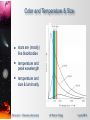
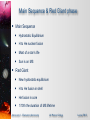
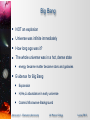
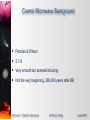
* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Review Astronomy 1 — Elementary Astronomy LA Mission College Spring F2015
Rossall School wikipedia , lookup
X-ray astronomy satellite wikipedia , lookup
Geocentric model wikipedia , lookup
Kepler (spacecraft) wikipedia , lookup
Extraterrestrial life wikipedia , lookup
Space Interferometry Mission wikipedia , lookup
International Ultraviolet Explorer wikipedia , lookup
Astrobiology wikipedia , lookup
Archaeoastronomy wikipedia , lookup
Chinese astronomy wikipedia , lookup
Constellation wikipedia , lookup
Timeline of astronomy wikipedia , lookup
Patronage in astronomy wikipedia , lookup
Astronomy in the medieval Islamic world wikipedia , lookup
Hebrew astronomy wikipedia , lookup
History of astronomy wikipedia , lookup
International Year of Astronomy wikipedia , lookup
Theoretical astronomy wikipedia , lookup
Review Astronomy 1 — Elementary Astronomy LA Mission College Spring F2015 Quotes & Cartoon of the Day “One may wonder, What came before? If space-time did not exist then, how could everything appear from nothing? . . . Explaining this initial singularity—where and when it all began—still remains the most intractable problem of modern cosmology. — Andrei Linde “But who shall dwell in these worlds if they be inhabited? ... Are we or they Lords of the World? ... And how are all things made for man?” — Johannes Kepler “Our sun is one of 100 billion stars in our galaxy. Our galaxy is one of billions of galaxies populating the universe. It would be the height of presumption to think that we are the only living things in that enormous immensity.” — Wernher von Braun Astronomy 1 - Elementary Astronomy LA Mission College Levine F2015 Announcements • Observing Project & Extra Credit Due • Midterm graded & gradebook updated to drop lowest • • remainder of grading (hopefully) updated this weekend Final 12/15 at 10-12 AM! Astronomy 1 - Elementary Astronomy LA Mission College Levine F2015 Last Class • • • • Debrief Midterm Debrief LT Cosmology & Fate of the Universe Exoplanets (time permitting) Astronomy 1 - Elementary Astronomy LA Mission College Levine F2015 This Class • • Review/Debrief Midterm Exoplanets (time permitting) Astronomy 1 - Elementary Astronomy LA Mission College Levine F2015 About the Final Astronomy 1 — Elementary Astronomy LA Mission College Spring F2015 About the Final • • Similar format to Midterms Similar length • • Little new material, mostly cumulative • • • a little longer, some choice of questions Study the stuff on the midterms! But don’t memorize the questions themselves, you probably won’t see many that are identical You may bring a full sheet of notes • • both sides handwritten Astronomy 1 - Elementary Astronomy LA Mission College Levine F2015 About the Final • Don’t leave stuff blank! • • Can you remember ANYTHING about the topic? Apply logic! • Comprehension before Computation -- Big Picture before Details • State units with numbers (except magnitude) Astronomy 1 - Elementary Astronomy LA Mission College Levine F2015 Topics Astronomy 1 — Elementary Astronomy LA Mission College Spring F2015 TOUR OF UNIVERSE Our “Cosmic Address” • • • • • • • • • • • LAMC Sylmar Los Angeles County CA US Earth Solar System Milky Way Galaxy Local Group Virgo Supercluster The Universe Astronomy 1 - Elementary Astronomy LA Mission College Levine F2015 SCIENCE Science • • Definition Method • • • • • • KEY: Hypothesis, Test, Revision Nomenclature -- Hypothesis, Theory Characteristics of Science & Belief System Be able to recognize science and not-science Be able to recognize a scientific hypothesis Be able to describe the scientific method Astronomy 1 - Elementary Astronomy LA Mission College Levine F2015 THE NIGHT SKY Diurnal Motion • • • • • Daily Everything Rises in East, sets in West Moves in circles around the NCP (and SCP) Earth is rotating Be able to answer questions using diagrams from the Position LT Astronomy 1 - Elementary Astronomy LA Mission College Levine F2015 Lunar Phases • • • Cause of phases ID of phases Timing of rise/set/transit Astronomy 1 - Elementary Astronomy LA Mission College Levine F2015 Eclipses • • • • • Solar and Lunar Cause Geometry Timing Why not every full/new moon Astronomy 1 - Elementary Astronomy LA Mission College Levine F2015 Zodiac & Apparent Solar Motion Name:____________________! ICE 2! • • • Ecliptic • Takes a year to cycle through ! ASTRO 110/120! Date:__________ Levine Spring 2013 Zodiac Meaning of “The Sun is in Taurus etc.” Astronomy 1 - Elementary Astronomy LA Mission College Levine F2015 Seasons • • • It’s the axial tilt It’s about energy transfer Be able to discuss observable consequences • when is the Sun high in the sky, day length etc. Astronomy 1 - Elementary Astronomy LA Mission College Levine F2015 OLD DEAD GUYS Greeks to Kepler • • • • Greek ideas Copernican Revolution Tycho Brahe Kepler the dude Astronomy 1 - Elementary Astronomy LA Mission College Levine F2015 Kepler’s 3 laws of Planetary Motion 1. The orbits of the planets are ellipses, with the Sun at one focus. 2. A line from a planet to the Sun sweeps out equal areas in equal periods of time • Planets move fastest when physically closest to the Sun, and slowest when farthest. 3. A planet’s orbital period squared, is proportional to it’s farthest distance from the Sun cubed: • P2 = a3 • • • Be able to recognize these • Possible calculation with 3rd law Work with ellipses and eccentricity Recognize examples of 2nd and 3rd law (faster/slower longer period/ shorter period) Astronomy 1 - Elementary Astronomy LA Mission College Levine F2015 Kepler to Sir Issac • • Galileo Sir Issac • • Contributions and fields of study Law of Universal Gravity Astronomy 1 - Elementary Astronomy LA Mission College Levine F2015 Law of Universal Gravity • Be able to explain how the force varies (larger or smaller) with mass of either object, both objects and distance • Be able to work the inverse square relationship -- how does force change if distance doubles.... Astronomy 1 - Elementary Astronomy LA Mission College Levine F2015 LIGHT, OPTICS, TELESCOPES Nature of Light • • • • • Why this is important for Astronomy electromagnetic radiation waves, particles, duality all light, from radio to gamma ray is same thing all light travels at the same speed in vacuum • c=3x108 m/s Astronomy 1 - Elementary Astronomy LA Mission College Levine F2015 Properties of Light • Waves • • • • λ = c/f Interference Particles • • • • • • Relationship of wavelength and frequency Photoelectric effect E = h f = hc/λ h = 6.6 x 10-34 Js = 6.6 x 10-34 J/Hz Know what these relationships mean Know how the ranking task worked Possibility of seeing a a simple calculation Astronomy 1 - Elementary Astronomy LA Mission College Levine F2015 Electromagnetic Spectrum • • • difference between red and blue light Basic bands of EMR (e.g. radio, visible, IR etc.) Relationship between band, wavelength & Energy Astronomy 1 - Elementary Astronomy LA Mission College Levine F2015 Telescopes and Observatories • • • • Refractors and Reflectors Size (of primary) matters Atmospheric Transmission & Seeing Multiwavelength Astronomy • • What are IR and Radio good for? Cameras & Spectroscopes Astronomy 1 - Elementary Astronomy LA Mission College Levine F2015 SOLAR SYSTEM Solar System Properties • Overall “bulk” properties • • • • Disk shape two types of planets Space “debris” common age Astronomy 1 - Elementary Astronomy LA Mission College Levine F2015 Solar System Properties • “Anatomy” What and Where • • • • • • • • Sun Inner SS & terrestrial planets Asteroid Belt Outer SS & Jovian planets Kuiper Belt Heliopause Oort cloud Size/Distance Scales Astronomy 1 - Elementary Astronomy LA Mission College Levine F2015 Solar System Formation • • • • • • • • Raw materials -- big bang, role of supernovae Theories of Formation Solar Nebula Theory Differentiation Frost line Planet formation -- both types Disk clearing Cratering & Craters Astronomy 1 - Elementary Astronomy LA Mission College Levine F2015 Solar System Bodies • Terrestrial Planets • • • • • dynamo effect What went wrong for Venus and Mars Greenhouse effect Jovian Planets • • • common properties common properties Why are Titan and Enceladus interesting Why isn’t Pluto a “planet” and what it is Astronomy 1 - Elementary Astronomy LA Mission College Levine F2015 STARS & GALAXIES Stellar Properties • • Luminosity Magnitude system • • • Apparent vs. Absolute magnitude review the ranking tasks Distance ladder & difficulty of distances • Stellar parallax • • know how angle & distance relate Standard Candle • how does a standard candle work Astronomy 1 - Elementary Astronomy LA Mission College Levine F2015 Color and Temperature & Size • stars are (mostly) like blackbodies • temperature and peak wavelength • temperature and size & luminosity Astronomy 1 - Elementary Astronomy LA Mission College Levine F2015 Spectral Type • Color ~ temperature ~ spectral class • • Harvard computers & Harvard classification scheme • • be able to answer questions based on the blackbody LT OBAFGKM Brightness and temperature and size (Giants) Astronomy 1 - Elementary Astronomy LA Mission College Levine F2015 HR Diagram • • What is it? • • • • • Main sequence What can be plotted on it? Red giants Supergiants White Dwarfs Evolution Astronomy 1 - Elementary Astronomy LA Mission College Levine F2015 Stellar Lifecycles © NASA • • • • Star formation Main Sequence lifetime End states and what determines them Mass is everything!!!!! • More mass means shorter life Astronomy 1 - Elementary Astronomy LA Mission College Levine F2015 Main Sequence & Red Giant phase • Main Sequence • • • • • Hydrostatic Equilibrium H to He nuclear fusion Most of a star’s life Sun is on MS Red Giant • • • • New hydrostatic equilibrium H to He fusion in shell He fusion in core 1/10th the duration of MS lifetime Astronomy 1 - Elementary Astronomy LA Mission College Levine F2015 Endgame Scenarios • • • • • • • Giant stars Planetary nebulae White dwarfs Type II supernovae neutron stars & pulsars black holes type Ia supernovae Astronomy 1 - Elementary Astronomy LA Mission College Levine F2015 The Milky Way • • Barred Spiral General structure • • • disk, bulge, halo General Content Where are we? Astronomy 1 - Elementary Astronomy LA Mission College Levine F2015 Galaxy Classification NASA/ESA Astronomy 1 - Elementary Astronomy LA Mission College Levine F2015 Characteristics of types • • • • • Describe spirals, barred spirals, ellipticals, irregulars Which are most common? What are their overall properties? Which tend to have older or younger stars Which tend to have black holes (all) Astronomy 1 - Elementary Astronomy LA Mission College Levine F2015 COSMOLOGY Telescopes are Time machines • • Lookback time Concept of the Observable Universe Astronomy 1 - Elementary Astronomy LA Mission College Levine F2015 Expanding Universe • • • • Space is expanding, not stuff Raisin bread & balloons Role of gravity in holding structures together Cosmological principle Astronomy 1 - Elementary Astronomy LA Mission College Levine F2015 Big Bang • • • • NOT an explosion Universe was infinite immediately How long ago was it? The whole universe was in a hot, dense state • • energy became matter became stars and galaxies Evidence for Big Bang • • • Expansion H,He,Li abundance in early universe Cosmic Microwave Background Astronomy 1 - Elementary Astronomy LA Mission College Levine F2015 Cosmic Microwave Background • • • • Penzias & Wilson 2.7 K Very smooth but somewhat bumpy Not the very beginning, 380,000 years after BB Astronomy 1 - Elementary Astronomy LA Mission College Levine F2015 Fate of Universe • 3 fates: Open, Closed, Critical or Big Crunch, Big Chill/ Big Rip • Dark Matter & Dark Energy • • • • Most of universe is dark Dark Matter Dark energy dominates universe Dark energy is unknown cause of local expansion Astronomy 1 - Elementary Astronomy LA Mission College Levine F2015 EXOPLANETS Exoplanets • If we get to them today… Astronomy 1 - Elementary Astronomy LA Mission College Levine F2015 IN SUMMARY… The Galaxy Song Astronomy 1 - Elementary Astronomy LA Mission College Levine F2015 So Long and Thanks for All the Fish! Astronomy 1 - Elementary Astronomy LA Mission College Levine F2015 Other Worlds Extrasolar planets and systems Astronomy 1 — Elementary Astronomy LA Mission College Spring F2015 There are a lot of planets out there! • 1879-1935 extrasolar planets around 1225 stars • 471-484 multiple planet systems • http://exoplanet.eu/ catalog/ • • Simple flat-table list 4696 Kepler candidates! Astronomy 1 - Elementary Astronomy LA Mission College Levine F2015 There are a lot of planets out there! • 298 are very large • • Radius larger than 6x Earth 150 are small • Radius less than 1.25 x Earth Astronomy 1 - Elementary Astronomy LA Mission College Levine F2015 DETECTION METHODS How do we find them? • Direct imaging • • Radial Velocity (RV) • • Planet blocks light from parent star Gravitational microlensing • • Planet induces doppler shift in parent star Transit photometry • • Rare Planet causes background object to brighten Astrometry • Planet causes parent star to shift position periodically Astronomy 1 - Elementary Astronomy LA Mission College Levine F2015 Exoplanet Image Beta Pictoris b (bright spot) orbiting its star (center) Credit: Bruce Macintosh et al. • Beta Pictoris about 63.5 light years from Earth • Beta Pic b (planet) • dist from Beta Pic about 9x dist Earth from Sun • VERY large, ~ 1.6x radius of Jupiter Astronomy 1 - Elementary Astronomy LA Mission College Levine F2015 RV Animation Astronomy 1 - Elementary Astronomy LA Mission College Levine F2015 Transit Method Animation Astronomy 1 - Elementary Astronomy LA Mission College Levine F2015 KEPLER Kepler • Capable of finding earth-sized planets in the habitable zone of nearby stars • • Transit method • Now in modified extended mission K2 (has lost 2 reaction wheels) 962 confirmed planets to date Astronomy 1 - Elementary Astronomy LA Mission College Levine F2015 Kepler Overview Astronomy 1 - Elementary Astronomy LA Mission College Levine F2015 Astronomy 1 - Elementary Astronomy LA Mission College Levine F2015 MOST EARTHLIKE PLANET “EARTH 2.0” KEPLER 452B Transit Graph Astronomy 1 - Elementary Astronomy LA Mission College Levine F2015 Artist’s Concept Astronomy 1 - Elementary Astronomy LA Mission College Levine F2015 Kepler 452b Astronomy 1 - Elementary Astronomy LA Mission College Levine F2015 Kepler 186-f came first • Kepler 186f discovered April 2014 was first Earth-size planet in Habitable zone. • • • Composition not as clearly confirmed as rocky Orbits very close to a dim M-type Star about 500 ly distant Astronomy 1 - Elementary Astronomy LA Mission College Levine F2015 Astronomy 1 - Elementary Astronomy LA Mission College Levine F2015 “Earth 2.0” Kepler 452b • • • Discovered July 2015 (press con 7/23) Orbits G-type Star about 1400 ly distant Astronomy 1 - Elementary Astronomy LA Mission College Levine F2015