* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download The Celestial Sphere
Survey
Document related concepts
Copernican heliocentrism wikipedia , lookup
Corvus (constellation) wikipedia , lookup
History of astronomy wikipedia , lookup
Planetarium wikipedia , lookup
Theoretical astronomy wikipedia , lookup
Equation of time wikipedia , lookup
Archaeoastronomy wikipedia , lookup
Dyson sphere wikipedia , lookup
Timeline of astronomy wikipedia , lookup
Dialogue Concerning the Two Chief World Systems wikipedia , lookup
Constellation wikipedia , lookup
Geocentric model wikipedia , lookup
Tropical year wikipedia , lookup
Epoch (astronomy) wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
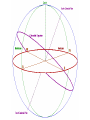
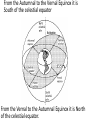
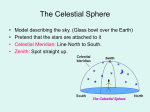
The Night Sky And The Celestial Sphere The Celestial Sphere The ancients thought the stars were stuck in a sphere half of which could be seen as a dome overhead at any given time This they called the celestial sphere. The celestial sphere does not actually exist But it is still a useful way to think about the sky. Diurnal Motion, Celestial Poles and The Celestial Equator The spinning of the Earth makes the celestial sphere appear to spin. Thus as time goes by all stars move completing a circle every 24 hours… “Diurnal Motion” Except the points directly above the north and south poles which do not appear to move. The sphere spins around them. They are called the North and South Celestial Poles. Half-way between the poles, above the Equator, lies the Celestial Equator it spins the most. Annual Motion As the year passes the direction to the Sun relative to the celestial sphere changes. Obviously the stars in the direction of the sun cannot be seen as they are up during the day. Thus as the year goes by the stars that you can see at night change And The time that a star rises and sets changes as the year goes by too. The Ecliptic Because of the 23.5° tilt of the Earth’s axis. The path of the Sun in the sky does not follow the celestial equator. It is tilted 23.5° from it. The Sun’s path is called the Ecliptic It crosses the Celestial Equator twice: On about September 22nd,the Autumnal or Fall Equinox And on about March 21st, the Vernal or Spring Equinox From the Autumnal to the Vernal Equinox it is South of the celestial equator From the Vernal to the Autumnal Equinox it is North of the celestial equator.