* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download PHY 231 Lecture 29 (Fall 2006)
Electric charge wikipedia , lookup
Casimir effect wikipedia , lookup
Neutron magnetic moment wikipedia , lookup
Superconducting magnet wikipedia , lookup
Earth's magnetic field wikipedia , lookup
Magnetometer wikipedia , lookup
Giant magnetoresistance wikipedia , lookup
Magnetotellurics wikipedia , lookup
Electromotive force wikipedia , lookup
Magnetic monopole wikipedia , lookup
Electricity wikipedia , lookup
Magnetochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Magnetoreception wikipedia , lookup
Magnetotactic bacteria wikipedia , lookup
Friction-plate electromagnetic couplings wikipedia , lookup
Magnetohydrodynamics wikipedia , lookup
Electromagnetic field wikipedia , lookup
Ferromagnetism wikipedia , lookup
Force between magnets wikipedia , lookup
Electromagnetism wikipedia , lookup
History of geomagnetism wikipedia , lookup
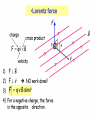
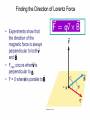
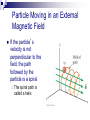
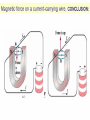
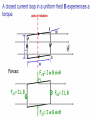
Physics 213 General Physics Lecture 9 Last Meeting: Magnetism & Magnetic Field Today: Lorentz Force and Torque 1 2 3 4 Determining the Direction of Force, the Right Hand Rule Point your fingers in the direction of v Curl the fingers in the direction of the magnetic field, B Your thumb points in the direction of the force, F , on a positive charge If the charge is negative, the force is opposite that determined by the right hand rule ┴ ┴ 6 7 Circular Orbit of Charged Particle in a Magnetic Field mv r qB Particle Moving in an External Magnetic Field If the particle’s velocity is not perpendicular to the field, the path followed by the particle is a spiral The spiral path is called a helix Force on a Wire B is into the page The current is up the page The force is to the left 10 Force on a Wire (cont.) B is into the page The current is down the page The force is to the right 11 Force on a Wire The magnetic force is exerted on each moving charge in the wire The total force is the sum of all the magnetic forces on all the individual charges producing the current F = B I ℓ sin θ θ is the angle between B and the direction of I The direction is found by the right hand rule, placing your fingers in the direction of I instead of v 12 How is force determined? Force on each charge carrier. Fi qvd B sin Total number of charge carriers. N nAl Total Force Ftotal nAqvd Bl sin IBl sin In lecture 5 we derived I nAqvd 13 14 Demo Wire in Magnetic Field 15 16 *Important: This is not the same as in the previous slide. is now the angle between the radius vector and the force vector. θ ┴ θ 17 Torque on a Current Loop, The Standard Convention Applies to any shape loop N is the number of turns in the coil Torque has a maximum value of NBIA When = 90° Torque is zero when the field is perpendicular to the plane of the loop 18 Motors 19 μ= ┴ θ μ μ θ 20