* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download HIV/AIDS 101 - Welcome to the Health Science Program
Survey
Document related concepts
Middle East respiratory syndrome wikipedia , lookup
West Nile fever wikipedia , lookup
Human cytomegalovirus wikipedia , lookup
Tuberculosis wikipedia , lookup
Hepatitis B wikipedia , lookup
Hepatitis C wikipedia , lookup
Neonatal infection wikipedia , lookup
Hospital-acquired infection wikipedia , lookup
Sexually transmitted infection wikipedia , lookup
Diagnosis of HIV/AIDS wikipedia , lookup
Epidemiology of HIV/AIDS wikipedia , lookup
Microbicides for sexually transmitted diseases wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
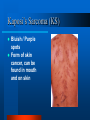
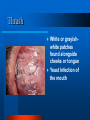
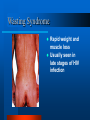
HIV / AIDS 101 Health Education / Risk Reduction Program Florida Department of Health Brooke Mootry OBJECTIVES What is HIV? How can I become infected? What is the difference between HIV and AIDS? Where can I get tested for HIV? How can I prevent HIV infection? What Is HIV? H - Human I - Immunodeficiency V - Virus HIV Infection Exchange of body fluids with an infected person: – Blood (including menstrual) – Semen (including pre-ejaculatory fluid/cum) – Vaginal Secretions – Breast Milk Ways of Transmitting HIV: Sexual Contact – Anal Sex – Vaginal Sex – Oral Sex Ways of Transmitting HIV: Blood-to-Blood Contact – Injecting Drug Needles – Tattoo and Body Piercing Needles – Razors – Toothbrushes Ways of Transmitting HIV: Mother-to-Baby – During Pregnancy – Through Childbirth – Breastfeeding Ways of NOT Transmitting HIV – Shaking Hands / Hugging – Sharing Food Utensils – Tears, Sweat, Urine – Dry Kissing – Mosquitoes HIV Risk Factors ANY person who is involved in any behavior or activity in which the fluids of an infected individual are exchanged. Having more than one sexual partner. Using drugs and/or alcohol during sexual activity. Being infected with an STD (i.e. syphilis, gonorrhea or herpes) HIV vs. AIDS ? A – Acquired I – Immune D – Deficiency S - Syndrome Progression of AIDS Diagnosed by a Physician – “Asymptomatic Period” varies between each individual, though average time is around 10 years. – T-cell count falls to 200 or below – Presence of one or more “Opportunistic Infections” Opportunistic Infections Tuberculosis (TB) PCP – Pneumonia Kaposi’s Sarcoma Wasting Syndrome Thrush Cytomegalovirus HIV-associated dementia (HAD) Kaposi’s Sarcoma (KS) Bluish / Purple spots Form of skin cancer, can be found in mouth and on skin Thrush White or grayishwhite patches found alongside cheeks or tongue Yeast Infection of the mouth Wasting Syndrome Rapid weight and muscle loss Usually seen in late stages of HIV infection HIV Testing Test looks for the presence of HIV antibodies found in blood or in mucous membranes of the mouth. Test is more accurate after close of “window period” Two Types of Testing: - Anonymous - Confidential Testing Sites Broward County Health Departments & Clinics Some Community Organizations Private Physicians * 954-467-4749 * 1-800-FLA-AIDS Prevention of HIV Abstinence Monogamous Relationships Correct and Consistent Use of Barriers – Male / Female Condoms – Dental Dams – Rubber Gloves REVIEW… HIV is the virus that causes AIDS Can be found in ANYONE, you cannot tell by looking at someone HIV Testing Is Important to learn your status REMEMBER! It’s not WHO you are, but WHAT you do, that places you at risk for HIV infection.