* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Causes of Motor Failures
Ground (electricity) wikipedia , lookup
Electrification wikipedia , lookup
Electric machine wikipedia , lookup
Transformer wikipedia , lookup
Pulse-width modulation wikipedia , lookup
Power inverter wikipedia , lookup
Electrical ballast wikipedia , lookup
Power engineering wikipedia , lookup
Current source wikipedia , lookup
Brushless DC electric motor wikipedia , lookup
Electric motor wikipedia , lookup
Schmitt trigger wikipedia , lookup
Transformer types wikipedia , lookup
Electrical substation wikipedia , lookup
Resistive opto-isolator wikipedia , lookup
History of electric power transmission wikipedia , lookup
Power electronics wikipedia , lookup
Power MOSFET wikipedia , lookup
Distribution management system wikipedia , lookup
Opto-isolator wikipedia , lookup
Buck converter wikipedia , lookup
Voltage regulator wikipedia , lookup
Switched-mode power supply wikipedia , lookup
Three-phase electric power wikipedia , lookup
Induction motor wikipedia , lookup
Rectiverter wikipedia , lookup
Surge protector wikipedia , lookup
Stray voltage wikipedia , lookup
Brushed DC electric motor wikipedia , lookup
Alternating current wikipedia , lookup
Mains electricity wikipedia , lookup
Variable-frequency drive wikipedia , lookup
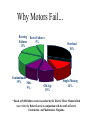
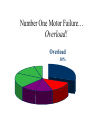
RMM Systems, LLC By Sam Rietta RMM Systems, LLC is a manufacturer's representative firm focused on providing value added sales solutions by providing customer service, technical support and application assistance to our customers, design engineering firms and specification authorities. It is our goal to provide a high degree of professionalism to complement the image and objectives of the leading manufacturer's of electrical equipment we represent. Have you ever lost a motor? • • • • • Caused a loss of production? After a storm? Same motor over and over again? While you were away from the plant? Something happened on the power company side. • Didn’t know why? Why Do Motors Fail? Common Causes of Motor Failures Costs Associated with Motor Failures • • • • • • Equipment downtime $$$$ Loss of production Collateral equipment damage Equipment replacement Work in process damage Overtime for repair crews Motor Windings Breakdown • Thermal • Mechanical • Environmental Thermal Breakdown • Rule of thumb: A 10o C temperature rise above rated temperature will half the life of a motor • Motor operating temperature is based on: • 40o C ambient temperature • Class B Insulation limit is 130o C • Class F Insulation limit is 155o C Thermal Breakdown Causes: • Overload • Voltage Variations • Single Phasing • Short Cycle • Lightning and Surges • Improper Ventilation • Dirt & Dust Accumulation Mechanical Breakdown Causes: • Bearing failure resulting in rotor or stator rubbing insulation off • Vibration • Improper Alignment Bearing Failure Causes • Improper lubrication • Excessive belt tension • Mis-alignment Environmental Breakdown Causes: • Moisture / Water • Corrosion/ Chemicals • Rodents & Insects • Age Causes of Motor Failures Overcurrent 30% Mechanical 44% Other 12% 44 % of all motors failures are due to overloads and Single Phasing single-phasing. 14% Why Motors Fail... Bearing Failures 13% Rotor Failures 5% Contaminants 19% Misc 9% Old Age 10% Overload 30% Single Phasing 14% * Based on 9,000 failure events researched by the Electric Motor Manual which was written by Robert Lawrie in conjunction with the staff at Electric Construction and Maintenance Magazine. Number One Motor Failure… Overload! Overload 30% Overloads “ It is practically impossible to burn out a motor from overload when it is protected by properly sized and maintained motor protection devices”. William P. Maples, P.E. Motor Protection Device % FLA Overloads Fuses (Dual Element) Fuses (Fast Acting) Circuit Breakers MCP 115% 125%-225% 400%a 400%b 800%-1700% NEC 430-32,52 A 300% FLA for non time delay fuses exceeding 601 amps B 300% FLA for inverse time circuit breakers for motor FLA exceeding 100 amps Motor Service Factor Motor service factor of 1.15 means that the temperature rise of a motor will not exceed design temperature even if the motor is carrying a continuous overload of 15% U.L and IEC Test Procedures • U.L. 508 Determines test procedures for motor starters. • U.L. Short Circuit test procedures – Starter door cannot be blown open – Contacts must not disintegrate – Overload burnout is allowed with breaker tests. Short Circuit Protection of Motor Controllers Motor Controller HP Rating Test Short Circuit Current Available 1 HP or less and 300V or less 1,000 A 50 HP or less 5,000 A Greater than 50 HP to 200 HP 10,000 A 201 HP to 400 HP 18,000 A IEC Standards • IEC Publication 947 “Low Voltage Switchgear and Control” IEC Levels of Motor Starter Protection • Type 1 Protection. – No discharge of parts beyond the enclosure is allowed – Damage to the contactor and overload relay is acceptable IEC Levels of Motor Starter Protection • Type 2 Protection. – No damage is allowed to either the contactor or overload relay – Light contact welding is allowed, but must be easily separable Voltage • Voltage Variations • Phase imbalance • Phase loss (Single Phasing) Voltage Variation Nema Standards states that motors shall operate successfully at rated load under the following conditions: • +/- 10% variation of rated voltage at rated frequency • Any voltage drop below 10% will reduce starting torque which can be serious because starting times may increase beyond allowable limits. Winding failure from extreme voltage variations are identical to those of overloads because the input current is uniformily excessive. • Low Voltage… Cause • Demand for power is greater than the supply • Long cable runs • Overloaded transformers • Distribution system Low Voltage… Effect • Reduced efficiency • Reduced life expectancy • Increased temperatures • Increased current • Lower torque High Voltage… Definition Operating a motor above 110% of nameplate voltage High Voltage… Cause • Poor line regulation • Incorrect transformer tap • Utility demand down High Voltage… Effect • • • • • Reduced efficiency Reduced power factor Increased power consumption Increased current Increased temperature Voltage Unbalance Percent voltage unbalance = 100 x Maximum voltage deviation from average voltage average voltage Voltage Unbalance example: Assume voltages to a motor are 228 V to Phase A, 220V to Phase B and 236 V to Phase C. The average voltage is 228 V. The voltage unbalance is as follows: Voltage imbalance = 236-228 x 100 = 3.5% 228 Effect of Voltage Unbalance on Motor Longevity Effects of Voltage Unbalance Horsepower Derating Another Rule of Thumb…………. A 3.5% voltage unbalance will cause a 25% temperature rise. An increase in temperature rise in the phase with the highest current is 2 times the square of the voltage imbalance Causes of Voltage Unbalance: • • • • • • • Unequal loading of a three phase system Unequal tap settings on transformers Loose connections in the power system Damaged starter contacts Open delta transformer systems Storms (wind, fallen trees, lightning) Poor regulation by utility Example of heat rise due to voltage variations 50 HP Motor Heat rise Ambient Temperature 8% Unbalance Effect: 60oC 40oC 76oC (8x8=64 x 2= 128% x 60oC= 76oC) 176oC Result: Motor Failure 14% of All Motor Failures Single Phasing Single Phasing 14% Secondary Single Phasing Secondary Single Phasing Causes of Secondary Single Phasing • • • • • • • Damaged motor starter contact Burned open overload relay Damaged switch or circuit breaker Blown fuse Open cable or bus on transformer secondary Open motor winding Open transformer winding Primary Single Phasing Primary Single Phasing Causes of Primary Single Phasing • Open line on primary – Storm (wind, ice, fallen trees, lightning) – Vehicle striking utility pole – Construction mishaps • Blown Primary fuse • Open contact on utility contactor or re-closer • Open winding on transformer RMM Systems In conclusion: • Motors will last a long time if operated within their design parameters. ( Voltage, current & temperature) • Identify the cause of your motor failure • When replacing motors also consider changing overloads and motor start contacts • For critical motors incorporate the latest motor monitoring products. Thank you! From RMM Systems