* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Heater Controls & Components
Survey
Document related concepts
Variable-frequency drive wikipedia , lookup
Control theory wikipedia , lookup
Buck converter wikipedia , lookup
Distributed control system wikipedia , lookup
Power engineering wikipedia , lookup
Voltage optimisation wikipedia , lookup
Immunity-aware programming wikipedia , lookup
Electrical substation wikipedia , lookup
Alternating current wikipedia , lookup
Distribution management system wikipedia , lookup
Power electronics wikipedia , lookup
Mains electricity wikipedia , lookup
Switched-mode power supply wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
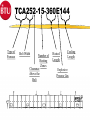
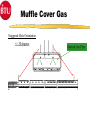
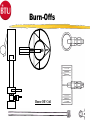
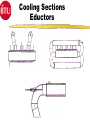
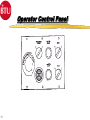
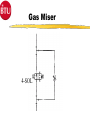
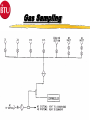
Introduction 1 TCA- Explosive 2 TCA252-15-360E144 Type of Furnace Belt Width Number of Heating Zones Clearance Above the Belt Heated Length Cooling Length Explosive Process Gas Course Prerequisites 4 Trained in use and correct disposal of hazardous materials. Trained in Lockout/Tagout procedures. Trained in the correct use of PPE. Electromechanical Skills Understand Windows and Dos basics. COURSE OBJECTIVES Upon successfully completion of this course you will be able to: 1 Identify all safety features and functions of the TCA. 2 Locate major systems components and understand their theory of operations, maintenance and troubleshooting of the components. 3 Demonstrate the ability to use the TCA Owner’s Manual and it’s drawings to support operations and maintenance responsibilities. 5 COURSE OBJECTIVES 4. Operate WINCON software to support normal operations, (nonyearly) preventative maintenance and troubleshooting. 6 Perform (non-yearly) preventative maintenance. 6 COURSE OUTLINE 7 Introduction ~ .5 Hours TCA - Safety ~1.5 Hours System Documentation & Drawings ~2.0 Hours System Operational Theory, Maintenance and Troubleshooting ~6.0 Hours WINCON for Operators and PM Applications ~6.0 Hours System Operations, PM, & Testing Applications Lab ~8.0 Hours Topic Two Safety Upon successfully completion of this topic you will be able to: 1 State all system safety features and have an understanding of their purpose, functions and operations. 2 Demonstrate an understanding of good safety practices used by operators and technicians, related to the TCA. 3 Understand the MSDS for materials used in the furnace and indicate an understanding of the hazards, the PPE and the first aid needed to use those materials. 8 Safety Conventions - Used Safety precautions and notes described in the manual are identified within the text using the following four types of headers. Danger, warnings and cautions are designated by a dark frame with a shaded background. The level of safety hazard for each heading is described in the following example illustrations: DANG ER Danger indicates imminently hazardous situations where a potential hazard or unsafe practice will cause death or serious personal injury. W ARNI NG Warning indicates hazardous situations where a potential hazard or unsafe practice could cause death or personal injury. CAUTION Caution indicates situations where a potential hazard or unsafe practice could cause equipment or products to be damaged or minor injury if the instructions that follow the notice are not strictly observed. Notes relate to additional information about a procedure but do not usually relate to safety. They have a light frame border with no shading. An example of a note is illustrated below: NOTE: Note indicates any additional information about a procedure. 9 Furnace Safety Features The model TCA furnace contains the following safety features: 1. 2. Emergency Stop Buttons Over Temperature Protection Heating Zone Over-Temperature Cooling Section Over-Temperature 10 3. Conveyor Protection 4. Lockable Power Disconnect Switch 5. System Interlocks Emergency Stop Buttons (EMO’s) EMO EMO The Start power will be turned off, which turns off heat and will cause the zone temperature to slowly drop. This furnace configuration also turns off, the conveyor and gas controls, cooling system, and case cooling. 11 EMO Over-Temperature Protection WINCON Temperature Deviation Alarm Alarm Level 10°C 810°C Alert Level 5° C 805°C Setpoint 800°C 800°C When the FCU senses 810°C it will generate a signal that will deenergizes the Heater Power Contactor. 12 Recipe Over-Temperature Protection Alarm LED Indicators OVER TEMPERATURE MODULE 1 CH 1 2 3 CH 2 4 5 6 7 J2 J1 9 CH 5 10 CH 6 RESET PWR ON J3 13 CH 7 CH 8 J4 CH 3 CH 4 8 Reset Button (Same Function as Heat Off/On Switch) T/C Input Connecto rs J1, J3, and J4 CH 9 CH 10 Channels 7 through 10 are Omitted in 6 Channel Version. The Overtemperature Module’s setpoints are preset at the factory (to ≃ 25°C above system software limits) and should not be changed. Each heated zone is monitored by an overtemperature T/C that is independent from the zone control circuitry. If any zone exceeds the preset safe maximum temperature, the overtemp condition causes the module to shut off all heater power and generates an alarm with the WINCON software, puts the system into a purge mode but the Conveyor is maintained running for removal of product. Module Conveyor Protection 120 VAC C360-TR 333-LS C370-TR Conveyor Spocket As the Conveyor drive shaft rotates the sprocket turns moving C360-LS, which supplies 120 VAC power to either the C360-TR or the C370-TR. These relay are Time Delay to Make (TDM), set for the minimum conveyor speed. If the conveyor stops moving or is to slow, one of the relays will energize and provide an alarm to the WINCON software. Safety Labels ! CAUTION EMO EMERGENCY STOP BUTTON (Yellow and Black) MECHANICAL OR PINCH POINT HAZARD (Yellow and Black) ! CAUTION Hot internal surface use caution when opening the lid. TEMPERATURE HAZARD (Yellow and Black) 15 EMERGENCY OFF OR EMERGENCY STOP BUTTON (Red and White) Safety Labels ! DANGER ! DANGER HIGH VOLTAGE Hot internal surface use caution when opening the lid. ELECRICAL HAZARD (Red and Black) TEMPERATURE HAZARD (Yellow and Black) ELECRICAL HAZARD (Red and Black) ! ! DANGER TEMPERATURE HAZARD (Yellow and Black) DANGER ! our hands. CRUSH HAZARD (Red and Black) 16 WARNING This equipment contains Refractory Ceramic Fibers (RCF) that have been identified by the International Agency for Research on Cancer (IARC) as a possible human carcinogen (Group 2B). Exposure to RCF may be hazardous to your health. Under normal operating conditions, exposure should not occur. If maintenance is to be performed on this equipment, or if exposure to RCF otherwise occurs, then precautions should be taken for the handling of RCF. The necessary precautions and emergency procedures are described in the MSDS sheets included in the technical manual supplied with this equipment. Further information on RCF may also be obtained from: The Carborundum Company - Fibers Division. HOTLINE NUMBER (716) 278-2183. CRUSH HAZARD (Yellow and Black) VAPOR HAZARD (Red and Black) Lockable Power Disconnect Switch Tab may be pulled out when switch is in the OFF Position and Locked Out A000-DISC System Interlocks Burn-Off Failure Turns off Cover Gas Auto Purge On Low H2 Pressure Turns off Cover Gas Auto Purge On Low N2 Pressure Turns off Cover Gas Auto Purge On Low AR Pressure Turns off Cover Gas Auto Purge On System Alarms (External) Over Temp Conveyor Belt Fail Emergency Stop Water Flow Fail Water O/T Low Hydrogen Pressure Low Nitrogen Pressure Low Argon Pressure Gas Safety Good Safety Practices Some general safety practices are: Perform maintenance procedures with teams of two or more people. Wear safety glasses and protective clothing when working on the system. Whenever possible, make sure that both compressed gases and electric power are turned off at the source prior to beginning any maintenance task. Do not attempt to defeat any of the interlock switches or the safety features that are built into the system. Make sure that all access panels or doors are closed and latched when they are not being used for maintenance. 20 Good Safety Practices Periodically check the operation of all the safety interlock in the system Be careful when using flammable solvents such as alcohol for cleaning. Make sure that the electric power is off and the equipment is cool enough to prevent a fire hazard.Observe all safety warning labels. Never remove a warning label from the system. Never operate damaged or leaking equipment. Make sure that the electric power to the system is turned off using the lockout/tagout procedure before connecting or disconnecting cables. 21 Good Safety Practices Turn off the furnace and disconnect the power from the source before moving the system. Move the furnace with care. Sudden jolt or drops can damage the equipment. Report any unsafe conditions or situations immediately. 22 MSDS Material Safety Data Sheet Three questions to ask 1. What is the Hazard ? 2. How do you protect yourself ? 3. What is the First Aid ? 23 FiberFax Topic 3 System Documentation & Drawings Upon successfully complete of this topic you will be able to: 1 Demonstrate the ability to use the System Owner’s Manual to determine but not limited to the following: a Identification of system specifications. (Appendix A) b Performance of preventative maintenance. (Section-5) b Removal and replacement of system components.(Section-5) 24 System Documentation & Drawings 2 Demonstrate the ability to use the system drawings to determine, but not limited to the following: a. b. c. d. e. Layout of the system, assemblies, wiring, and plumbing. Reference connections to other diagrams. Source voltage information. Component identification. Component specification. 3 Demonstrate an ability to use the electrical systems drawing to isolate and diagnose problems. 25 System Owner’s Manual Section 1 Safety Section 2 System Overview Section 3 System Operations Section 4 System Troubleshooting Section 5 System Maintenance Section 6 Spare Parts Section 7 System Drawings Section 8 Appendices Appendix A System Specifications Appendix B Glossary of Terms Appendix C Reference Manuals Appendix D MSDS Index System Drawings Installation Drawing TCA252-15-360E144 Heater Current Data Drawing W/D FCU 3615 Controller Drawing FCU to PC Connecting Cable Program Data Sheets Electrical Circuits Drawings Ground Layout Drawing Terminal Block Layout Operator Panel Assembly & Layout Drawings Calibration Procedure for Drive Controllers Calibration Procedure for Temperature Sensor Inputs Plumbing Schematics Line Numbering Line Numbering Electrical drawings have line numbers drawn along the left side. Each line number contains both a letter and a number. The letter designates a circuit group. The number locates a position on the drawing. Circuit groups may be designated differently from one BTU product to another, depending on the types of circuits included. This table shows an EXAMPLE of a circuit group set contained in a typical BTU oven or furnace A Input Power/ Heaters B Instrument Control C Drive Control D Gas Control E Controller E Alarms G – Z Optional Equipment The Circuit Groups for your BTU product are listed next. Reference Connections to Other Diagrams Ladder Logic Designation A000 – A650 Input/Heaters440-480V TCA252-15-360 B000 – B130 Instrument Power w/ UPS 120V B300 – B430 Instrument Power B900 – B990 Profile T/C C000 - C130 MC95/(2) OT/2 FCU’s/2 Contactors C300 - C430 Belt Speed/ (2) OT/ ENCDR/ Honeywell OT C600 - C730 Computer D000 - D120 3615 Alarm Inputs G000 - G120 Case Cooling H000 - H250 ACS H260 - H380 Atmosphere Control System H2/N2/AR H390 - H510 Gas Miser J000 - J110 Hygrometer K000 - K130 Water Jacket Sensor Inputs Reference Connections Reference pointer with line numbers Reference pointers direct you to the next drawing or to drawings for other circuits. The line number with each pointer identifies • The circuit group of the next drawing (D or L in the example). • The position of the connection on the next drawing (150, 430, 010). Reference pointer line numbers may also be enclosed in a box as shown in the following example. You match the drawings on the right has reference pointers. The example on the top left shows it’s reference pointer exiting on the bottom of the drawing, as you would normally hold it, but the example on the bottom has it’s reference pointer pointing to the right, both are outputs. The top right drawing section has a reference pointer coming in from the top, this indicates an input and shows where the input is coming from. Source Voltage Information Electrical diagrams which have voltages originating from other electrical diagrams are marked with the voltage level, voltage type (AC or DC) and the wire size and insulation type. A description may be included to describe the general origination of the source voltage (I.e. from input power circuits). This general description, if used, is immediately below the voltage level/type information. Source Voltage & Information Source Location Wire Information Wire Numbers Wire Color Codes COLOR Black Red CIRCUIT AND CONDUCTORS Line, load, and control circuits at line voltage AC control circuits at less than line voltage White Grounded circuit conductor (neutral) Blue DC control circuits Gray Grounded circuit conductor for UPS control circuits Yellow Green/Yellow Interlock control circuits supplied from and external power source Equipment grounding conductor Exceptions: Multi-conductor cables present an exception to the above standard color codes. Light Blue is used for the Neutral for equipment shipped to Europe (European Community). Customer specified color codes are used as required. 32 Device Codes and Types CODE TYPE OF DEVICE CODE TYPE OF DEVICE AH Alarm Horn or Audible Alarm PB Push Button CB Circuit Breaker PL Plug CR Control Relay POT Potentiometer CON Contactor PS Pressure Switch CT Current Transformer PWRS Power Supply DISC Disconnect Switch PRX Proximity Switch ENCO Optical Encoder RES Resistor EPB Emergency Push Button RECP Receptacle FS Flow Switch SOL Solenoid FU Fuse SS Selector Switch GND Ground SSR Solid State Relay HTR Heater T Transformer INST Instrument TAS Temperature Actuated Switch LS Limit Switch TB Terminal Block LT Pilot Light T/C Thermocouple MTR Motor TR Timing Relay OL Overload UPS Uninterruptable Power Supply SST - Solid State Timer Set for 30 Min 33 Component Specifications Details of component ratings etc. are shown adjacent to the symbol to add supplementary data for the component. This supplementary data indicates applicable values such as amperage, voltage, or KVA rating and the like. The following lists the minimum supplementary data for different types of components: Component Transformers (T) Circuit Breakers (CB) Motor (M) Fuse (FU) Overload (OL) Disconnect Switch (DISC) Data KVA, Primary & Secondary Voltage Amperage Rating HP, Full Load Amperage (FLA) Amperage and Type Trip Point and Range (if available) Voltage Rating, Amperage Rating Electronic Controls & Components Solid State Relays Fuses and Circuit Breakers Control Relays & Contactors Timing Relays 35 Solid State Relays 1 1 2 Heater SSR 3 1 SSR 4 3 2 Control SSR 3 2 4 + 5VDC FCU 4 E020-INST 36 Fuses & Circuit Breakers FU Fuse Symbol CB’s Circuit Breaker Symbol 1-Pole 37 2-Pole w/Thermal 3-Pole w/Magnetic Overload device Overload device Control Relays & Contactors 2 7 (Coil) N.O. Contact N.C. Contact Control Relay Types VOLTAGES - 24, 120, & 240 VAC 24 VDC # OF Pins - 5 Pin - 1 Control Legs/Contacts 8 Pin - 2 Control Legs/Contacts 11 Pin - 3 Control Legs/Contacts 38 Contactors - Used for High Voltage and High Current Needs usually at or above 120 VAC, dependent upon system needs. Additional contacts may be added. Timing Relays TDM A1 Control Voltage A2 Return/Neutral A3 May be Assumed (Coil) A1 TDB (N.O.) (N.C.) Return/Neutral A2 Control Voltage A3 Never Assumed (Coil) 39 (N.O.) (N.C.) Topic Four Objectives System Operational Theory, Maintenance and Troubleshooting 1 Understand the system theory and operation of the Paragon to include: A Oven Description B Furnace Sections 1 2 3 4 Entrance Section Process Chamber Sections Cooling Section Exit Section C Sequence of Operation 2.Understand system components and their operations, to support maintenance and troubleshooting efforts, to include: A System Features B System Controls C System Optional Equipment & Features 40 FURNACE SPECIFICATIONS Maximum Temperature Normal Operating Temperature Number of Controlled Heating Zones Working Dimensions Heated Length Belt Height Above Floor Furnace Atmosphere 41 1160°C 200-1130°C 15 Zones (Top & Bottom L,C,R) 25” Belt 2” Clearance above belt 360” 36.0” N2/H2/AR Furnace Description TCA Case Cooling Exhaust Stacks Atmosphere Curtain Cooling Section with Optional Eductors H2 Burn-Off Atmosphere Curtain H2 Burn-Off Exit Section Entrance Section Process Chamber Section 42 MC-95 & ACS Furnace Sections P150 LAYOUT System dimensions Loading Table Entrance w/ Baffle Assembly, N2 Fiberglass Curtain and Ignitor Burnoff Entrance Vestibule Zones # 1 through # 15 (24” each) Exit Vestibule Hearth Plate Cooling Water Cooling # 1 Water Cooling # 2 w/ Cross Flow Eductors Water Cooling # 3 w/ Dual Parallel Eductors Exit w/ Baffle Assembly, N2 Fiberglass Curtains and Ignitor Burnoff Frame Allowance Unloading Table Approximate System Working Length Approximate System Total Length 43 Inches 24.0” 43.0” 18.0” 360.0” 20.0” 24.0” 24.0” 36.0” 54.0” 36.0” 9.0” 24.0” 52’ 0” 56’ 0” Furnace Layout Cover Gas Inlets Ent/Exit (2 Inputs each) Fiberglass Curtain Assembly Gas Sample Lines Zones 1,4,12,15 Water Cooling # 1 Water Cooling # 3 w/ Dual Eductor Fiberglass Curtain Assembly Gas Sample Line Cooler Section 15 Heating Zones Water Cooling # 2 w/ Cross Eductor 44 Sequence of Operation Standard Features Fully Enclosed IR Heaters (Top & Bottom - L, C, R) Cover Gas Recirculation Gas Tight Redundant Overtemp Protection 3 Profile Thermocouple Ports Windows Based Operating Software 45 Redundant Conveyor Protections Emergency Off Push-Buttons Product Transport System Components and Specifications Belt type material……………Inconel 601 GC (B36-10-10) Mesh Belt Belt Type Width……………………………………………………..25” Speed, Nominal…………………………………………….….……14 IPM Speed, Range…………………………………………….……….…4-24 IPM Speed Control Accuracy…………………………..……...……..± 0.1 IPM Belt Loading…………………………..……………………...……..0.9 lb/ft2 46 Transport Conveyor Controls and Components Brushes Minimum ware is .2 Inches A1 MTR L1 L2 - BSM 0-90VDC Sig Max Sig Min Max Min IR Torque Comp + A2 0-6.72VDC +5VDC C6-9 0-5VDC Square Wave ENCO C1-3 C1-2 FCU GND Light Emitting Diode 30 Counts per Revolution C6-10 GND C6-10 C1-1 Feedback Isolation Resistor 47 5182385 560 Ω Operation BSM Potentiometers A1 L1 L2 - BSM + Sig Max SIGNAL ADJ Min/Max Set for a 0-90 VDC output at A1 and A2 Sig Min Min Max Torque IR Comp IR COMP Set to 2 O’Clock A2 TORGUE Set to 9 O’Clock MIN Set Fully Counter Clockwise (CCW) MAX Set Fully Clockwise (CW) 48 Transport Ends Heater Controls & Components Control Signal FCU Controller Thermocouple Input (Zone Temperature) Solid State Relay AC Power Input 49 Zone Heater Heater Controls & Components Control Signal FCU Controller Thermocouple Input (Zone Temperature) Solid State Relay AC Power Input 50 Zone Heater TC Heater Controls & Components T/C Troubleshooting 1. Open T/C 2. Shorted within the Zone 3. Shorted outside the Zone + 51 - 4. Reversed Wiring T/C Issues Heater Controls & Components Electrical Connections Protection Tube T/C Tips 52 Heater Controls & Components Control Signal FCU Controller PID Thermocouple Input (Zone Temperature) Solid State Relay AC Power Input 53 Zone Heater PID Algorithm P = Proportional Band (Pro-bands) 54 I = Intergral (Reset) D = Derivative (Rate) Control Coefficients PID Algorithm TEMP PRO BAND HIGH PB Power + Reset Power + Rate Power Pro Band, Reset and Rate Pro Band Only Pro Band and Reset SP PRO BAND LOW SYSTEM CALLS FOR 100 % POWER TIME 55 Heater Controls & Components Control Signal PWM FCU Controller Thermocouple Input (Zone Temperature) Solid State Relay AC Power Input 56 Zone Heater Pulse Width Modulation ZONE 57 FCU INPUT Z1T 1 Z1B 2 Z2T 3 Z2B 4 Z3T 5 Z3B 6 Z4T 7 Z4B 8 Z5T 9 Z5B 10 Z6T 11 Z6B 12 Z7T 13 Z7B 14 PWM CYCLE 1 2 3 4 1 2 3 4 1 2 3 4 1 2 2 Second Time Period PWM Time period is 1/2 of a second Pulse Width Modulation ZONE 58 FCU INPUT Z1T 1 Z1B 2 Z2T 3 Z2B 4 Z3T 5 Z3B 6 Z4T 7 Z4B 8 Z5T 9 Z5B 10 Z6T 11 Z6B 12 Z7T 13 Z7B 14 PWM CYCLE 1 2 3 4 1 2 3 4 1 2 3 4 1 2 2 Second Time Period The #1 PWM’s turns on the SSR for 1/2 of a second @ 100 % Power. Pulse Width Modulation ZONE 59 FCU INPUT Z1T 1 Z1B 2 Z2T 3 Z2B 4 Z3T 5 Z3B 6 Z4T 7 Z4B 8 Z5T 9 Z5B 10 Z6T 11 Z6B 12 Z7T 13 Z7B 14 PWM CYCLE 1 2 3 4 1 2 3 4 1 2 3 4 1 2 2 Second Time Period The #2 PWM’s turns on the SSR for 1/2 of a second @ 100 % Power. Pulse Width Modulation ZONE 60 FCU INPUT Z1T 1 Z1B 2 Z2T 3 Z2B 4 Z3T 5 Z3B 6 Z4T 7 Z4B 8 Z5T 9 Z5B 10 Z6T 11 Z6B 12 Z7T 13 Z7B 14 PWM CYCLE 1 2 3 4 1 2 3 4 1 2 3 4 1 2 1 Second Time Period The #3 PWM’s @ 100 % Power turns on the SSR for 1/2 of a second Pulse Width Modulation ZONE 61 FCU INPUT Z1T 1 Z1B 2 Z2T 3 Z2B 4 Z3T 5 Z3B 6 Z4T 7 Z4B 8 Z5T 9 Z5B 10 Z6T 11 Z6B 12 Z7T 13 Z7B 14 PWM CYCLE 1 2 3 4 1 2 3 4 1 2 3 4 1 2 2 Second Time Period The #4 PWM’s turns on the SSR for 1/2 of a second @ 100 % Power. Pulse Width Modulation ZONE 62 FCU INPUT Z1T 1 Z1B 2 Z2T 3 Z2B 4 Z3T 5 Z3B 6 Z4T 7 Z4B 8 Z5T 9 Z5B 10 Z6T 11 Z6B 12 Z7T 13 Z7B 14 PWM CYCLE 1 2 100 % 3 4 1 2 3 4 1 2 3 4 1 2 2 Second Time Period 75 % 50 % 25 % Heater Controls & Components Control Signal FCU Controller Thermocouple Input (Zone Temperature) Solid State Relay AC Power Input 63 Zone Heater HEATERS Heater Controls & Components Top Heaters Power KW at 109.3 / 218.5 / 109.3 Line Voltage Heater Current Ohms (HOT) Watts / SQ. Inch Plate Length Plate Width Plate Thickness Wire Gage Material 0.750 Dia Grooves_Wire Groove Space Total Groove Length Close Wound Coil Stretch Lead Gage Ohms Cold Total Ohms Cold Min. Ohms Cold Max. Parallel Windings R 64 R L C R 1.6 3.2 220 14.6 14.9 4.9 24.00 33.00 2.5 10 KA-1 10 1.50 220.0 102.9 2.8 5 14.4 13.7 15.1 No 1.6 7.5 5 1.50 110.0 51.4 7.2 6.8 7.5 No C C L 7.5 5 1.50 110.0 51.4 7.2 6.8 17.5 No L Heater Controls & Components Bottom Heaters Power KW at 54.6 / 109.3 / 54.6V Line Voltage Heater Current Ohms (HOT) Watts / SQ. Inch Plate Length Plate Width Plate Thickness Wire Gage Material 0.750 Dia Grooves_Wire Groove Space Total Groove Length Close Wound Coil Stretch Lead Gage Ohms Cold Total Ohms Cold Min. Ohms Cold Max. Parallel Windings 65 L C R 1.20 2.40 220 22.0 5.0 7.7 11.00 31.00 2.00 9 KA-1 10 1.50 100.0 49.2 2.0 5 4.8 4.6 5.0 No 1.20 2.5 5 1.50 50.0 24.6 2.4 2.3 2.5 No 2.5 5 1.50 50.0 24.6 2.4 2.3 2.5 No Heater Layout 66 Over-Temperature Protection Alarm LED Indicators OVER TEMPERATURE MODULE 1 CH 1 2 3 CH 2 4 5 6 7 J2 J1 9 CH 5 10 CH 6 RESET PWR ON J3 67 CH 7 CH 8 J4 CH 3 CH 4 8 Reset Button (Same Function as Heat Off/On Switch) T/C Input Connecto rs J1, J3, and J4 CH 9 CH 10 Channels 7 through 10 are Omitted in 6 Channel Version. The Overtemperature Module’s setpoints are preset at the factory (to 315°C) and should not be changed. Each heated zone is monitored by an overtemperature T/C that is independent from the zone control circuitry. If any zone exceeds the preset safe maximum temperature, the overtemp condition causes the module to shut off all heater power (C060-CON) and generates an alarm with the WINCON software. Conveyor is maintained running. Over-Temperature Protection Module System Gas Feed Flowmeters Gas Feed Flowmeters 70 Entrance Curtain Bottom/Top (N2) 2 Flowmeters Entrance Venturi (N2) 1 Flowmeter Argon Cover Gas (AR) 1 Flowmeter Nitrogen Cover Gas (N2) 1 Flowmeter Hydrogen Cover Gas (H2) 1 Flowmeter Nitrogen Purge Gas (N2) 1 Flowmeter Exit Venturi (N2) 1 Flowmeter Exit Curtains (N2) 1 Flowmeter Eductor Criss Cross Cooling Section (H2) 2 Regulator Eductor Dual Feed Cooling Section (N2 or AR) 2 Regulators Gas Plumbing Entrance Curtain Bottom Entrance Curtain Top Muffle Cover Gas Entrance Venturi Exit Venturi FA Exit Curtains Eductor Criss Cross FA FA 1-FM N2 2-FM N2 3-FM N2 4-FM AR 5-FM N2 6-FM H2 7-FM Purge 3-SOL Notes: 1. All H2 Flowmeters are to be 100 % Inspected. 3-PS Sample 8-FM N2 2-SOL 1-SOL 5-SOL 7-FM N2 4-SOL 2-PS Sample Gas Miser 1-PS Sample 2. Customer to supply 10 Micron Filter for H2 Gas. 3. H2 Gas must be free of oil. 4. Set all pressure switches at 9 PSIG. 5. N2 May mix on power failure. AR H2 N2 10-20 PSIG 10-20 PSIG 10-20 PSIG Eductor Dual Feed Gas Modes Mode 1-SOL 2-SOL 3-SOL 4-SOL 5-SOL Purge OFF OFF OFF OFF OFF N2/H2 ON ON ON OFF OFF GAS MISER OFF OFF OFF ON OFF AR/H2 ON OFF ON OFF ON Muffle Cover Gas Staggered Hole Orientation +/- 30 degrees Internal Gas Flow Burn-Offs Burn-Off Coil Cooling Sections Cooling Sections Eductors Cooling Monitoring 77 Furnace Controls WINCON / 3615 FCU Controller System Software OPERATOR Controls 78 WINCON / 3615 FCU Controller Minimum recommended computer requirements: IBM compatible with MS-DOS and WINDOWS 8MB main memory and battery backup clock 120MB hard drive and one 3-1/2” high density floppy drive One parallel printer port, and two RS-232 serial ports 14” VGA color graphics monitor Keyboard (mouse or trackball optional) 79 5057631 RS232-3615 WINCON Software Operating Software 80 Windows TM Platform GEM Available Extensive Security Features Extensive data Collection Capability Flexible Time and Sequence Scheduling Operator Control Panel 81 Atmosphere Control Panel ATMOSPHERE CONTROL SYSTEM BURNOFF FAILURE ON/OFF 1 TIMED 2 3 4 5 PURGE PURGE RESET FAILURE PURGE 1 2 OPERATING MODE PURGE TIMED PURGE COVER GAS 3 4 6 PURGE TIME HEATER POWER OFF SAFE EXTERNAL FAIL READY Gas Miser 4-SOL Gas Sampling 84 Topic 5 WINCON Upon successfully complete of this topic you will be able to: 1 Given a PC Loaded with WINCON software, log on, change recipes, view alarms, open System Monitor Pages, monitor system performance and log off the system. 2 Given a PC Loaded with WINCON software, acknowledge, silence and clear alarms, perform preventative maintenance on the PC and perform (non-yearly) system calibrations. 85 Furnace Control Unit (FCU) Board FCU description: The Furnace Control Unit (FCU) is an independent Z80 based Microprocessor controller board. The board will operate with only a 15 volt DC power supply. No other external connections and apparatus are need for it to operate. The FCU is normally connected to a IBM compatible PC, to simplify programming and for storage of information. A PC with WINCON® software operating an a RS-232 (COM) port interface with the FCU. The FCU is equipped with 31 analog inputs and 36 analog output, they are generally used as closed looped controlled I/Os. These ports are used to control heated zones, static pressure in a close loop configurations. The analog inputs can be used without outputs to monitor activities like O2 or dew point. The analog outputs can also used independent of inputs. Equipment with cooling fan control operate this way, to allow the FCU to control fan RPM. We utilize 16 digital output to control external options like Gas flow. Sixteen digital inputs, monitor external events and alarm condition such as Low Pressure switches. There is Lithium battery pack on every FCU board to maintain data time and configurations for a ten year period. This allows the FCU board to maintain information on how long it has been on or off and all calibration values. 86 Tool Bar Status Indicator Display Status Button INIT Description This is your furnace’s state when first turned on (i.e., initializing). In this state, communication between the PC and the FCU are established, but the FCU has not completed its initialization. The initialization process may take several seconds. (Displayed in black text with a yellow background). The furnace is in the idle state when the heater power contactor has not been turned on yet. (Shown in black text on a yellow background). IDLE SETUP READY After changing the recipe, the furnace stays in the SETUP state until the temperature reaches the alert band and remains within this band during the preready dwell time with no alarms. (Black text, yellow background). Furnace has stabilized and is ready to process (shown in black text with a green background). The READY state occurs after the time-out of the pre-ready dwell period if no alert or alarm conditions exist. In addition, the following conditions must also be met: Temperature is within the alert/alarm band Conveyor speed is within the alert/alarm band Edge conveyor chain is at the correct width Other conditions may exist depending on options HOLD 87 Power has been off longer than the power down time limit (shown with black text on a yellow background). In the HOLD state, the controller maintains the temperature levels that existed in the furnace when power was restored Tool Bar Status Indicator Alarm States Display Status Button Description Indicates the presence of alert conditions (shown in flashing black text on a yellow background). You must correct the problem to clear the alert ALERT ALARM 88 Indicates the presence of alarm conditions (shown in flashing white text on a red background). You can silence the audible alarm by acknowledging it in the Status/Alarms screen. You must correct the problem to clear the alarm. Recipe Windows and Tables Recipe Window Setpoints Recipe Window Included Tables Temperature Zone Setpoint Table Conveyor Fields Setpoint Table Equipment Options Setpoint Table Pressure Zone Setpoint Table Product Line Setpoint Table Mass Flow Setpoint Table PID/Trim Recipe Window Temperature Zone PID/Trim Settings Table Pressure Zone PID/Trim Settings Table Atmosphere Control Table Alarms Recipe Window Temperature Setpoint Alarms Table Conveyor Belt Speed Alarms Table Pressure Zone Setpoint Alarms Table Mass Flow Alarms Table Atmosphere Monitoring Thresholds Table Atmosphere Control Alarms Table Temperature Output Alarms Table Mass Flow Output Alarms Table Pressure Zone Output Alarms Table 89 Topic 6 Preventative Maintenance Applications 90