cell anemia-hemoglobin c. Colorblindness a. b. Harmful mutations a. c. Disappear in the gene pool Beneficial mutations Become common in gene pool b. Provide adaptationevolution a. d. Cancer a. Caused by carcinogens