* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Ch18 Student Presentation
Survey
Document related concepts
Island restoration wikipedia , lookup
Reforestation wikipedia , lookup
Theoretical ecology wikipedia , lookup
Ecological resilience wikipedia , lookup
Ecosystem services wikipedia , lookup
Mission blue butterfly habitat conservation wikipedia , lookup
Restoration ecology wikipedia , lookup
Operation Wallacea wikipedia , lookup
Biological Dynamics of Forest Fragments Project wikipedia , lookup
Reconciliation ecology wikipedia , lookup
Private landowner assistance program wikipedia , lookup
Biodiversity action plan wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
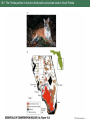
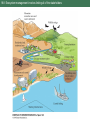
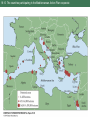
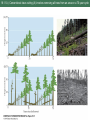
-more than 80% of the world's land will remain outside of protected areas according to even the most optimistic predictions and numerous rare species will occur outside of protected areas -60% of species that are globally rare or listed under ESA are found on private land -human use of these unprotected lands vary and significant portions harbor some of the original biota Figure 18.1 18.1 Landscapes vary in the extent to which humans have altered patterns of species composition and natural vegetation cover Strategies that encourage private landowners and government managers of resource protected areas to protect rare species and communities is essential for conservation Ex Florida panther has ½ land in its range privately owned and 200,000 ha more are needed to ensure survival Instead, paying willing landowners to minimize habitat fragmentation and to maintain forest and swamp habitats. Also have built road underpasses to minimize road kills Exs. Florida panther Figure 18.2 Management of species on military lands like the Regal fritilary butterfly Box 18.1 European NATURA program pays farmers to maintain traditional wildflowers of farmland Figure 18.5 and coffee plantations that cultivate beans in the shade with high biodiversity are subsidized in Latin America Figure 18.6 18.2 The Florida panther is found on both public and private lands in South Florida Box 18.1 Military management of the regal fritillary butterfly 18.5 Wildflowers of European cultivated fields increase due to less herbicides and fertilizers 18.6 Two types of coffee management systems: (A) Shade coffee (B) Monoculture of sun coffee 18.7 In west, agencies of the U.S. government owns most land and uses ecosystem management Ecosystem Management -discipline that integrates scientific knowledge of ecology with the sociopolitical values with the goal of protecting native ecosystem integrity over the long term Figure 18.8 Important considerations in ecosystem management: 18.8 Ecosystem management involves linking all of the stakeholders Example of Ecosystem Management Malpai Borderlands Group -partnership between ranchers, government agencies, and the Nature Conservancy using ecosystem management on over 400,000 ha (one million acres) of unique, rugged mountain and desert habitat along the Arizona and New Mexico border -one of the richest biological areas in the USA with Mexican jaguars, 265 species of birds, 90 species of mammals, 19 threatened and endangered species and many rare and endemic species -doing controlled burns, re-introducing native grasses, and avoiding habitat fragmentation 18.9 The Malpai Borderlands Group encourages ecosystem management Bioregional Management -ecosystem management that focuses on a large single ecosystem Examples: 1) Mediterranean Action Plan Figure 18.10 -21 countries with numerous pnas work together to try and control pollution, which is one of the biggest threats to pnas 2) Management of Pacific Northwest Forests -partnership between states, ranchers, government agencies, and various private organizations -coniferous forest of the Pacific Northwest have at least a few old trees, dead standing trees and fallen trees -conventional logging practice was clearcutting where all living and dead trees of all ages are removed -ecosystem managers use a method called ecological forestry that involves leaving a low density of large live trees, standing dead, and fallen trees Figure 18.11 B -less profits for timber companies and environmentalist want to preserve some old growth forest. Compromises will have to be reached. Bioregional Management Examples (cont.) 3) Africa -many of Africa’s large animals are not in pnas -many new programs are allowing rural communities and private landowners to profit from the presence of these large animals -50 conservancies exist in Namibia protecting 14% of Namibia’s area Figure 18.12 -many of these conservancies are financially benefitting and improving their towns and number of animals is increasing Figure 18.13 18.10 The countries participating in the Mediterranean Action Plan cooperate 18.11 A) Conventional clear-cutting (A) involves removing all trees from an area on a 70-year cycle 18.12 The distribution of community conservancies and state protected lands in Namibia 18.13 Number of animals observed in aerial censuses of the Nyae Nyae Community Conservancy