* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download ASSIGNMENT FOR MONDAY, MARCH 21 ... CHAPTER 15
Survey
Document related concepts
Nominal rigidity wikipedia , lookup
Fear of floating wikipedia , lookup
Fiscal multiplier wikipedia , lookup
Non-monetary economy wikipedia , lookup
Modern Monetary Theory wikipedia , lookup
Interest rate wikipedia , lookup
Edmund Phelps wikipedia , lookup
Money supply wikipedia , lookup
Inflation targeting wikipedia , lookup
Monetary policy wikipedia , lookup
Full employment wikipedia , lookup
Early 1980s recession wikipedia , lookup
Business cycle wikipedia , lookup
Post-war displacement of Keynesianism wikipedia , lookup
Keynesian economics wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
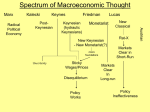
ASSIGNMENT FOR MONDAY, MARCH 21 NAME:__________________HOUR:_____ CHAPTER 15 FUNDAMENTAL QUESTIONS 1. Is there a tradeoff between inflation and the unemployment rate? 2. How does the tradeoff between inflation and the unemployment rate vary from the short to the long run? 3. What is the relationship between unexpected inflation and the unemployment rate? 4. Graph and correctly label a short run Phillips Curve and a long run Phillips Curve. CHAPTER 16 Macroeconomic Viewpoints: New Keynesian, Monetarist, and New Classical OVERVIEW AND OBJECTIVES The primary purpose of this chapter is to introduce the major alternative schools of macroeconomic thought. The unique feature of the chapter is the discussion of the policy prescriptions of Keynesian, monetarist, and new classical economists. Each group differs in its view of the role that government should play in the economy. Keynesians tend to argue for activist monetary and fiscal policies. Monetarists and new classical economists argue for nonactivist rules with respect to monetary policy and a balanced budget on the fiscal side. Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Company. All rights reserved. Chapter 15: Macroeconomic Policy 99 1. What is the difference between the short run Phillips Curve and the long run Phillips Curve? Use AS/AD graph to explain why there is a difference between them. 2. Give 2 reasons why there may be a short run tradeoff between unexpected inflation and the unemployment rate. 3. Read the article on page 355. Explain how that in Wisconsin 2011 it is possible that wages aren’t sticky downward. 4. What is the difference between traditional Keynesian and New Keynesian economics? 5. What is the difference between old classical and new classical economics? 6. Draw an AS/AD graph for each theory of economics. Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Company. All rights reserved. 100 Chapter 15: Macroeconomic Policy Name the economist who would make each of these statements. “Changes in prices and wages are too slow to support the new classical assumption of persistent economic equilibrium.” “The best monetary policy is to keep the money supply growing at a slow and steady rate.” “Frictional unemployment is the result of workers voluntarily substituting leisure for labor when wages fall.” “A change in the money supply will affect GDP after a long and variable lag, so it is difficult to predict the effects of money on output.” “Government policymakers should use fiscal policy to adjust aggregate demand in response to aggregate supply shocks.” “The economy is subject to recurring disequilibrium in labor and goods markets, so the government can serve a useful function of helping the economy adjust to equilibrium.” “Since the aggregate supply curve is horizontal, aggregate demand will determine the level of real GDP.” “If everyone believed that the monetary authority was going to cut the inflation rate from 6 to 3 percent, such a reduction in inflation could be achieved without any significant increase in unemployment.” Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Company. All rights reserved.