* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download C2 Why are high voltages used for transmission?
Electric power system wikipedia , lookup
Variable-frequency drive wikipedia , lookup
Buck converter wikipedia , lookup
Utility frequency wikipedia , lookup
Electrification wikipedia , lookup
Switched-mode power supply wikipedia , lookup
Transmission tower wikipedia , lookup
Telecommunications engineering wikipedia , lookup
Stray voltage wikipedia , lookup
Overhead power line wikipedia , lookup
Voltage optimisation wikipedia , lookup
Three-phase electric power wikipedia , lookup
Mains electricity wikipedia , lookup
Alternating current wikipedia , lookup
Distribution management system wikipedia , lookup
Power engineering wikipedia , lookup
Rectiverter wikipedia , lookup
Electric power transmission wikipedia , lookup
Electrical substation wikipedia , lookup
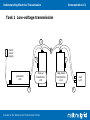
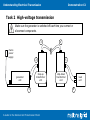
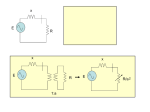
Understanding Electrical Transmission Demonstration C2 Demonstration C2 Why are high voltages used for transmission? A Guide to the National Grid Transmission Model Understanding Electrical Transmission Demonstration C2 Task 1 Low-voltage transmission 3 mains power supply 2 step-up transformer unit generator unit 1 A Guide to the National Grid Transmission Model 4 5 step-down transformer unit load unit 6 Understanding Electrical Transmission Demonstration C2 1. Can the generator provide enough power for the maximum load on the load unit? The voltage across the transmission leads is now measured at the start and at the end. 2. What is the voltage across the transmission leads at the start? What is the voltage across the transmission leads at the end? 3. What causes this difference? A Guide to the National Grid Transmission Model Understanding Electrical Transmission Demonstration C2 Task 2 High-voltage transmission Make sure the generator is switched off each time you connect or disconnect components. 3 mains power supply 2 step-up transformer unit generator unit 1 A Guide to the National Grid Transmission Model 4 5 step-down transformer unit load unit 6 Understanding Electrical Transmission Demonstration C2 4. Can the generator provide enough power for the maximum load on the load unit? 5. What effect does using a higher voltage for the transmission leads have? Why is this? The voltage across the transmission leads is now measured at the start and at the end. 6. What is the voltage across the transmission leads at the start? What is the voltage across the transmission leads at the end? 7. How does the voltage drop for high-voltage transmission compared to that for low-voltage transmission? Why is this? A Guide to the National Grid Transmission Model Understanding Electrical Transmission Demonstration C2 Task 3 Measuring frequency 8. How does the frequency at the generator compare to the frequency at the load? 9. What effect does increasing the load have on the frequency? 10. How can a constant frequency be maintained even if the size of the load varies? A Guide to the National Grid Transmission Model