* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download CH-47D Electrical System Operation
Standby power wikipedia , lookup
Electric machine wikipedia , lookup
Power over Ethernet wikipedia , lookup
Voltage optimisation wikipedia , lookup
Electrical substation wikipedia , lookup
Mechanical filter wikipedia , lookup
Audio power wikipedia , lookup
Switched-mode power supply wikipedia , lookup
Electric power system wikipedia , lookup
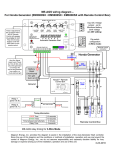
Wireless power transfer wikipedia , lookup
Portable appliance testing wikipedia , lookup
History of electric power transmission wikipedia , lookup
Alternating current wikipedia , lookup
Amtrak's 25 Hz traction power system wikipedia , lookup
Stray voltage wikipedia , lookup
Ground (electricity) wikipedia , lookup
Mechanical-electrical analogies wikipedia , lookup
Electronic engineering wikipedia , lookup
Electrification wikipedia , lookup
Mains electricity wikipedia , lookup
London Electrical Engineers wikipedia , lookup
Power engineering wikipedia , lookup
CH-47D Electrical System CH-47D Electrical System Terminal Learning Objective ACTION: Analyze electrical system malfunctions and prescribe corrective actions. CONDITION: While serving as a Maintenance Test Pilot (MTP) or Flight Engineer. STANDARD: In Accordance With (IAW) TM 55-1520-240-Series. 2 CH-47D Electrical System Administrative Notes Safety Requirements: None. Risk Assessment Level: Low. Environmental Considerations: None. Evaluation: Written examination. 3 CH-47D Electrical System Introduction Electricity is a fundamental force found everywhere in nature and has become one of the most powerful tools put to use by mankind. 4 CH-47D Electrical System Overview For the next 4 hours, we will be discussing: The CH-47D AC and DC electrical systems, how they function, some basic components. There are 16 Enabling Learning Objectives (ELO). 5 CH-47D Electrical System ELO A ACTION: Student read ahead assignment: Identify the basic properties of electricity. CONDITION: Given a student handout. STANDARD: IAW TM 55-1520-240-Series. 6 CH-47D Electrical System Questions ? 7 CH-47D Electrical System ELO B ACTION: Student read ahead assignment: List the six common ways to produce electricity. CONDITION: Given a student handout. STANDARD: IAW TM 55-1520-240-Series. 8 CH-47D Electrical System Questions ? 9 CH-47D Electrical System ELO C ACTION: Identify the electrical symbols used in CH-47D troubleshooting manual schematics. CONDITION: Given a student handout and TM 55-1520-240-T-1 and 2. STANDARD: IAW TM 55-1520-240-Series. 10 CH-47D Electrical System Notes Pay attention to the notes shown on the electrical schematics in the T-Manuals. 11 CH-47D Electrical System Schematics Standardized and universally accepted methods used to diagram the flow of electricity from one component to the next. 12 CH-47D Electrical System Schematics Each Component has a unique: Symbol Part number Label 13 CH-47D Electrical System Schematics 14 CH-47D Electrical System Schematics Linking components together: Wires Terminal Boards Diodes Ground Points 15 CH-47D Electrical System Schematics Wires: Have a unique number assigned. Either ink stamped or labeled. 16 CH-47D Electrical System Schematics Terminal Boards: Provide for the connection of one wire or component to another. Are located throughout the airframe. 17 CH-47D Electrical System Schematics Diodes: Are one-way streets for electricity. Most visible in the CH-47D connected to relays. 18 CH-47D Electrical System Schematics Ground Points: Allow a common return path for the flow of electricity. Used for either AC or DC. 19 CH-47D Electrical System Schematics 20 CH-47D Electrical System Schematics Linking components together: Switches Relays 21 CH-47D Electrical System Schematics Switches: Turns on or off the flow of electricity. Used for either AC or DC. 22 CH-47D Electrical System Schematics Relays: Nothing more than remotely controlled switches. Often used to switch components or circuits with high power requirements. Can be used to set up a “logic flow”. 23 CH-47D Electrical System Schematics Battery Switch (161S1) and Battery Relay (161K1). 24 CH-47D Electrical System Schematics 25 CH-47D Electrical System Schematics Questions ? 26 CH-47D Electrical System Schematics Press-To-Test Annunciator Lights. 27 CH-47D Electrical System Schematics Transformers. 28 CH-47D Electrical System ELO D ACTION: Identify the physical location of components listed on the CH-47D troubleshooting manual schematics. CONDITION: Given a student handout and TM 55-1520-240-T-2. STANDARD: IAW TM 55-1520-240-Series. 29 CH-47D Electrical System Locating Components Simple Methodology Using the schematic, start with components unique number. Use the T-Manual to see what the component looks like. Look up the number in the T-Manual to find the physical location. Find the component on the airframe. 30 CH-47D Electrical System Locating Components Questions ? 31 CH-47D Electrical System ELO E ACTION: Chart the flow of current through an electrical schematic. CONDITION: Given a student handout and TM 55-1520-240-T-2. STANDARD: IAW TM 55-1520-240-Series. 32 CH-47D Electrical System Electron Flow When tracing electrical flow on a schematic, start at the source of power and go towards ground. 33 CH-47D Electrical System Electron Flow “Ground” A a point that, if voltage was measured, the reading would be zero volts (DC circuit). A common connection related to all other components in a circuit (AC or DC). 34 CH-47D Electrical System Electron Flow “De-Energized” Note that most schematics are drawn with the power turned off. When troubleshooting, the mechanic must mentally turn on the circuit and trace the flow. Note: Using a High-Lighter often helps the beginner. 35 CH-47D Electrical System Electron Flow Battery plugged in, but not turned on. 36 CH-47D Electrical System Electron Flow Battery plugged in, and turned on. 37 CH-47D Electrical System Electron Flow Questions ? 38 CH-47D Electrical System Electron Flow Practical Exercise 39 CH-47D Electrical System Electron Flow Searchlight switch turned on, closing relay. 40 CH-47D Electrical System Electron Flow Searchlight light bulb on. 41 CH-47D Electrical System Electron Flow Searchlight extending, an example of “Logic”. 42 CH-47D Electrical System ELO F ACTION: List the sources of AC electrical power for the CH-47D. CONDITION: Given a student handout and TM 55-1520-240-Series. STANDARD: IAW TM 55-1520-240-Series. 43 CH-47D Electrical System AC Power Sources 3 Sources of AC Power External Power. Auxiliary Power Unit (APU) Generator. Main Generator. 44 CH-47D Electrical System AC Power Sources External Power Lowest priority of power. If the APU or a Main Generator is turned on, External Power will be disconnected. “EXT PWR” Caution Light usually illuminated. 45 CH-47D Electrical System AC Power Sources External Power Usually supplied via AGPU, a GPU, or special hangar power supply. Most commonly used as a source of power during post-phase or post-modification work order (MWO) power-on checks. 46 CH-47D Electrical System AC Power Sources APU Second highest priority of power. As the APU generator comes on, External Power goes off. The APU Generator will disconnect if a Main Generator comes on-line. 47 CH-47D Electrical System AC Power Sources The APU is most commonly used for: Start-up and shut-down of the helicopter. Ground check-out and troubleshooting of systems. During an in-flight emergency (dual generator failure). 48 CH-47D Electrical System AC Power Sources Main Generators Highest priority of power. Turning on a Main Generator will disconnect the APU Generator or External AC Power. Usable when the Rotor RPM is greater than 86%. 49 CH-47D Electrical System ELO G ACTION: List the major components of the main AC generating system. CONDITION: Given a student handout and TM 55-1520-240-Series. STANDARD: IAW TM 55-1520-240-Series. 50 CH-47D Electrical System Main AC System Components Main Generator OIL INLET PORT PMG SECTION EXCITOR / ROTATING RECTIFIER ASSEMBLY MAIN ROTOR WINDINGS OIL OUTLET PORT 51 CH-47D Electrical System Main AC System Components Generator Control Unit (GCU) Located in the left and right electrical compartments. Receives power to operate from the PMG section of the Main Generator. 52 CH-47D Electrical System Main AC System Components Generator Control Unit (GCU) Monitors operation of the generator for: Over-Voltage. Under-Voltage. Under-Frequency (an MTP check). Feeder Fault. 53 CH-47D Electrical System Main AC System Components GCU – Feeder Fault Protection 54 CH-47D Electrical System Main AC System Components Main Generator Contactor Located in the respective PDP. Allows Generator to connect to Bus. Relay power comes from GCU (28 VDC). Permits Cross-Tie. 55 CH-47D Electrical System ELO H ACTION: List the components of the APU AC system. CONDITION: Given a student handout and TM 55-1520-240-Series. STANDARD: IAW TM 55-1520-240-Series. 56 CH-47D Electrical System APU AC System Components APU Generator A 20 KVA, air cooled Generator mounted on the APU. 57 CH-47D Electrical System APU AC System Components APU Generator – 3 Sections: A PMG section. An Exciter section. A main generator section (rotor and stator). Functions similar to the Main Generator. 58 CH-47D Electrical System APU AC System Components APU Generator Control Unit (GCU): Located in right electrical compartment. Receives power from the PMG. Requires a conversion plug. 59 CH-47D Electrical System APU AC System Components APU (GCU) provides protection for: Under-Voltage. Over-Voltage. Under-Frequency. Feed Fault. Functions similar to Main Generator System, voltages are slightly different. 60 CH-47D Electrical System APU AC System Components APU Generator Slave Relay: APU Generator Slave Relay Located in # 2 PDP. Requires 28 VDC from APU GCU to operate. Provides Cross-Tie. 61 CH-47D Electrical System APU AC System Components APU Generator Contactor: Located in # 2 PDP. Connects APU Generator to the Bus. Requires 28 VDC from APU GCU to operate. Provides Cross-Tie. 62 CH-47D Electrical System APU AC System Components APU Generator Contactor: 63 CH-47D Electrical System ELO I ACTION: List the components of the External AC Power System. CONDITION: Given a student handout and TM 55-1520-240-Series. STANDARD: IAW TM 55-1520-240-Series. 64 CH-47D Electrical System External AC Power System Components External Power Receptacle: Located just forward of the left electrical compartment. AC power plug utilizes the lower connector. 65 CH-47D Electrical System External AC Power System Components External Power Monitor: Located in the Left Electrical Compartment. Monitors for: - Proper Voltage, Frequency, and Phase Sequence. 66 CH-47D Electrical System External AC Power System Components External Power Contactor: Located in the # 1 PDP. Connects External AC Power to the Bus. Provides AC Cross-Tie. 67 CH-47D Electrical System External AC Power System Components External Power Contactor: 68 CH-47D Electrical System ELO J ACTION: Analyze the application of External AC Power to the aircraft electrical system. CONDITION: Given a student handout and TM 55-1520-240-Series. STANDARD: IAW TM 55-1520-240-Series. 69 CH-47D Electrical System Analyze External Power Application 70 CH-47D Electrical System Analyze External Power Application 71 CH-47D Electrical System Analyze External Power Application 72 CH-47D Electrical System Analyze External Power Application 73 CH-47D Electrical System Analyze External Power Application 74 CH-47D Electrical System ELO K ACTION: Analyze the application of the # 1 Main Generator AC Power to the aircraft electrical system. CONDITION: Given a student handout and TM 55-1520-240-Series. STANDARD: IAW TM 55-1520-240-Series. 75 CH-47D Electrical System Analyze #1 Generator Power Application 76 CH-47D Electrical System Analyze #1 Generator Power Application 77 CH-47D Electrical System Analyze #1 Generator Power Application 78 CH-47D Electrical System Analyze #1 Generator Power Application 79 CH-47D Electrical System Analyze #1 Generator Power Application 80 CH-47D Electrical System ELO L ACTION: List the sources of DC power for the CH-47D. CONDITION: Given a student handout and TM 55-1520-240-Series. STANDARD: IAW TM 55-1520-240-Series. 81 CH-47D Electrical System DC Power Sources 3 DC Power Sources: External DC. Transformer-Rectifier. Battery 82 CH-47D Electrical System DC Power Sources External DC Power: Highest priority of DC power. Supplied by AGPU, GPU, or hangar power supply. 83 CH-47D Electrical System DC Power Sources Transformer-Rectifier (T/R): Second highest priority of DC power. Normally powers the Bus when a Generator is on-line. Will power all DC Buses except Battery Bus. 84 CH-47D Electrical System DC Power Sources Battery: When no other source is available, the Battery will power – The Battery Bus, the Switched Battery Bus, and the Essential Bus. 85 CH-47D Electrical System ELO M ACTION: List the components of the Transformer-Rectifier system. CONDITION: Given a student handout and TM 55-1520-240-Series. STANDARD: IAW TM 55-1520-240-Series. 86 CH-47D Electrical System T/R System Components Transformer-Rectifier (T/R). Reverse Current Cutout (RCCO). 87 CH-47D Electrical System T/R System Components Transformer-Rectifier: Located in the Left and Right Electrical compartments. Converts 115 VAC to 28 VDC via a step-down transformer and a rectifier (diode) circuit. Can supply up to 200 amps. 88 CH-47D Electrical System T/R System Components Reverse Current Cutout (RCCO): Located in the respective PDP. Protects the T/R from reverse current (voltage). Connects T/R output to the DC Bus. 89 CH-47D Electrical System ELO N ACTION: List the components of the battery and charging system. CONDITION: Given a student handout and TM 55-1520-240-Series. STANDARD: IAW TM 55-1520-240-Series. 90 CH-47D Electrical System Battery and Charging System Components Battery Charger (NICAD only). Battery (NICAD). Battery (SLAB). 91 CH-47D Electrical System Battery and Charging System Components Battery Charger (NICAD only): Located in the Left Electrical Compartment. Monitors and controls the state of charge. Converts 115 VAC to 28 VDC Is slowly being phased out. 92 CH-47D Electrical System Battery and Charging System Components Battery Charger monitors Battery for: Over-temperature. Cell imbalance. Open circuit. Charger fault. 93 CH-47D Electrical System Battery and Charging System Components Battery (NICAD): Located in the Left Electrical Compartment. It is a nickel-cadmium battery that uses potassium hydroxide (base) as an electrolyte. 94 CH-47D Electrical System Battery and Charging System Components Battery (SLAB): Newest Battery used in Army aviation. Sealed Lead Acid Battery (SLAB) utilizing sulfuric acid as the electrolyte. Different design, same rating as NICAD. Lower maintenance requirement. 95 CH-47D Electrical System ELO O ACTION: List the components of the DC External Power System. CONDITION: Given a student handout and TM 55-1520-240-Series. STANDARD: IAW TM 55-1520-240-Series. 96 CH-47D Electrical System DC External Power System Components External Power Receptacle: Used to connect External DC (or AC) power. Located on the forward side of the Left Electrical Compartment. 97 CH-47D Electrical System DC External Power System Components 4 DC Relays provide a Logic circuit: External Power Relay (161K7). External Power Control Relay (161K9). Both RCCO Relays (161K3 and 161K4). 98 CH-47D Electrical System DC External Power System Components Reverse DC Polarity Protection (Blocking) Diode: Prevents voltage with incorrect polarity from being applied to the DC Bus. Won’t allow 161K7 and 161K9 to operate. 99 CH-47D Electrical System DC External Power System Components Practical Exercise: Complete the final Practical Exercise in the Student Handout at your leisure. 100 CH-47D Electrical System Summary & Questions? 101