* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Plants – Characteristics and Function --
Gartons Agricultural Plant Breeders wikipedia , lookup
Photosynthesis wikipedia , lookup
History of herbalism wikipedia , lookup
Plant stress measurement wikipedia , lookup
Plant secondary metabolism wikipedia , lookup
Plant use of endophytic fungi in defense wikipedia , lookup
Plant breeding wikipedia , lookup
History of botany wikipedia , lookup
Plant defense against herbivory wikipedia , lookup
Venus flytrap wikipedia , lookup
Historia Plantarum (Theophrastus) wikipedia , lookup
Ornamental bulbous plant wikipedia , lookup
Plant nutrition wikipedia , lookup
Plant physiology wikipedia , lookup
Plant morphology wikipedia , lookup
Plant ecology wikipedia , lookup
Evolutionary history of plants wikipedia , lookup
Perovskia atriplicifolia wikipedia , lookup
Plant evolutionary developmental biology wikipedia , lookup
Plant reproduction wikipedia , lookup
Flowering plant wikipedia , lookup
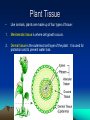
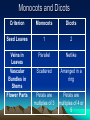
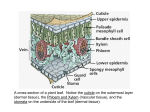
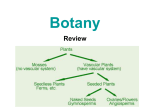
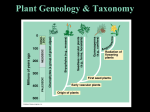
Plants – Characteristics and Function Evolution of Plants • Scientists believe that terrestrial plants evolved from green algae as both show the following similarities: • Use starch as their primary food reserve • Have cellulose in their cell walls • Use chlorophyll a and b for photosynthesis Evolution of Plants • In order to adapt to the drier, terrestrial environment, plants developed specialized structures to avoid water loss (bark), obtain nutrients (roots, stems, leaves) and reproduce/grow (spores, seeds, flowers) Evolution of Plants • The first plants were nonvascular, like moss, that depended on osmosis and diffusion to get water and nutrients. • Vascular plants evolved which had specialized cells used for the transport of water (Xylem) and nutrients (Phloem), called vascular tissue. Plant Tissue • Like animals, plants are made up of four types of tissue: 1. Meristematic tissue is where cell growth occurs. 2. Dermal tissue is the outermost cell layer of the plant. It is used for protection and to prevent water loss. Plant Tissue 3. Ground tissue is the inner cell layers of the plant that is not vascular tissue. This is where nutrients are stored and where the plant does photosynthesis. 4. Vascular tissue are the cells involved in transporting water and nutrients through the plant. Main types of vascular plants • Gymnosperms: mainly coniferous trees, seeds appear on cones, make up the majority of Canadian forests, termed ‘softwood’ by lumber companies and provide most of the money earned by Canada’s forestry industry. Main Types of Vascular Plants • Angiosperms: many more species than gymnosperms, live in a wider variety of habitats, use flowers to reproduce and encase the seed in a ‘fruit’, divided into monocots and dicots. Monocots and Dicots Criterion Monocots Dicots Seed Leaves 1 2 Veins in Leaves Vascular Bundles in Stems Flower Parts Parallel Netlike Scattered Arranged in a ring Petals are multiples of 3 Petals are multiples of 4 or 5 Monocots • Only about 10% have a woody stem (bamboo and palm trees). • Most have a herbaceous stem which is soft and fleshy (grass, tulips, etc…) • Rice, corn, wheat, onions, carrots, … Dicots • Deciduous trees are dicots. • Termed ‘hardwood’ and make up a good portion of the lumber industry in Canada. • Other dicots: beans, potatoes, most wildflowers and salad ingredients (tomatoes, lettuce, cabbage, radishes…)