* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download esters - wellswaysciences
Survey
Document related concepts
Woodward–Hoffmann rules wikipedia , lookup
Asymmetric induction wikipedia , lookup
Bottromycin wikipedia , lookup
George S. Hammond wikipedia , lookup
Physical organic chemistry wikipedia , lookup
Ring-closing metathesis wikipedia , lookup
Wolff–Kishner reduction wikipedia , lookup
Wolff rearrangement wikipedia , lookup
Ene reaction wikipedia , lookup
Baylis–Hillman reaction wikipedia , lookup
Hofmann–Löffler reaction wikipedia , lookup
Hydroformylation wikipedia , lookup
Petasis reaction wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
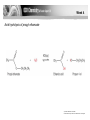
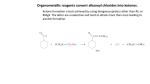
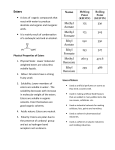
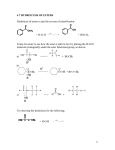
Week 4 • Describe the esterification of carboxylic acids with alcohols in the presence of an acid catalyst, and also of acid anhydrides with alcohols. • Describe the hydrolysis of esters. • State the uses of esters in perfumes and flavourings. © Pearson Education Ltd 2009 This document may have been altered from the original Esters • Esters are characterised by the functional group They have no free OH groups so they cannot hydrogen bond. They are volatile compared to acids and alcohols of similar mass and are not very soluble in water. Flavourings etc. • Volatile esters have light, fruity smells and the flavour and smells of many fruits and flowers are due to mixtures of esters. • Artificial flavourings are made by mixing synthetic esters but they are only ever approximate because it would be too expensive to include all the flavour compounds present in real fruit etc. Flavour Ester apple Ethyl-2methylbutanoate 3-methylbutyl ethanoate 1-methylbutyl ethanoate Phenylmethyl ethanoate Butyl butanoate pear banana Oil of jasmine pineapple Formation of Esters • 1. By the reaction of an alcohol with a carboxylic acid. This is ESTERIFICATION. reflux the mixture with conc. sulphuric acid catalyst. It is an equilibrium reaction and rarely goes to completion. Week 4 An acid anhydride is formed by removal of a molecule of water from two carboxylic acid molecules. © Pearson Education Ltd 2009 This document may have been altered from the original Week 4 Ethanoic anhydride reacts with methanol to make the ester methyl ethanoate Carried out by gentle heating and since it is not an equilibrium reaction it goes in far better yield. © Pearson Education Ltd 2009 This document may have been altered from the original Naming Esters • Remember! • Esters are regarded as carboxylic acid derivatives. • Divide the formula into 2 portions by drawing a line after the bridging oxygen of the COO group. • Name the portion which does NOT carry the COO as the alkyl radical. • Name the portion that carries the COO group as the carboxylate radical. • Combine the 2. Examples • • • • • • • • • Draw displayed formulae and name: C6H5COOCH3 Methyl benzoate HCOOCH2CH3 Ethyl methanoate CH3CH2COOCH3 Methyl propanoate CH3CH2OOCCH2CH3 Ethyl propanoate Naming Cont: • • • • • • • Draw displayed formulae for : Heptyl decanoate Phenyl benzoate Butyl methanoate Benzyl ethanoate 1-methylethylpropanoate For each of the above state the acid and the alcohol required to make them. More Exercises • Draw skeletal formulae for the isomers of ethyl propanoate that are straight chain esters and name them. • Draw the structural formula of 1-methylethyl propanoate. • Name the carboxylic acid and alcohol that would form the ester. • Write a balanced equation for the reaction. Hydrolysis of Esters • Since the reaction of an acid with an alcohol to form an ester and water is an equilibrium reaction the back reaction of this is the hydrolysis of an ester to reform the acid and the alcohol. • The reaction uses an aqueous (dilute) acid catalyst and is refluxed as before. • As before the reaction does not go to completion so all reactants and products are present in the reaction vessel. Week 4 Acid hydrolysis of propyl ethanoate © Pearson Education Ltd 2009 This document may have been altered from the original Alkaline Hydrolysis • The reaction goes faster and goes to completion in the presence of an alkali. • Why? • When some of the acid molecules have been formed in the reaction the hydroxide ions present react with them to form a salt. • This removes the acid from the reaction mixture and so the reaction moves RIGHT. • The base (or alkali) is used up in the reaction. • This is not strictly catalysed by the alkali. Why not? Week 4 Alkaline hydrolysis of ethyl propanoate © Pearson Education Ltd 2009 This document may have been altered from the original Exercise • Write a balanced equation for the base hydrolysis of methyl benzoate. • Name the products. • Write a balanced equation for the acid hydrolysis of methyl propanoate. • Name the products.