* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download SECTION 2 - Florida Union Free School District
Photosynthesis wikipedia , lookup
Plant stress measurement wikipedia , lookup
Plant secondary metabolism wikipedia , lookup
Plant nutrition wikipedia , lookup
Plant defense against herbivory wikipedia , lookup
Plant use of endophytic fungi in defense wikipedia , lookup
Plant breeding wikipedia , lookup
History of herbalism wikipedia , lookup
History of botany wikipedia , lookup
Plant evolutionary developmental biology wikipedia , lookup
Perovskia atriplicifolia wikipedia , lookup
Plant physiology wikipedia , lookup
Plant morphology wikipedia , lookup
Plant ecology wikipedia , lookup
Flowering plant wikipedia , lookup
Historia Plantarum (Theophrastus) wikipedia , lookup
Evolutionary history of plants wikipedia , lookup
Ornamental bulbous plant wikipedia , lookup
Sustainable landscaping wikipedia , lookup
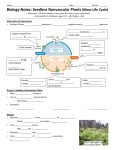
SECTION 2 SEEDLESS REPRODUCTION Importance of spores Use spores to reproduce In sporophyte stage, sex cells are produced in spore cases Spores are released and spread by wind, water, and animals becoming new plants Can be from vascular or nonvascular plants Nonvascular seedless plants Mosses, liverworts and hornworts Life cycle similar to sexual reproduction Moss lifecycle Plant looks green – (gametophyte stage). produces sex cells Moss looks brownish – (sporophyte stage). grows little stalks Tip of stalks contains spores for making new moss Nonvascular plants and asexual reproduction Pieces of plants (cuttings) can grow into new plants and form sex cells Vascular seedless plants and fern life cycle Most are ferns and have fronds as leaves Grow from a rhizome which can form new plant asexually Roots grow from rhizome Produce spores in sori, located on underside of frond Spores grow into a green, heart shaped prothallus that has chlorophyll