* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Chapter 4: Plants
History of herbalism wikipedia , lookup
Ecology of Banksia wikipedia , lookup
Photosynthesis wikipedia , lookup
Plant stress measurement wikipedia , lookup
Gartons Agricultural Plant Breeders wikipedia , lookup
History of botany wikipedia , lookup
Historia Plantarum (Theophrastus) wikipedia , lookup
Evolutionary history of plants wikipedia , lookup
Plant defense against herbivory wikipedia , lookup
Plant use of endophytic fungi in defense wikipedia , lookup
Plant nutrition wikipedia , lookup
Ornamental bulbous plant wikipedia , lookup
Plant secondary metabolism wikipedia , lookup
Plant breeding wikipedia , lookup
Plant physiology wikipedia , lookup
Pollination wikipedia , lookup
Plant evolutionary developmental biology wikipedia , lookup
Plant morphology wikipedia , lookup
Plant ecology wikipedia , lookup
Sustainable landscaping wikipedia , lookup
Perovskia atriplicifolia wikipedia , lookup
Plant reproduction wikipedia , lookup
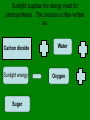
Chapter 4: Plants Mrs. Campogni Vocabulary Photosynthesis Xylem Phloem Pollen Pollination Embryo Spore Tropism Growth hormone Photosynthesis is the process that plants and some other organisms use to make sugar for food. A grainy, often yellow powder, made in a plant’s tissue at the top of each stamen is called pollen. These tubes carry materials from the roots to the leaves. They are called the xylem. Phloem tissues are tubes that carry sugar away from the leaves to the rest of the plant. Moving pollen from the stamen to the pistil is called pollination. Pollination takes place in different ways. Wind can move pollen. Water can move pollen. Insects going from flower to flower can move pollen. Bats going from flower to flower can move pollen. Birds going from flower to flower can move pollen. A seed is made of three main parts, the seed coat, embryo, and endosperm. Bean Seed An embryo has structures called seed leaves or cotyledons. Seeds with ONE cotyledon are called monocots. Seeds with TWO cotyledons are called dicots. Spreading Seeds Animals can spread seeds when they eat berries. The berry seeds pass through their digestive systems. Some seeds such as the coconut can float on ocean currents and be carried for many miles. Burrs can get tangled on an animal’s fur and may be carried far away from the parent plant. Once the seed is moved from the parent plant, the embryo will stay in the seed until the outside conditions, such as temperature and moisture, are right. Mosses and ferns are plants that do not make flowers. The life cycles of these plants have 2 parts. Part I: Fertilization Part II: Reproduction A plant spore is a single plant cell that can develop into a new plant. Examples of plants with spores = moss and ferns Tropisms are ways that plants change their direction of growth in response to the environment. It often occurs when the environment changes the amount that cells grow on different sides of a plant. A growth hormone is a kind of chemical that affects plant growth. These chemicals cause more cells to grow in the plant. These chemicals can also make plant cells grow larger. Plants make their own growth hormones. Sunlight supplies the energy need for photosynthesis. The process is often written as: Carbon dioxide Sunlight energy Sugar Water Oxygen Parts of a flower Can you answer the following questions? Record your answers in your science journal. Q. 1: In what part of the plant does photosynthesis occur? (page 96) Q. 2: Thousands of sugars combine in plants to form what chemical? (page 96) Q. 3: Plants that have a xylem and a phloem are called _____ plants. (page 98) Q. 4: Name two types of root systems. Provide a definition for each. (page 100) Q. 5: Why are roots important to plants? List three reasons. (page 101) Q. 6: What is the difference between a pistil and a stamen? (page 102) Q. 7: List the eight parts of a flower. Provide a definition of each. Draw a diagram of a flower and label the parts. (pages 102-103)