* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download International Lecture - Rockhurst University
Survey
Document related concepts
Full employment wikipedia , lookup
Foreign-exchange reserves wikipedia , lookup
Modern Monetary Theory wikipedia , lookup
Fiscal multiplier wikipedia , lookup
Balance of payments wikipedia , lookup
Nominal rigidity wikipedia , lookup
Pensions crisis wikipedia , lookup
Okishio's theorem wikipedia , lookup
Balance of trade wikipedia , lookup
Monetary policy wikipedia , lookup
Early 1980s recession wikipedia , lookup
Fear of floating wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
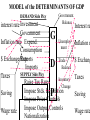
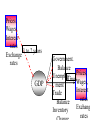
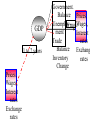
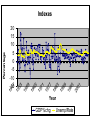
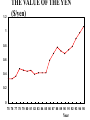
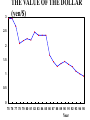
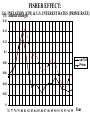
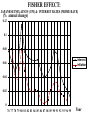
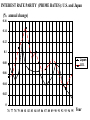
Major Categories of Data Stocks (measured at a point in time eg. Balance sheet items): - Money, Assets, Liabilities, Debt Flows (measured between two points in time) - National income and product accounts: GDP, federal deficit, trade deficit Prices (ratios of stocks or flows) - On goods ($/good) - on labor ($/hr.) interest rate ($ next year/$this year minus one) Exchange rate (unit of foreign currency/unit of domestic currency) Disequilibrium and Effects of disequilibrium (flows) - Inventory buildup, queues, order backlogs, capacity utilization, unemployment rate Unemployment rate NATIONAL INCOME AND PRODUCT ACCOUNTS EXPENDITURES “injections” (What institutions buy creating - jobs): Personal Consumption Expenditure (“consumption”): households] Investment (business purchases of capital to produce future consumption Government Expenditure net Exports (exports-imports) INCOME (Where factors (in blue) receive their money). Factor payments in - red Labor wages and salaries Land payments Capital payments Entrepreneur payment Wage rate Rent Interest rate Profit rate EXPENDITURES = INCOME=REAL OUTPUT C+I+XImp+F+S U.S. Accounts, 1984 ($billions) Personal consumption X Dep IndT ax (-SS-RECT+NI+Tr PT 2342 2342 Gross private domestic investment 637 637 Exports 364 364 Imports 430 -430 Federal government purchases 296 296 State and local government purchases 452 452 Depreciation 403 Indirect business taxes 304 Social security taxes 306 -306 Retained earnings 118 -118 88 -88 Net interest 150 150 Transfer payments 418 418 Personal taxes 435 Corporate profits tax liability -403 -304 -435 Cumulative: 3661 GDP 3661 NDP=GDP-Dep NI=NDP-IndTax PI=NI-SS-RE-CT+NI+Tr 2342 -403 -304 56 3258 2954 3010 -435 2342 Fundamental Balances Injections (create jobs)= Leakages (lose jobs) Investment+GovtExpend+Exports=Saving+Taxes+Imports In terms of balances this is rewritten: (Exports-Imports)=(Savings-Investment)+(Taxes-GovtExpend) External Balance =Private Balance +Government Balance MICRO: MARKET SUPPLY AND DEMAND Lower Price Lower Output Higher Price Less productivity (technological change) Higher price of resources Seller expectations of future surpluses Less number of sellers Leftward (downward) Shift of Demand less income less tastes for good less buyers less complement lower priuce for substitutes Buyer expectations about future shortages Higher Output Rightward (downward) Shift of Supply Leftward (upward) Shift of Supply More productivity (technological change) Lower price of resources Seller expectations of future shortages More number of sellers Rightward (upward) Shift of Demand Breakdown all shifts into their output and price vectors More income More tastes for good More buyers More complement Higher priuce for substitutes Buyer expectations about future shortages MACRO: AGGREGATE SUPPLY & DEMAND Lower Price (deflation) Higher Price (inflation) Lower Output (slow Growth) RECESSION/DEPRESSION Leftward (downward) Shift of Aggregate Demand: STAGFLATION Leftward (upward) Shift of Aggregate Supply: less injections, or more leakages Less factors or higher factor prices Higher Output (fast Growth) HIGH GROWTH -LOW INFLATION Rightward (downward) Shift of Supply : More factors or lower factor prices HIGH GROWTH -HIGH INFLATION Rightward (upward) Shift of Demand: mor injections, or less leakages Breakdown all shifts into their output and price vectors MODEL of the DETERMINANTS OF GDP Government. Balance DEMAND Side Plcy interest rate Investment Government UnemployInflation rate Expend. ment Consumption $ Exchange Exports Rate Trade Balance Imports SUPPLY Side Plcy Taxes Inventory Raise Tax Rates Change Impose Stds. Regulation Saving Impose Price Controls Impose Output Controls Wage rate Nationalization G D P Interest ra Inflation r $ Exchang Taxes Saving Wage rate MODEL of the DETERMINANTS OF GDP Government. Balance DEMAND Side Plcy interest rate Investment Government UnemployInflation rate Expend. ment Consumption $ Exchange Exports Rate Trade Balance Imports SUPPLY Side Plcy Taxes Inventory Raise Tax Rates Change Impose Stds. Regulation Saving Impose Price Controls Impose Output Controls Wage rate Nationalization G D P Interest ra Inflation r $ Exchang Taxes Saving Wage rate Prices, Wages, Interest rates 1 to 2 years Exchange rates GDP Government. Balance Prices, Unemploy6 mos.Wages, ment Interest Trade rates Balance Exchang Inventory rates GDP 1 to 2 years Prices, Wages, Interest rates Exchange rates Government. Balance Prices, Unemploy6 mos.Wages, ment Interest Trade rates Balance Exchang Inventory rates Change STOCK MARKET: Level, Change, & Change of change AT WHAT CHANGE & CHANGE OF CHANGE DO WE WANT TO INVEST IN THE STOCK MARKET? LEVEL + ++ ++++++ + + + + ++ CHANGE +0 - - - 0+++ 0 - - - - 0+ ++0- - - 0 + ++ CHANGE of CHANGE - - 0+ 19 47 Percentage 20 15 10 5 0 -5 -10 -15 GDP%chg Year UnemplRate 20 01 19 95 19 89 19 83 19 77 19 71 19 65 19 59 19 53 Indexes B A L A N C E O F P A Y M E N T S Currrent account = trade balance= net exports Real goods and services - imports Money Home Abroad Real goods and services - exports CAPITAL ACCOUNT Titles to foreign wealth sold to Americans Money Home Abroad Titles to American wealth sold to foreigners Unilateral transfers Home Money Abroad 1.2 THE VALUE OF THE YEN ($/yen) 1 0.8 0.6 0.4 0.2 0 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 Year 3 THE VALUE OF THE DOLLAR (yen/$) 2.5 2 1.5 1 0.5 0 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 Year FISHER EFFECT: U.S. (CPI) & U.S. INTEREST RATES (PRIME RATE) (% INFLATION annual change) 0.16 0.14 0.12 0.1 cpi %d Prime 0.08 0.06 0.04 0.02 0 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 Year FISHER EFFECT: JAPANESE INFLATION (CPI) & INTEREST RATES (PRIME RATE) (% annual change) 0.12 0.1 0.08 interest inflation 0.06 0.04 0.02 0 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 Year INTEREST RATE PARITY (PRIME RATES): U.S. and Japan (% annual change) 0.16 0.14 0.12 0.1 Japan U.S. 0.08 0.06 0.04 0.02 0 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 Year PURCHASING POWER PARITY: INFLATION (CPI): U.S. and Japan (% annual change) 0.14 0.12 0.1 0.08 U.S. Japan 0.06 0.04 0.02 0 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 Year REAL INTEREST RATE PARITY: U.S. and Japan (% annual change) 7 6 5 4 3 U.S. Japan 2 1 0 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 -1 -2 Year Difference in U.S. and Japanese Rates (% annual change) 8 7 6 5 4 Inflation Dif Interest Dif. 3 2 1 0 -1 -2 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 Year